Abstract
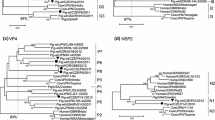
We determined the nucleotide sequences of the outer capsid glycoprotein (VP7) genes of 38 porcine group B rotaviruses (GBRs) from feces of pigs at 27 farms in Japan between 2000 and 2007. Substantial diversity among porcine GBR VP7 genes was observed, with up to 42.4% difference in nucleotides and 49.8% in amino acids. On comparison of VP7 genes, porcine GBRs were clearly distinct from the published corresponding genes from human, bovine and murine GBRs (53.7–70.8% identity in nucleotides and 45.8–73.4% identity in amino acids). Phylogenetic analysis showed that the VP7s of GBRs could be divided into five genotypes: the murine strain was genotype 1, human strains were genotype 2, bovine and some porcine strains were genotype 3, and other porcine strains belonged to genotype 4 or 5. In addition, GBR VP7s in genotypes 3 and 5 were further divided into four and five clusters, respectively. No relationship between VP7 genotype and double-stranded RNA migration patterns of porcine GBRs in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were observed. However, an antigen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using antiserum to recombinant bovine GBR VP6 did not react with fecal samples containing one cluster of genotype 5 of porcine GBRs. The abundant divergence of porcine GBR VP7 genes suggests that porcine species might be an original natural host of GBR infection and that different serotypes might exist among porcine GBRs. To our knowledge, this is the first report to describe the gene sequences and typing of porcine GBR VP7s.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball L (2005) The universal taxonomy of viruses in theory and practice. In: Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA (eds) Virus taxonomy, eighth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 3–8
Barman P, Ghosh S, Das S, Varghese V, Chaudhuri S, Sarkar S, Krishnan T, Bhattacharya SK, Chakrabarti A, Kobayashi N, Naik TN (2004) Sequencing and sequence analysis of VP7 and NSP5 genes reveal emergence of a new genotype of bovine group B rotaviruses in India. J Clin Microbiol 42:2816–2818
Bridger JC, Brown JF (1985) Prevalence of antibody to typical and atypical rotaviruses in pigs. Vet Rec 116:50
Bridger JC (1994) Non-group A rotaviruses. In: Kapikian AZ (ed) Viral infections of the gastrointestinal tract, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 369–407
Brown DW, Beards GM, Chen GM, Flewett TH (1987) Prevalence of antibody to group B (atypical) rotavirus in humans and animals. J Clin Microbiol 25:316–319
Chang KO, Parwani AV, Smith D, Saif LJ (1997) Detection of group B rotaviruses in fecal samples from diarrheic calves and adult cows and characterization of their VP7 genes. J Clin Microbiol 35:2107–2110
Chasey D, Bridger JC, McCrae MA (1986) A new type of atypical rotavirus in pigs. Arch Virol 89:235–243
Chen GM, Hung T, Bridger JC, McCrae MA (1985) Chinese adult rotavirus is a group B rotavirus. Lancet 326:1123–1124
Chen GM, Hung T, Mackow ER (1990) Identification of the gene encoding the group B rotavirus VP7 equivalent: primary characterization of the ADRV segment 9 RNA. Virology 178:311–315
Dai GZ, Sun MS, Liu SQ, Ding XF, Chen YD, Wang LC, Du DP, Zhao G, Su Y, Li J, Xu MX, Li TH, Chen XX (1987) First report of an epidemic of diarrhoea in human neonates involving the new rotavirus and biological characteristics of the epidemic virus strain (KMB/R85). J Med Virol 22:365–373
Eiden JJ, Nataro J, Vonderfecht S, Petric M (1992) Molecular cloning, sequence analysis, in vitro expression, and immunoprecipitation of the major inner capsid protein of the IDIR strain of group B rotavirus (GBR). Virology 188:580–589
Estes MK, Kapikian AZ (2007) Rotaviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, 5th edn. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1917–1974
Fang ZY, Ye Q, Ho MS, Dong H, Qing SM, Penaranda ME, Hung T, Wen LY, Glass RI (1989) Investigation of an outbreak of adult diarrhea rotavirus in China. J Infect Dis 160:948–953
Gentsch JR, Laird AR, Bielfelt B, Griffin DD, Banyai K, Ramachandran M, Jain V, Cunliffe NA, Nakagomi O, Kirkwood CD, Fischer TK, Parashar UD, Bresee JS, Jiang B, Glass RI (2005) Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: Implications for rotavirus vaccine programs. J Infect Dis 192:S146–S159
Ghosh S, Varghese V, Sinha M, Kobayashi N, Naik TN (2007) Evidence for interstate transmission and increase in prevalence of bovine group B rotavirus strains with a novel VP7 genotype among diarrhoeic calves in Eastern and Northern states of India. Epidemiol Infect 135:1324–1330
Gouvea V, Glass RI, Woods P, Taniguchi K, Clark HF, Forrester B, Fang ZY (1990) Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 28:276–282
Hung T, Wang CG, Fang ZY, Chou ZY, Chang XJ, Liong XQ, Chen GM, Yao HL, Chao TX, Ye WW, Den SS, Chang WC (1984) Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet 323:1139–1142
Janke BH, Nelson JK, Benfield DA, Nelson EA (1990) Relative prevalence of typical and atypical strains among rotaviruses from diarrheic pigs in conventional swine herds. J Vet Diagn Invest 2:308–311
Kelkar SD, Zade JK (2004) Group B rotaviruses similar to strain CAL-1, have been circulating in Western India since 1993. Epidemiol Infect 132:745–749
Kobayashi N, Naik TN, Kusuhara Y, Krishnan T, Sen A, Bhattacharya SK, Taniguchi K, Alam MM, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (2001) Sequence analysis of genes encoding structural and nonstructural proteins of a human group B rotavirus detected in Calcutta, India. J Med Virol 64:583–588
Lambden PR, Cooke SJ, Caul EO, Clarke IN (1992) Cloning of noncultivatable human rotavirus by single primer amplification. J Virol 66:1817–1822
Martella V, Banyai K, Lorusso E, Decaro N, Bellacicco A, Desario C, Corrente M, Greco G, Moschidou P, Tempesta M, Arista S, Ciarlet M, Lavazza A, Buonavoglia C (2007) Genetic heterogeneity in the VP7 of group C rotaviruses. Virology 367:358–366
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, Palombo EA, Iturriza-Gomara M, Maes P, Patton JT, Rahman M, Van Ranst M (2008) Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol 82:3204–3219
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Rahman M, Attoui H, Banyai K, Estes MK, Gentsch JR, Iturriza-Gomara M, Kirkwood CD, Martella V, Mertens PP, Nakagomi O, Patton JT, Ruggeri FM, Saif LJ, Santos N, Steyer A, Taniguchi K, Desselberger U, Van Ranst M (2008) Recommendations for the classification of group A rotaviruses using all 11 genomic RNA segments. Arch Virol 153:1621–1629
Mattion NM, Cohen J, Estes MK (1994) The rotavirus protein. In: Kapikian AZ (ed) Viral infections of the gastrointestinal tract, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 169–249
Nakata S, Estes MK, Graham DY, Loosle R, Tao H, Wang SH, Saif LJ, Melnick JL (1986) Antigenic characterization and ELISA detection of adult diarrhea rotaviruses. J Infect Dis 154:448–455
Pedley S, Bridger JC, Brown JF, McCrae MA (1983) Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol 64:2093–2101
Pedley S, Bridger JC, Chasey D, McCrae MA (1986) Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol 67:131–137
Petric M, Mayur K, Vonderfecht S, Eiden JJ (1991) Comparison of group B rotavirus genes 9 and 11. J Gen Virol 72:2801–2804
Rahman M, Hassan ZM, Zafrul H, Saiada F, Banik S, Faruque AS, Delbeke T, Matthijnssens J, Van Ranst M, Azim T (2007) Sequence analysis and evolution of group B rotaviruses. Virus Res 125:219–225
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sanekata T, Kuwamoto Y, Akamatsu S, Sakon N, Oseto M, Taniguchi K, Nakata S, Estes MK (1996) Isolation of group B porcine rotavirus in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol 34:759–761
Sanekata T, Ahmed MU, Kader A, Taniguchi K, Kobayashi N (2003) Human group B rotavirus infections cause severe diarrhea in children and adults in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol 41:2187–2190
Schumann T, Hotzel H, Otto P, Johne R (2009) Evidence of interspecies transmission and reassortment among avian group A rotaviruses. Virology 386:334–343
Sen A, Kobayashi N, Das S, Krishnan T, Bhattacharya SK, Naik TN (2001) The evolution of human group B rotaviruses. Lancet 357:198–199
Sigolo de San Juan C, Bellinzoni RC, Mattion N, La Torre J, Scodeller EA (1986) Incidence of group A and atypical rotaviruses in Brazilian pig herds. Res Vet Sci 41:270–272
Snodgrass DR, Herring AJ, Campbell I, Inglis JM, Hargreaves FD (1984) Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol 65:909–914
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Theil KW, Saif LJ, Moorhead PD, Whitmoyer RE (1985) Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol 21:340–345
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tsunemitsu H, Jiang B, Yamashita Y, Oseto M, Ushijima H, Saif LJ (1992) Evidence of serologic diversity within group C rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 30:3009–3012
Tsunemitsu H, Jiang B, Saif LJ (1996) Sequence comparison of the VP7 gene encoding the outer capsid glycoprotein among animal and human group C rotaviruses. Arch Virol 141:705–713
Tsunemitsu H, Morita D, Takaku H, Nishimori T, Imai K, Saif LJ (1999) First detection of bovine group B rotavirus in Japan and sequence of its VP7 gene. Arch Virol 144:805–815
Tsunemitsu H, Kamiyama M, Kawashima K, Katsuda K, Kohmoto M, Saif LJ, Shouji T, Onodera T (2005) Molecular characterization of the major capsid protein VP6 of bovine group B rotavirus and its use in seroepidemiology. J Gen Virol 86:2569–2575
Ursu K, Kisfali P, Rigo D, Ivanics E, Erdelyi K, Dan A, Melegh B, Martella V, Banyai K (2009) Molecular analysis of the VP7 gene of pheasant rotaviruses identifies a new genotype, designated G23. Arch Virol 154:1365–1369
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Kamiyama, M. Kohmoto, K. Kawashima, S. Nishi, T. Aita, T. Obara, Y. Sakai, T. Miyamoto, and N. Sawada for their technical assistance. This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institute of Animal Health, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuga, K., Miyazaki, A., Suzuki, T. et al. Genetic diversity and classification of the outer capsid glycoprotein VP7 of porcine group B rotaviruses. Arch Virol 154, 1785–1795 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0517-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0517-3