Abstract
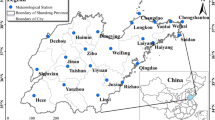
This study explores change of precipitation and temperature using the Mann–Kendall test and the spatiotemporal variation of dryness/wetness using the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index and empirical orthogonal function (EOF) analysis on 1-month time scales in Zhejiang Province, China, over 1971–2015. The results show that monthly precipitation had significant decreasing trends during April, May, September, and October, and significant increasing trends during November and December. Monthly temperatures had significant increasing trends in each month. Increasing temperature significantly increased drought events and intensity. There were consistent spatial patterns of dryness/wetness in Zhejiang. There were dryness trends in April, May, and September, a wetness trend in August, and no dryness/wetness pattern change in other months. The second EOF modes showed that dryness/wetness patterns were anti-phase between northern and southern Zhejiang during April–October. The third EOF modes showed that patterns were anti-phase between eastern and western Zhejiang in August and September.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Fao Irrigation and Drainage Paper, 56
Chen S (2014) A study of the climatic anomaly of the spring precipitation in southern China. Clim Chang Res Lett 03(1):6–12
Dubrovsky M, Svoboda MD, Trnka MJ et al (2009) Application of relative drought indices in assessing climate-change impacts on drought conditions in Czechia. Theor Appl Clim 96(1–2):155–171
Ercha A, Zhang D, Ridley AJ, Xiao Z, Hao Y (2012) A global model: empirical orthogonal function analysis of total electron content 1999-2009 data. J Geophys Res Atmos 117(A3):1–83
Feng S, Hu Q, Qian W (2004) Quality control of daily meteorological data in China 1951–2000: a new dataset. Int J Climatol 24:853–870
Fischer T, Gemmer M, Lüliu L et al (2011) Temperature and precipitation trends and dryness/wetness pattern in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China, 1961–2007. Quat Int 244(2):138–148
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2014) Drought characterisation based on water surplus variability index. Water Resour Manag 28(10):3179–3191
Guo L, Xia Z (2014) Temperature and precipitation long-term trends and variations in the Ili-Balkhash Basin. Theor Appl Clim 115(1–2):219–229
Huang J, Sun S, Xue Y et al (2014a) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation indices during 1961-2010 in Hunan Province, Central South China. Theor Appl Clim 118(3):581–595
Huang J, Sun S, Xue Y et al (2014b) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation and dryness/wetness during 1961–2008 in Sichuan Province, West China. Water Resour Manag 28(6):1655–1670
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2014) ‘Detection and Attribution of Climate Change: from Global to Regional ’ Chapter 10 in Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Available at: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/
Kaihatu JM, Handler RA, Marmorino GO, Shay LK (1998) Empirical orthogonal function analysis of ocean surface currents using complex and real-vector methods. J Atmos Ocean Technol 15:927–941
Liu Z, Zhou P, Zhang F et al (2013a) Spatiotemporal characteristics of dryness/wetness conditions across Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Agric For Meteorol 182–183:101–108
Liu T, Wu L, Zhang J, Ren F (2013b) Analysis of tropical cyclone precipitation changes in China in July-September during 1965-2010. Acta Meteorological Sinca 71(1):63–75
Livada I, Assimakopoulos VD (2007) Spatial and temporal analysis of drought in Greece using the standardized precipitation index (SPI). Theor Appl Climatol 89:143–153
Lorenzo-Lacruz J, Vicente-Serrano SM, López-Moreno JI et al (2010) The impact of droughts and water management on various hydrological systems in the headwaters of the Tagus River (Central Spain). J Hydrol 386(1–4):13–26
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Preprints, Eighth Conf. on Applied Climatology. Anaheim, CA, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 179–184
Patel NR, Chopra P, Dadhwal VK (2007) Analyzing spatial patterns of meteorological drought using standardized precipitation index. Meteorol Appl 14(4):329–336
Potop V, Možný M, Soukup J (2012) Drought evolution at various time scales in the lowland regions and their impact on vegetable crops in the Czech Republic. Agric For Meteorol 156(8):121–133
Potop V, Boroneanţ C, Možný M, Štěpánek P, Skalák P (2014) Observed spatiotemporal characteristics of drought on various time scales over the Czech Republic. Theor Appl Clim 115(3–4):563–581
Qian W, Lin X (2004) Regional trends in recent temperature indices in China. Clim Res 27:119–134
Qian W, Lin X (2005) Regional trends in recent precipitation indices in China. Meteorog Atmos Phys 90(3–4):193–207
Rebetez M, Mayer H, Dupont O et al (2006) Heat and drought 2003 in Europe: a climate synthesis. Ann For Sci 63:569–577
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Shen J, Hu B (2005) Analysis of laws and sudden-change of drought/flood for last 534 years in Zhejiang Province. Meteorological Monthly 31(10):76–79 (in Chinese)
Stagge JH, Tallaksen LM, Gudmundsson L et al (2015) Candidate distributions for climatological drought indices (SPI and SPEI). Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.4267
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI et al (2012) Performance of drought indices for ecological, agricultural, and hydrological applications. Earth Interact 16(3):1–27
Wang H (2001) The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv Atmos Sci 18(3):376–386
Yusof F, Hui-Mean F, Suhaila J et al (2014) Rainfall characterisation by application of standardised precipitation index (SPI) in peninsular Malaysia. Theor Appl Clim 115(3–4):503–516
Zhai J, Su B, Krysanova V et al (2010) Spatial variation and trends in PDSI and SPI indices and their relation to streamflow in 10 large regions of China. J Clim 23(3):649–663
Zhang Q, Xu CY, Zhang Z (2009) Observed changes of drought/wetness episodes in the Pearl River Basin, China, using the standardized precipitation index and aridity index. Theor Appl Clim 98(1–2):89–99
Acknowledgements
This paper was financially supported by a major agricultural grant from the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2011C22082), and by the Disaster Research Fund of the People’s Insurance Company of China (Study and Application on Weather Index Insurance).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, W., Wu, L., Mao, Y. et al. Precipitation and temperature trends and dryness/wetness pattern during 1971–2015 in Zhejiang Province, southeastern China. Theor Appl Climatol 133, 47–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2134-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2134-5