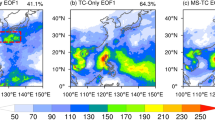
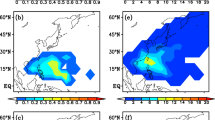
Summary
In 2002, India had experienced one of the most severe droughts. The severe drought conditions were caused by the unprecedented deficient rainfall in July 2002, in which only 49% of the normal rainfall was received. One of the major circulation anomalies observed during July 2002, was the active monsoon trough over Northwest (NW) Pacific and enhanced typhoon activity over this region. The present study was designed to examine the long-term relationships between Tropical Cyclone (TC) activity over NW Pacific and monsoon rainfall over India in July.
A statistically significant negative correlation between TC days over NW Pacific and July rainfall over India was observed. Spatial dependence of the relationship revealed that TCs forming over NW Pacific east of 150° E and moving northwards have an adverse effect on Indian monsoon rainfall. It was observed that TCs forming over the South China Sea and moving westwards may have a positive impact on monsoon rainfall over India. Enhanced TC activity over NW Pacific during July 2002 induced weaker monsoon circulation over the Indian region due to large-scale subsidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JCL Chan (1985) ArticleTitleTropical cyclone activity in the Northwest Pacific in relation to the El Niño/Southern Oscillation phenomenon Mon Wea Rev 113 599–606 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<0599:TCAITN>2.0.CO;2
JCL Chan RHF Kwok (1999) ArticleTitleTropical cyclone genesis in a global NWP model Mon Wea Rev 127 611–624 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127<0611:TCGIAG>2.0.CO;2
JCL Chan (2000) ArticleTitleTropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific associated with El Niño and La Niña events J Climate 13 2960–2972 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<2960:TCAOTW>2.0.CO;2
Chia Hsin Hsing CF Ropelewski (2002) ArticleTitleThe interannual variability in the genesis location of tropical cyclones in the Northwest Pacific J Climate 15 2934–2944 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<2934:TIVITG>2.0.CO;2
K Dong (1988) ArticleTitleEl Niño and tropical cyclone frequency in the Australian region and the Northwest Pacific Aust Meteor Mag 28 219–225
PV Joseph (1990) ArticleTitleMonsoon variability in relation to equatorial trough activity over Indian and West Pacific Oceans Mausam 41 291–296
Kalsi SR, Hatwar HR, Jayanthi N, Subramanian SK, Shyamala B, Rajeevan M, Jenamani RK (2004) Some abnormal features of 2002 southwest monsoon. Meteor Monogr Synoptic Met 1/76
E Kalnay et al. (1996) ArticleTitleThe NCEP/NCAR 40 year re-analysis project Bull Amer Meteor Soc 77 437–471 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
V Kumar R Krishnan (2005) ArticleTitleOn the association between the Indian summer monsoon and the tropical cyclone activity over Northwest Pacific Curr Sci 88 602–612
MA Lander (1993) ArticleTitleComments on “A GCM simulation of the relationship between tropical storm formation and ENSO.” Mon Wea Rev 121 2137–2143 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<2137:COGSOT>2.0.CO;2
MA Lander (1994) ArticleTitleAn exploratory analysis of the relationship between tropical storm formation in the western North Pacific and ENSO Mon Wea Rev 122 636–651 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1994)122<0636:AEAOTR>2.0.CO;2
Landsea CW (2000) El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the seasonal predictability of tropical cyclones El Niño. In: Impacts of multiscale variability on natural ecosystems and society (Diaz HF, Markgraf V, eds). Cambridge University Press, pp 149–181
J McBride R Zehr (1981) ArticleTitleObservational analysis of tropical cyclone formation. Part II: Comparison of non-developing versus developing systems J Atmos Sci 38 1132–1151 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0469(1981)038<1132:OAOTCF>2.0.CO;2
M Rajeevan (1993) ArticleTitleInter-relationship between NW Pacific typhoon activity and Indian summer monsoon on inter-annual and intraseasonal time-scales Mausam 44 97–101
GR Ramanna (1969) ArticleTitleRelation between depressions of Bay of Bengal and tropical storms of the China Sea Indian J Met Geophys 19 148–150
Rao YP (1976) Southwest monsoon. Meteor Monogr Synoptic Met 1/76
K Saha F Sanders J Shukla (1981) ArticleTitleWestward propagating predecessors of monsoon depression Mon Wea Rev 109 330–343 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0493(1981)109<0330:WPPOMD>2.0.CO;2
MS Swaminathan (1998) ArticleTitlePadma Bhusan Prof. P. Koteswaram First Memorial Lecture – 23rd March 1998: Climate and sustainable food security Vayu Mandal 28 3–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pattanaik, D., Rajeevan, M. Northwest Pacific tropical cyclone activity and July rainfall over India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 95, 63–72 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-006-0193-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-006-0193-0