Abstract
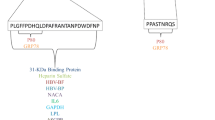
Both fibronectin and the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) have been identified by some investigators as partners for hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope proteins. Because fibronectin is a natural ligand for ASGPR, we speculated that HBV might attach to ASGPR expressed on the hepatocyte surface via fibronectin. To test this hypothesis, we first confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation that ASGPR, fibronectin and HBsAg bind to each other in HepG2.2.15 cells, and possible binding domains were identified by GST pull-down. In addition, by measuring binding of HBsAg to cells, we found that ASGPR and fibronectin enhanced the binding capability of HBsAg to HepG2 cells, and even to 293T and CHO cells, which normally do not bind HBV. In conclusion, our findings suggest that both fibronectin and ASGPR mediate HBsAg binding to the cell surface, which provides further evidence for the potential roles of these two proteins in mediating HBV binding to liver cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASGPR:
-
Asialoglycoprotein receptor
- HBsAg:
-
HBV surface antigen
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- MAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- CRD:
-
Carbohydrate recognition domain
References
Gripon P, Cannie I, Urban S (2005) Efficient inhibition of hepatitis B virus infection by acylated peptides derived from the large viral surface protein. J Virol 79(3):1613–1622
Glebe D, Urban S (2007) Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry. World J Gastroenterol 13(1):22–38
Petit MA, Capel F, Dubanchet S, Mabit H (1992) PreS1-specific binding proteins as potential receptors for hepatitis B virus in human hepatocytes. Virology 187:211–222
Duclos-Vallee JC, Capel F, Mabit H, Petit MA (1998) Phosphorylation of the hepatitis B virus core protein by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protein kinase activity. J Gen Virol 79:1665–1670
Neurath AR, Strick N, Sproul P (1992) Search for hepatitis B virus cell receptors reveals binding sites for interleukin 6 on the virus envelope proteins. J Exp Med 175:461–469
Neurath AR, Strick N, Li YY (1992) Cells transfected with human interleukin 6 cDNA acquire binding sites for the hepatitis B virus envelop protein. J Exp Med 176:1561–1569
Gong ZJ, De Meyer S, Van Pelt J, Hertogs K, Depla E, De Bruin WC, Meheus L, Soumillion A, Fevery J, Yap SH (1999) Transfection of a rat hepatoma cell line with a construct expressing human liver annexin V confers susceptibility to hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 29:576–584
Mehdi H, Kaplan MJ, Anlar FY, Yang X, Bayer R, Sutherland K, Peeples ME (1994) Hepatitis B virus surface antigen binds to apolipoprotein H. J Virol 68:2415–2424
Mehdi H, Yang X, Peeples ME (1996) An altered form of apolipoprotein H binds hepatitis B virus surface antigen most efficiently. Virology 217:58–66
Yang J, Bo XC, Ding XR, Dai JM, Zhang ML, Wang XH, Wang SQ (2006) Antisense oligonucleotides targeted against asialoglucoprotein receptor 1 block human hepatitis B virus replication. J Viral Hepat 13(3):158–165
Yang J, Ding X, Zhang Y, Bo X, Zhang M, Wang S (2006) Fibronectin is essential for hepatitis B virus propagation in vitro: may be a potential cellular target? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344(3):757–764
Takahashi M, Takahashi M, Hamano S et al (2005) In vitro attachment of bovine hatched blastocysts on fibronectin is mediated by integrin in a RGD dependent manner. J Reprod Dev 51(1):47–57
Beer C, Pedersen L (2007) Matrix fibronectin binds gammaretrovirus and assists in entry: new light on viral infections. J Virol 81(15):8247–8257
Takahashi M, Takahashi M, Hamano S et al (2005) In vitro attachment of bovine hatched blastocysts on fibronectin is mediated by integrin in a RGD dependent manner. J Reprod Dev 51(1):47–57
Schwarz-Linek U, Hook M, Potts JR (2004) The molecular basis of fibronectin-mediated bacterial adherence to host cells. Mol Microbiol 52(3):631–641
Bozzini S, Falcone V, Conaldi PG et al (1998) Heparin-binding domain of human fibronectin binds HIV-1 gp120/160 and reduces virus infectivity. J Med Virol 54:44–53
Julkunen I, Hautanen A, Keski-Oja J (1983) Interaction of viral envelope glycoproteins with fibronectin. Infect Immun 40:876–881
Keski-Oja J, Hautanen A, Julkunen J (1987) Fibronectin and viral pathogenesis. Rev Infect Dis 9:404–411
Greco G, Pal S, Pasqualini R, Schnapp LM (2002) Matrix fibronectin increases HIV stability and infectivity. J Immunol 168(11):5722–5729
Liu X, Collodi P (2002) Novel form of fibronectin from zebrafish mediates infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus infection. J Virol 76(2):492–498
Boshuizen JA, Rossen JW, Sitaram CK, Kimenai FF, Simons-Oosterhuis Y, Laffeber C, Büller HA, Einerhand AW (2004) Rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 binds to the extracellular matrix proteins laminin-β3 and fibronectin. J Virol 78(18):10045–10053
Grubman MJ, Baxt B (2004) Foot-and-mouth disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 17(2):465–493
Budkowska A, Bedossa P, Groh F, Louise A, Pillot J (1995) Fibronectin of human liver sinusoids binds hepatitis B virus: identification by an anti-idiotypic antibody bearing the internal image of the pre-S2 domain. J Virol 69(2):840–848
Treichel U, Buschenfelde KHMZ, Stockert RJ et al (1994) The asialoglycoprotein receptor mediates hepatic binding and uptake of natural hepatitis B virus particles derived from viraemic carriers. J Gen Virol 75:3021–3029
Treichel U, Buschenfelde KHMZ, Gerken G et al (1997) Receptor-mediated entry of hepatitis B virus particles into liver cells. Arch Virol 142:493–498
Paietta E, Stockert RJ, Racevskis J (1992) Differences in the abundance of variably spliced transcripts for the second asialoglycoprotein receptor polypeptide, H2, in normal and transformed human liver. Hepatology 15(3):395–402
Owada T, Matsubayashi K, Sakata H et al (2006) Interaction between desialylated hepatitis B virus and asialoglycoprotein receptor on hepatocytes may be indispensable for viral binding and entry. J Viral Hepat 13:11–18
Yang J, Bo XC, Yao J, Yang NM, Wang SQ (2005) Differentially expressed cellular genes following HBV: potential targets of anti-HBV drugs? J Viral Hepat 12:357–363
Otsuka M, Aizaki H, Kato N et al (2003) Differential cellular gene expression induced by hepatitis B and C viruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300(2):443–447
Rotundo RF, Rebres RA, Mckeown-Longo PJ, Blumenstock FA, Saba TM (1998) Circulating cellular fibronectin may be a natural ligand for the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor: possible pathway for fibronectin deposition and turnover in the rat liver. Hepatology 28:475–485
Sells MA, Zelent AZ, Shvartsman M, Acs G (1988) Replication hepatitis B virus in HepG2 cells that produce infectious virions. J Virol 62:2836–2844
Sells MA, Chen ML, Acs G (1987) Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1005–1009
Falco SD, Ruvoletto G, Verdoliva A, Ruvo M, Raucci A et al (2001) Cloning and expression of a novel hepatitis B virus-binding protein from HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem 276(39):36613–36623
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by three grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30530650, 30600531, and 30625041) and special funding from the Major State Basic Research Program of China (973 program) (no. 2005CB522902). We are grateful to Caibing Cui for providing plasmids expressing FN fragments and to many colleagues for helpful discussion during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Yang and F. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Wang, F., Tian, L. et al. Fibronectin and asialoglyprotein receptor mediate hepatitis B surface antigen binding to the cell surface. Arch Virol 155, 881–888 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0657-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0657-5