Abstract
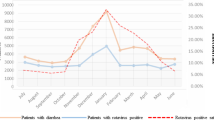
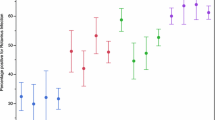
Rotavirus is the most important etiological agent in children with acute gastroenteritis (AGE). The recent implementation of a rotavirus vaccine in Korea requires the monitoring of prevailing rotavirus strains in order to control the infection. One hundred thirty-nine rotavirus strains were detected in children hospitalized with AGE in Seoul, Korea from 2007 to 2009. The most frequent combination of genotypes was G9P[8] (32.1%), followed by G1P[8] (20.7%) and G3P[8] (11.7%). Mixed G-types were detected in 14 samples (10.0%), and mixed P-types were found in six samples (4.3%). G9 genotypes were predominant from 2007 to 2008, whereas G1 and G3 genotypes were predominant from 2008 to 2009. G1 strains clustered mostly in the Id lineage, and some clustered in the Ic, IId, and Ia lineages. G2 strains clustered in the IV and V lineages. G3 and G9 strains clustered in the IIId and Id lineages, respectively. This study shows a rapid change of the prevalent genotype from G9 to G1 and G3 genotypes, suggesting that continuous surveillance of rotavirus strains is important for rotavirus vaccination.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo IT, Assis RMS, Fianho AM, Mascarhensas JDP, Heinemann MB, Leite JPG (2007) Brazilian P[8], G1, P[8], G5, P[8], G9, and P[4], G2 rotavirus strains: nucleotide sequence and phylogenetic analysis. J Med Virol 79:995–1001
Arista S, Giammanco GM, De Grazia S, Ramirez S, Lo Biundo C, Colomba C, Cascio A, Martella V (2006) Heterogeneity and temporal dynamics of evolution of G1 human rotaviruses in a settled population. J Virol 80:10724–10733
Aupiais C, de Rouqemont A, Menager C, Vallet C, Brasme JF, Kaplon J, Pothier P, Gendrel D (2009) Severity of acute gastroenteritis in infants infected by G1 or G9 rotaviruses. J Clin Virol 46:282–285
Banerjee I, Ramani S, Primrose B, Iturriza-Gomara M, Gray JJ, Brown DW, Kang G (2007) Modification of rotavirus multiplex RT-PCR for the detection of G12 strains based on characterization of emerging G12 rotavirus strains from South India. J Med Virol 79:1413–1421
Castello A, Nakagomi T, Nakagomi O, Kang JO, Glass RI, Glikmann G, Gentsch JR (2009) Characterization of genotype P[9]G12 rotavirus stains from Argentina: high similarity with Japanese and Korean G12 strains. J Med Virol 81:371–381
Esona MD, Geyer A, Page N, Trabelsi A, Fodha I, Aminu M, Abgaya VA, Tsion B, Kerin TK, Armah GE, Steele AD, Glass RI, Gentsch JR (2009) Genomic characterization of human rotavirus G8 strains from the African rotavirus network: relationship to animal rotaviruses. J Med Virol 81:937–951
Espinola EE, Parra GI, Russomando G, Arbiza J (2008) Genetic diversity of the VP4 and VP7 genes affect the genotyping of rotaviruses: analysis of Paraguayan strains. Infect Genetics Evol 8:94–99
Estes MK, Kapikian AZ (2007) Rotaviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Grffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA (eds) Fields Virology, 5th ed. edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1917–1974
Gentsch JR, Glas RI, Woods P, Gouvea V, Gorziglia M, Flores J, Das BK, Bhan MK (1992) Identification of group A rotavirus gene 4 types by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 30:1365–1373
Gentsch JR, Laird AR, Biefelt B, Griffin DD, Banyai K, Ramachandran M, Jain V, Cunliffe NA, Nakagomi O, Kirwood CD, Fischer TK, Parashar UD, Bresee JS, Jiang B, Glass RI (2005) Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: implications for rotavirus vaccine program. J Infect Dis 192:146–159
Gouvea V, Glass RI, Woods P, Taniguchi K, Clark HF, Forrester B, Fang ZY (1990) Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 28:276–282
Grazia SD, Martella V, Colomba C, Cascio A, Arista S, Giammanco GM (2009) Genetic characterization of G3 rotaviruses detected in Italian children in the years 1993–2005. J Med Virol 81:20892095
Gurgel RQ, Cuevas LE, Vieira SCF, Barros VCF, Fontes PB, Salustino EF, Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T, Dove W, Cunliffe N, Hart CA (2007) Predominance of rotavirus P[4]G2 in a vaccinated population, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 13:1571–1573
Hasing ME, Trueba G, Baquero MI, Ponce K, Cevallos W, Solberg OD, Eisenberg JN (2009) Rapid changes in rotaviral genotypes in Ecuador. J Med Virol 81:2109–2113
Hong SK, Lee SG, Lee SA, Kang JH, Lee JH, Kim JH, Kim DS, Kim HM, Jang YT, Ma SH, Kim SY, Paik SY (2007) Characterization of a G11P[4] strain of human rotavirus isolated in South Korea. J Clin Microbiol 45:3759–3761
Huh JW, Kim WH, Yoon MH, Lim YH (2009) Genotypic distribution of rotavirus strains causing severe gastroenteritis in Gyeonggi province, South Korea, from 2003–2005. Arch Virol 154:167–170
Iturriza-Gomara M, Green J, Brown DW, Desselberger U, Gray JJ (2000) Diversity within VP4 gene of rotavirus P[8] strains: implications for reverse transcription-PCR genotyping. J Clin Microbiol 38:898–901
Iturriza-Gomara M, Isherwood B, Desselberger U, Gray J (2001) Reassortment in vivo: driving force for diversity of human rotavirus strains isolated in the United Kingdom between 1995 and 1999. J Virol 75:3696–3705
Iturriza-Gomara M, Kang G, Gray J (2004) Rotavirus genotyping: keeping up with an evolving population of human rotaviruses. J Clin Virol 31:259–265
Jin Q, Ward L, Knownlton DR, Gabbay YB, Linhares AC, Rappaport R, Woods PA, Glass RI, Gentsch JR (1996) Divergence of VP7 genes of G1 rotaviruses isolated from infants vaccinated with reassortment rhesus rotviruses. Arch Virol 141:2057–2076
Kang JO, Kilgore P, Kim JS, Nyambat B, Kim J, Suh HS, Yoon Y, Jang S, Chang C, Choi S, Kim MN, Gentsch J, Bresee J, Glass R (2005) Molecular epidemiological profile of rotavirus in South Korea, July 2002 through June 2003: emergence of G4P[6] and G9P[8] strains. J Infect Dis 192:s57–s63
Khamrin P, Peerakome S, Tonusin S, Malasao R, Okitsu S, Mizuguchi M, Ushijima H, Maneekarn N (2007) Changing pattern of rotavirus G genotype distribution in Chiang Mai, Thailand from 2002 to 2004: decline of G9 and reemergence of G1 and G2. J Med Virol 79:1775–1782
Kim KH, Yang JM, Joo SI, Cho YG, Glass RI, Cho YJ (1990) Importance of rotavirus and adenovirus types 40 and 41 in acute gastroenteritis in Korean children. J Clin Microbiol 28:2279–2284
Cha KJ, Song JO, Cho CH, Yu JH, Kim YH, Yu DY, Lee JB, Lee CK, Koki T (1999) Serotype and nucleotide analysis of human rotavirus isolates in Korea. J Korean Soc Virology 29:75–85
Kim JS, Kang JO, Cho SC, Jang YT, Min SA, Park TH, Nyambat B, Jo DS, Gentsch J, Bresee JS, Mast TC, Kilgore PE (2005) Epidemiological profile of rotavirus infection in the republic of Korea: results from prospective surveillance in the Jeongub District, 1 July 2002 through 30 June 2004. J Infect Dis 192:S49–S56
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetic analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Le VP, Kim JY, Cho SL, Nam SW, Lim IS, Lee HJ, Kim K, Chung SI, Song W, Lee KM, Rhee MS, Lee JS, Kim W (2008) Detection of unusual rotavirus genotypes G8P[8] and G12P[6] in South Korea. J Med Virol 80:175–182
Le VP, Chung YC, Kim KJ, Chung SI, Lim IS, Kim WY (2010) Genetic variation of prevalent G1P[8] human rotaviruses in South Korea. J Med Virol 82:886–896
Lee JI, Song MO, Chung JY, Han TH, Ahn YM, Seo JW, Kim MS, Kim MY, Kim WY, Lee CH (2008) Outbreak of rotavirus variant P[8] in Seoul, South Korea. J Med Virol 80:1661–1665
Linhares AC, Verstraeten T, Wolleswinkel-van den Bosch J, Clemens R, Breuer T (2006) Rotavirus serotype G9 is associated with more severe disease in Latin America. Clin Infect Dis 43:312–314
Martella V, Pratelli A, Elia G, Decaro N, Tempesta M, Buonavoglia C (2001) Isolation and genetic characterization of two G3P5A[3] canine rotavirus strains in Italy. J Virol Methods 96:43–49
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Rahman M, Attoui H, Banyai K, Estes MK, Gentsch JR, Iturriza-Gomara M, Kirkwood CD, Martella V, Mertens PP, Nakagomi O, Patton JT, Ruggeri FM, Saif LJ, Santos N, Steyer A, Taniguchi K, Desselberger U, Van Ranst M (2008) Recommendations for the classifications of group A rotaviruses using all 11 genomic RNA segments. Arch Virol 153:1621–1629
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, Palombo EA, Iturriza-Gómara M, Maes P, Patton JT, Rahman M, Van Ranst M (2008) Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-Like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol 82:3204–3219
Min BS, Noh YJ, Shin JH, Baek SY, Kim JO, Min KI, Ryu SR, Kim BG, Kim DK, Lee SH, Min HK, Ahn BY, Park SN (2004) Surveillance study (2000 to 2001) of G- and P-type human rotaviruses circulating in South Korea. J Clin Microbiol 42:4297–4299
Moon SS, Green YS, Song JW, Ahn CN, Kim H, Park KS, Song KJ, Lee JH, Baek LJ (2007) Genetic distribution of group A human rotavirus types isolated in Gyunggi province of Korea, 1999–2002. J Clin Virol 38:57–63
Muhsen K, Shulman L, Rubinstein U, Kasem E, Kremer A, Goren S, Zilberstein I, Chodick G, Ephros M, Cohen D; TAU-HCLV Rota Study Group (2009) Incidence, characteristics, and economic burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis associated with hospitalization of Israeli children <5 years of age, 2007–2008. J Infect Dis 200 Suppl 1: S254–263
Parashar UD, Hummelman EG, Bresee JS, Miller MA, Glass RI (2003) Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis 9:565–572
Parashar UD, Gibson CJ, Bresee JS, Glass RI (2006) Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg Infect Dis 12:304–306
Phan TG, Okitsu S, Maneekarn N, Ushijima Hiroshi (2007) Genetic heterogeneity, evolution and recombination in emerging G9 rotaviruses. Infect Genet Evol 7:656–663
Pietsch C, Libert UG (2009) Human infection with G12 rotaviruses, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis 15:1512–1515
Rahman M, Matthijnssens J, Goegebuer T, Leener KD, Vanderwegen L, van der Donck I, van Hoovels L, De Vos S, Azim T, van Ranst M (2005) Predominance of rotavirus G9 genotype in children hospitalized for rotavirus gastroenteritis in Belgium during 1999–2003. J Clin Virol 33:1–6
Rahman M, Matthijnssens J, Yang X, Delbeke T, Arijs I, Taniguchi K, Iturriza-Gomara M, Iftekharuddin N, Azim T, Van Ranst M (2007) Evolutionary history and global history and global spread of the emerging G12 human rotaviruses. J Virol 81:2382–2390
Schumann T, Hotzel H, Otto P, Johne R (2009) Evidence of interspecies transmission and reassortment among avian group A rotaviruses. Virology 386:334–343
Sherchand JB, Nakagomi O, Dove W, Nakagomi T, Yokoo M, Pandey BD, Cuevas LE, Hart CA, Cunliffe NA (2009) Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus diarrhea among children aged <5 years in Nepal: predominance of emergent G12 strains during 2 years. J Infect Dis 200:S182–S187
Shim SY, Jung YC, Le VP, Son DW, Ryoo E, Shim JO, Lim I, Kim W (2010) Genetic variation of G4P[6] rotaviruses: evidence for novel strains circulating between the hospital and community. J Med Virol 82:700–706
Solberg OD, Hasing ME, Trueba G, Eisenberg JN (2009) Characterization of novel VP7, VP4, and VP6 genotypes of a previously untypeable group A rotavirus. Virology 385:58–67
Song MO, Kim KJ, Chung SI, Lim I, Kang SY, An CN, Kim W (2003) Distribution of human group a rotavirus VP7 and VP4 types circulating in Seoul, Korea between 1998 and 2000. J Med Virol 70:324–328
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Kobayashi N, Gorziglia M, Urasawa S (1990) Nucleotide sequence of VP4 and VP7 genes of human rotaviruses with subgroup I specificity and long RNA pattern: implication of new G serotype specificity. J Virol 64:5640–5644
Trinh QD, Pham NT, Nguyen T, Phan TG, Khamrin P, Yan H, Hoang PL, Maneekarn N, Li Y, Kozlov V, Kozlov A, Okitsu S, Ushijima H (2007) Amino acid substitutions in the VP7 protein of human rotavirus G3 isolated in China, Russia, Thailand, and Vietnam during 2001–2004. J Med Virol 79:1611–1616
Ursu K, Kisfali P, Rigó D, Ivanics E, Erdélyi K, Dán A, Melegh B, Martella V, Bányai K (2009) Molecular analysis of the VP7 gene of pheasant rotaviruses identifies a new genotype, designated G23. Arch Virol 154:1365–1369
Wang YH, Kobayashi N, Zhou DJ, Yang ZQ, Zhou X, Peng JS, Zhu ZR, Zhao DF, Liu MQ, Gong J (2007) Molecular epidemiologic analysis of group A rotaviruses in adults and children with diarrhea in Wuhan city, China 2000–2006. Arch Virol 152:669–685
Wang YH, Kobayashi N, Zhou X, Nagashima S, Zhu ZR, Peng JS, Liu MQ, Hu Q, Zhou DJ, Watanabe S, Ishino M (2009) Phylogenetic analysis of rotaviruses with predominant G3 and emerging G9 genotypes from adults and children in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol 81:382–389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T.-H. Han and C.-H. Kim contributed equally for this work.
This study was partly supported by the research grant (2009) by Inje University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, TH., Kim, CH., Chung, JY. et al. Genetic characterization of rotavirus in children in South Korea from 2007 to 2009. Arch Virol 155, 1663–1673 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0752-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0752-7