Summary
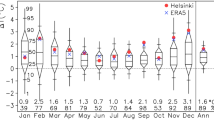
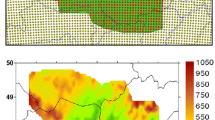
A new statistical method for regional climate simulations is introduced. Its simulations are constrained only by the parameters of a linear regression line for a characteristic climatological variable. Simulated series are generated by resampling from segments of observation series such that the resulting series comply with the prescribed regression parameters and possess realistic annual cycles and persistence. The resampling guarantees that the simulated series are physically consistent both with respect to the combinations of different meteorological variables and to their spatial distribution at each time step. The resampling approach is evaluated by means of a cross validation experiment for the Elbe river basin: Its simulations are compared both to an observed climatology and to data simulated by a dynamical RCM. This cross validation shows that the approach is able to reproduce the observed climatology with respect to statistics such as long-term means, persistence features (e.g., dry spells) and extreme events. The agreement of its simulations with the observational data is much closer than for the RCM data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J Beersma T Buishand (2003) ArticleTitleMulti-site simulation of daily precipitation and temperature conditional on the atmospheric circulation Climate Res 25 121–133 Occurrence Handle10.3354/cr025121
R Benestad (2004) ArticleTitleTentative probabilistic temperature scenarios for northern Europe Tellus 56A 89–101
R Blender K Fraedrich (2003) ArticleTitleLong time memory in global warming simulations Geophys Res Lett 30 1769–1772 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2003GL017666
R Cleveland W Cleveland J McRae I Terpenning (1990) ArticleTitleSTL: a seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on loess J Official Statistics 6 3–33
Déqué M (2004) Uncertainties in PRUDENCE simulations: global high resolution models. Tech. rep., DMI. http://prudence.dmi.dk/
DVWK (1996) Ermittlung der Verdunstung von Land- und Wasserflächen. DVWK Merkblätter zur Wasserwirtschaft 238, DVWK
W Enke A Spekat (1997) ArticleTitleDownscaling climate model outputs into local and regional weather elements by classification and regression Climate Res 8 195–207 Occurrence Handle10.3354/cr008195
M Fox-Rabinovitz J Côté B Dugas M Déqué J McGregor (2006) ArticleTitleVariable resolution general circulation models: Streched-grid model intercomparison project (SGMIP) J Geophys Res 111 1–21 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2005JD006520
K Fraedrich R Blender (2003) ArticleTitleScaling of atmosphere and ocean temperature correlations in observations and climate models Phys Rev Lett 90 108501 Occurrence Handle10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.108501
Gerstengarbe FW, Werner P (2005) Katalog der Großwetterlagen Europas (1881–2004) nach Paul Hess und Helmut Brezowsky, 6. verbesserte und ergänzte Auflage. PIK Report 100, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
J Hartigan (1975) Clustering algorithms Wiley New York, USA
JA Hartigan MA Wong (1979) ArticleTitleA K-means clustering algorithm Appl Stat 28 100–108 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2346830
J Houghton Y Ding D Griggs M Noguer P van der Linden X Dai K Maskell C Johnson (2001) Climate Change 2001, the scientific bases SeriesTitleContribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the IPCC Cambridge University Press Cambridge
D Jacob (2001) ArticleTitleA note to the simulation of the annual and inter-annual variability of the water budget over the Baltic Sea drainage basin Meteorol Atmos Phys 77 61–73 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007030170017
Jacob D (2007a) Hinweise für REMO-Datennutzer. http://www.mad.zmaw.de/fileadmin/extern/documents/REMO-UBA-H%inweise.pdf
Jacob D (2007b) The REMO UBA project. http://www.mad.zmaw.de/projects-at-md/sg-adaptation/links-to%-other-regional-model-data/remouba-project/
Mitchell J, Ewins P (2003) The Scientific and Technical Review 2002/3. Tech. rep., Met Office, Exceter, UK
J Murphy (1999) ArticleTitleAn evaluation of statistical and dynamical techniques for downscaling local climate J Climate 12 2256–2284 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<2256:AEOSAD>2.0.CO;2
J Murphy D Sexton D Barnett G Jones M Webb M Collins D Stainforth (2004) ArticleTitleQuantification of modelling uncertainties in a large ensemble of climate change simulations Nature 430 768–772 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02771
Österle H (2005) Annual mean temperatures of Germany according to ECHAM4 present climate simulation. Personal Communication at Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Germany
R Development Core Team (2004) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org, iSBN 3-900051-00-3
Richter D (1995) Ergebnisse methodischer Untersuchungen zur Korrektur des systematischen Messfehlers des Hellmann-Niederschlagsmesser. Bericht des DWD 194, Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Germany
A Ruiz-Barradas S Nigam (2006) ArticleTitleIPCC’s twentieth-century climate simulations: varied representations of north American hydroclimate varaibility J Climate 19 4041–4058 Occurrence Handle10.1175/JCLI3809.1
M Semenov EM Barrow (1997) ArticleTitleUse of a stochastic weather generator in the development of climate change scenarios Climatic Change 35 397–414 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005342632279
D Steinhausen K Langer (1977) Clusteranalyse – Einführung in Methoden und Verfahren der automatischen Klassifikation Walter de Gruyter Berlin
B Timbal B McAvaney (2001) ArticleTitleAn analogue-based method to downscale surface air temperature: application for Australia Clim Dynam 17 947–963 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820100156
von Storch H, Hewitson B, Mearns L (2000) Review of empirical downscaling techniques. In: Iversen T, Hoiskar B (eds) Regional climate development under global warming. No. 4 in General Technical Report, RegClim, Jevnaker, Torbjornrud, Norway, pp 29–46
H von Storch F Zwiers (1999) Statistical Analysis in Climate Research Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
C Wallace T Osborn (2002) ArticleTitleRecent and future modulation of the annual cycle Climate Res 22 1–11 Occurrence Handle10.3354/cr022001
Wessel P, Smith W (2006) The Generic Mapping Tools – GMT. University of Hawai’i at Manoa, NOAA. http://gmt.soest.hawaii.edu/
R Wilby T Wigley (1997) ArticleTitleDownscaling general circulation model output: a review of methods and limitations Prog Phys Geog 21 530–548 Occurrence Handle10.1177/030913339702100403
R Wilby T Wigley D Conway P Jones B Hewitson J Main D Wilks (1998) ArticleTitleStatistical downscaling of general circulation model output: a comparison of methods Water Resour Res 34 2995–3008 Occurrence Handle10.1029/98WR02577
D Wilks (1999) ArticleTitleInterannual variability and extrem-value characterisitcs of several stochastic daily precipitation models Water Resour Res 34 2995–3008
E Zorita H von Storch (1999) ArticleTitleThe analog method as a simple statistical downscaling technique: comparison with more complicated methods J Climate 12 2474–2489 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<2474:TAMAAS>2.0.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Correspondence: B. Orlowsky, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, P.O. Box 60 12 03, 14412 Potsdam, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlowsky, B., Gerstengarbe, FW. & Werner, P. A resampling scheme for regional climate simulations and its performance compared to a dynamical RCM. Theor Appl Climatol 92, 209–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0352-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0352-y