Abstract
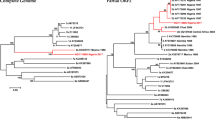
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) was originally identified as the etiological agent of non-HAV enterically transmitted hepatitis. One HEV strain (FJ763142) was identified from an acute viral hepatitis E patient with IgM anti-HEV in Korea. The complete genome sequence consisted of 7,238 nucleotides (nt) plus a 22-nt poly(A) tail. The strain belongs to genotype IV, with 91% homology compared with AB197674, which was found in a Japanese patient who had traveled to China. This finding suggests that HEV genotype IV already circulates in Korea, and this HEV might be the first example of an indigenous strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JM, Kang SG, Lee DY, Shin SJ, Yoo HS (2005) Identification of novel human hepatitis E virus (HEV) isolates and determination of the seroprevalence of HEV in Korea. J Clin Microbiol 43:3042–3048
Arankalle VA, Paranjape S, Emerson SU, Purcell RH, Walimbe AM (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus isolates from India (1976–1993). J Gen Virol 80(Pt 7):1691–1700
Billam P, Sun ZF, Meng XJ (2007) Analysis of the complete genomic sequence of an apparently avirulent strain of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) identified major genetic differences compared with the prototype pathogenic strain of avian HEV. J Gen Virol 88:1538–1544
Choi IS, Kwon HJ, Shin NR, Yoo HS (2003) Identification of swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) and prevalence of anti-HEV antibodies in swine and human populations in Korea. J Clin Microbiol 41:3602–3608
Emerson SU, Purcell RH (2003) Hepatitis E virus. Rev Med Virol 13:145–154
Graff J, Torian U, Nguyen H, Emerson SU (2006) A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J Virol 80:5919–5926
Haqshenas G, Shivaprasad HL, Woolcock PR, Read DH, Meng XJ (2001) Genetic identification and characterization of a novel virus related to human hepatitis E virus from chickens with hepatitis-splenomegaly syndrome in the United States. J Gen Virol 82:2449–2462
Huang FF, Sun ZF, Emerson SU, Purcell RH, Shivaprasad HL, Pierson FW, Toth TE, Meng XJ (2004) Determination and analysis of the complete genomic sequence of avian hepatitis E virus (avian HEV) and attempts to infect rhesus monkeys with avian HEV. J Gen Virol 85:1609–1618
Ishikawa K, Matsui K, Madarame T, Sato S, Oikawa K, Uchida T (1995) Hepatitis E probably contracted via a Chinese herbal medicine, demonstrated by nucleotide sequencing. J Gastroenterol 30:534–538
Koonin EV, Gorbalenya AE, Purdy MA, Rozanov MN, Reyes GR, Bradley DW (1992) Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8259–8263
Krawczynski K (1993) Hepatitis E. Hepatology 17:932–941
Mayo MA (2005) Changes to virus taxonomy 2004. Arch Virol 150:189–198
Meng XJ, Purcell RH, Halbur PG, Lehman JR, Webb DM, Tsareva TS, Haynes JS, Thacker BJ, Emerson SU (1997) A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9860–9865
Meng XJ (2000) Novel strains of hepatitis E virus identified from humans and other animal species: is hepatitis E a zoonosis? J Hepatol 33:842–845
Ohnishi S, Kang JH, Maekubo H, Arakawa T, Karino Y, Toyota J, Takahashi K, Mishiro S (2006) Comparison of clinical features of acute hepatitis caused by hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotypes 3 and 4 in Sapporo, Japan. Hepatol Res 36:301–307
Panda SK, Ansari IH, Durgapal H, Agrawal S, Jameel S (2000) The in vitro-synthesized RNA from a cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus is infectious. J Virol 74:2430–2437
Pudupakam RS, Huang YW, Opriessnig T, Halbur PG, Pierson FW, Meng XJ (2009) Deletions of the hypervariable region (HVR) in open reading frame 1 of hepatitis E virus do not abolish virus infectivity: evidence for attenuation of HVR deletion mutants in vivo. J Virol 83:384–395
Purcell RH, Emerson SU (2001) Hepatitis E virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, vol 4. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 3051–3061
Purcell RH, Emerson SU (2008) Hepatitis E: an emerging awareness of an old disease. J Hepatol 48:494–503
Reyes GR, Purdy MA, Kim JP, Luk KC, Young LM, Fry KE, Bradley DW (1990) Isolation of a cDNA from the virus responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science 247:1335–1339
Reyes GR, Huang CC, Yarbough PO, Tam AW (1991) Hepatitis E virus. Comparison of ‘New and Old World’ isolates. J Hepatol 13(Suppl 4):S155–S161
Sainokami S, Abe K, Kumagai I, Miyasaka A, Endo R, Takikawa Y, Suzuki K, Mizuo H, Sugai Y, Akahane Y, Koizumi Y, Yajima Y, Okamoto H (2004) Epidemiological and clinical study of sporadic acute hepatitis E caused by indigenous strains of hepatitis E virus in Japan compared with acute hepatitis A. J Gastroenterol 39:640–648
Schlauder GG, Mushahwar IK (2001) Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis E virus. J Med Virol 65:282–292
Takahashi K, Iwata K, Watanabe N, Hatahara T, Ohta Y, Baba K, Mishiro S (2001) Full-genome nucleotide sequence of a hepatitis E virus strain that may be indigenous to Japan. Virology 287:9–12
Takahashi K, Kang JH, Ohnishi S, Hino K, Mishiro S (2002) Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis E virus recovered from Japanese patients with acute sporadic hepatitis. J Infect Dis 185:1342–1345
Wang Y, Zhang H, Ling R, Li H, Harrison TJ (2000) The complete sequence of hepatitis E virus genotype 4 reveals an alternative strategy for translation of open reading frames 2 and 3. J Gen Virol 81:1675–1686
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Korea National Institute of Health (KNIH; Intramural Fund, Grant No. 4800-4863-300). The authors are grateful to Drs. Mishiro and Takahashi for designing primers to analyze the full genome of Korean HEV.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
GenBank accession numbers: KNIH-hHEV4: FJ763142, KNIH-hHEV4-ORF1: EU849133, KNIH-hHEV4-ORF2: EU849134
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, H., Kim, J.S., Lee, H.J. et al. The complete genome sequence and molecular analysis of human hepatitis E virus genotype IV identified from a Korean patient. Arch Virol 155, 1003–1008 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0661-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0661-9