Abstract
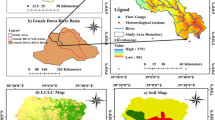
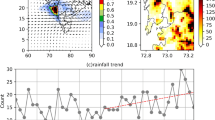
This study evaluated the skills of global climate models (GCMs) of the fifth and sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP5 and CMIP6) in simulating observed rainfall climatology, seasonal variability, and probability distribution function (PDF) in Peninsular Malaysia. Monthly rainfall records of eighty stations for 1975 − 2005 were employed for this purpose. The Kling-Gupta efficiency was applied to estimate GCMs’ skill to reconstruct rainfall climatology and seasonal variability, while Perkins skill score to replicate PDF. The GCMs of individual CMIP were initially ranked based on the individual metric, and then a compromise rating matric was then employed for the grading. Finally, the highest-ranking CMIP6 GCMs were identified and employed for rainfall projections over Peninsular Malaysia for different shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs). Results revealed higher bias in CMIP6 GCMs than CMIP5 GCMs but the better association in replicating rainfall climatology and seasonal variability. The EC-ERATH was the best performing model in CMIP5, followed by MPI-ESM-LR, FGOALS-g2, and CanESM2. In contrast, MPI-ESM-MR showed the highest skill among CMIP6 models, followed by MPI-ESM-LR, MIROC-ESM, and GFDL-ESM2M. The employment of the most skilled four GMIP6 GCMs in projecting rainfall in the peninsula revealed a non-linear rainfall change for SSPs—an increase in rainfall for SSP1-26 and SSP5-85 and a decrease for SSP2-45 and SSP3-70. Overall, rainfall was projected to increase in the northwest and central south by 10 − 20% and decrease in the northeast and far south by 1 to 30%.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data are available in the public domain at the links provided in the text.
Code Availability
The codes used for data processing can be provided on request to the corresponding author.
References
Ahmed K, Sachindra DA, Shahid S et al (2019) Selection of multi-model ensemble of general circulation models for the simulation of precipitation and maximum and minimum temperature based on spatial assessment metrics. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 23:4803–4824. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-4803-2019
Ahmed K, Iqbal Z, Khan N et al (2020) Quantitative assessment of precipitation changes under CMIP5 RCP scenarios over the northern sub-Himalayan region of Pakistan. Environ Dev Sustain 22:7831–7845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00548-5
Chen W, Jiang Z, Li L (2011) Probabilistic projections of climate change over China under the SRES A1B scenario using 28 AOGCMs. J Clim 24:4741–4756. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4102.1
Chen CC, Lo MH, Im ES et al (2019) Thermodynamic and dynamic responses to deforestation in the maritime continent: a modeling study. J Clim 32:3505–3527. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0310.1
Chen CA, Hsu HH, Liang HC (2021) Evaluation and comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 model performance in simulating the seasonal extreme precipitation in the Western North Pacific and East Asia. Weather Clim Extrem 31:100303.: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2021.100303
Eyring V, Bony S, Meehl GA et al (2016) Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci Model Dev 9:1937–1958. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016
Eyring V, Cox PM, Flato GM et al (2019) Taking climate model evaluation to the next level. Nat Clim Chang 9:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0355-y
Flato G, Marotzke J, Abiodun B, et al (2013) Evaluation of climate models. In: Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA., pp 741–866
Goldenson N, Mauger G, Leung LR et al (2018) Effects of ensemble configuration on estimates of regional climate uncertainties. Geophys Res Lett 45:926–934. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076297
Gupta HV, Kling H, Yilmaz KK, Martinez GF (2009) Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: implications for improving hydrological modelling. J Hydrol 377:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.003
Hamed MM, Nashwan MS, Shahid S (2021) Intercomparison of historical simulation and future projections of rainfall and temperature by CMIP5 and CMIP6 GCMs over Egypt. Int J Climatol 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7468
Hamed MM, Nashwan MS, Shahid S, et al (2022) Inconsistency in historical simulations and future projections of temperature and rainfall: a comparison of CMIP5 and CMIP6 models over Southeast Asia. Atmos Res 265:105927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105927
Iqbal Z, Shahid S, Ahmed K, et al (2021) Evaluation of CMIP6 GCM rainfall in mainland Southeast Asia. Atmos Res 254:105525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105525
Jourdain NC, Gupta Sen A, Taschetto AS et al (2013) The Indo-Australian monsoon and its relationship to ENSO and IOD in reanalysis data and the CMIP3/CMIP5 simulations. Clim Dyn 41:3073–3102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1676-1
Kamruzzaman M, Shahid S, Islam ARMT et al (2021) Comparison of CMIP6 and CMIP5 model performance in simulating historical precipitation and temperature in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Theor Appl Climatol 145:1385–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03691-0
Khadka D, Babel MS, Abatan AA, Collins M (2021) An evaluation of CMIP5 and CMIP6 climate models in simulating summer rainfall in the Southeast Asian monsoon domain. Int J Climatol 1–22 https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7296
Khan N, Shahid S, Ahmed K, et al (2018) Performance assessment of general circulation model in simulating daily precipitation and temperature using multiple gridded datasets. Water 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121793
Khan N, Pour SH, Shahid S et al (2019) Spatial distribution of secular trends in rainfall indices of Peninsular Malaysia in the presence of long-term persistence. Meteorol Appl 26:655–670. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1792
Kulkarni S (2014) Assessment of global model simulations of present and future climate. Arizona State University
Lan CW, Lo MH, Chou C, Kumar S (2016) Terrestrial water flux responses to global warming in tropical rainforest areas. Earth’s Futur 4:210–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015EF000350
Liang J, Tan ML, Hawcroft M, et al (2021) Monsoonal precipitation over Peninsular Malaysia in the CMIP6 HighResMIP experiments: the role of model resolution. Clim Dyn 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-06033-y
Lun Y, Liu L, Cheng L et al (2021) Assessment of GCMs simulation performance for precipitation and temperature from CMIP5 to CMIP6 over the Tibetan Plateau. Int J Climatol 41:3994–4018. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7055
Meehl GA, Covey C, Delworth T et al (2007) THE WCRP CMIP3 multimodel dataset: a new era in climate change research. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 88:1383–1394. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-88-9-1383
Muhammad MKI, Shahid S, Ismail T et al (2021) The development of evolutionary computing model for simulating reference evapotranspiration over Peninsular Malaysia. Theor Appl Climatol 144:1419–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03606-z
Muhammad MKI, Nashwan MS, Shahid S, et al (2019) Evaluation of empirical reference evapotranspiration models using compromise programming: a case study of Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability 11:4267. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164267
Nashwan MS, Shahid S (2020) A novel framework for selecting general circulation models based on the spatial patterns of climate. Int J Climatol 40:4422–4443. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6465
Nashwan SM, Shahid S, Chung E-S et al (2018) Development of climate-based index for hydrologic hazard susceptibility. Sustainability 10:2182
Noor M, Ismail T, Bin T, Shahid S et al (2019) Selection of CMIP5 multi-model ensemble for the projection of spatial and temporal variability of rainfall in peninsular Malaysia. Theor Appl Climatol 138:999–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02874-0
Noor M, Ismail T, Shahid S et al (2019) Development of multi-model ensemble for projection of extreme rainfall events in Peninsular Malaysia. Hydrol Res 50:1772–1788. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2019b.097
Noor M, Ismail T, Chung ES, et al (2018) Uncertainty in rainfall intensity duration frequency curves of peninsular Malaysia under changing climate scenarios. Water 10:1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121750
O’Neill BC, Tebaldi C, van Vuuren DP et al (2016) The scenario model intercomparison project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6. Geosci Model Dev 9:3461–3482. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-9-3461-2016
Perkins SE, Pitman AJ, Holbrook NJ, McAneney J (2007) Evaluation of the AR4 climate models’ simulated daily maximum temperature, minimum temperature, and precipitation over Australia using probability density functions. J Clim 20:4356–4376. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4253.1
Pour S, Harun S, Shahid S (2014) Genetic programming for the downscaling of extreme rainfall events on the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos (Basel) 5:914–936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040914
Pour SH, Shahid S, Chung ES, Wang XJ (2018) Model output statistics downscaling using support vector machine for the projection of spatial and temporal changes in rainfall of Bangladesh. Atmos Res 213:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.06.006
Pour SH, Wahab AKA, Shahid S (2020) Physical-empirical models for prediction of seasonal rainfall extremes of Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos Res 233:104720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104720
Sa’adi Z, Shahid S, Chung ES, Ismail bin T (2017) Projection of spatial and temporal changes of rainfall in Sarawak of Borneo Island using statistical downscaling of CMIP5 models. Atmos Res 197:446–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2017.08.002
Salman SA, Nashwan MS, Ismail T, Shahid S (2020) Selection of CMIP5 general circulation model outputs of precipitation for peninsular Malaysia. Hydrol Res 51:781–798. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2020.154
Schiemann R, Demory ME, Mizielinski MS, et al (2014) The sensitivity of the tropical circulation and Maritime Continent precipitation to climate model resolution. Clim Dyn 42:2455–2468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1997-0
Shahid S, Pour SH, Wang X et al (2017) Impacts and adaptation to climate change in Malaysian real estate. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 9:87–103. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2016-0001
Shiru MS, Chung ES (2021) Performance evaluation of CMIP6 global climate models for selecting models for climate projection over Nigeria. Theor Appl Climatol 146:599–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03746-2
Shiru MS, Shahid S, Chung ES et al (2019) A MCDM-based framework for selection of general circulation models and projection of spatio-temporal rainfall changes: a case study of Nigeria. Atmos Res 225:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.03.033
Stouffer RJ, Eyring V, Meehl GA et al (2017) CMIP5 scientific gaps and recommendations for CMIP6. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 98:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00013.1
Tan ML, Liang J, Hawcroft M, et al (2021) Resolution dependence of regional hydro-climatic projection: a case-study for the Johor River Basin, Malaysia. Water 13:3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223158
Toh YY, Turner AG, Johnson SJ, Holloway CE (2018) Maritime Continent seasonal climate biases in AMIP experiments of the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble. Clim Dyn 50:777–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3641-x
Wright DB, Knutson TR, Smith JA (2015) Regional climate model projections of rainfall from U.S. landfalling tropical cyclones. Clim Dyn 45:3365–3379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2544-y
Ziarh GF, Asaduzzaman M, Dewan A, et al (2021a) Integration of catastrophe and entropy theories for flood risk mapping in peninsular Malaysia. J Flood Risk Manag 14:e12686. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12686
Ziarh GF, Shahid S, Ismail T Bin, et al (2021b) Correcting bias of satellite rainfall data using physical empirical model. Atmos Res 251:105430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105430
Acknowledgements
The authors are also thankful to the WCRP Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (Phase 6) website of the Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison (PCMDI) for providing GCM simulation data through the data portal. The authors are also grateful to the Department of Drainage (DID), Malaysia, for providing rainfall records.
Funding
The authors are grateful to Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for providing financial support to conduct this research through Postdoctoral Fellowship (Teaching & Learning) Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors equally contributed to conceptualizing and designing the study. Sahar Hadi Pour collected data, performed necessary analysis, prepared results, and the first draft; Shamsuddin Shahid wrote the programming code for data analysis and repeatedly revised the initial draft to generate the final version. Mohammed Mainuddin performed investigation, revision, and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pour, S.H., Shahid, S. & Mainuddin, M. Relative performance of CMIP5 and CMIP6 models in simulating rainfall in Peninsular Malaysia. Theor Appl Climatol 149, 709–725 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04076-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04076-7