Summary.
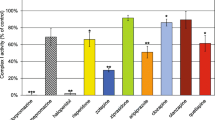
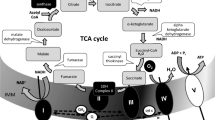
We report effect of various tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives on mitochondrial respiration and the electron transfer complexes. Generally these compounds were potent inhibitors of NADH-linked mitochondrial state 3 respiration and complex I. Presence of a phenyl group at the C1 position or oxidation of N-methylated isoquinones into N-methylisoquinolinium ion augmented the potency to inhibit mitochondrial respiration and complex I. Many of these compounds have been identified in human brains. In view of the mitochondrial and oxidative stress hypothesis, our results suggest involvement of these neurotoxins as potential causes of mitochondrial failure in Parkinson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted June 18, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morikawa, N., Naoi, M., Maruyama, W. et al. Effects of various tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives on mitochondrial respiration and the electron transfer complexes. J Neural Transm 105, 677–688 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050087
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050087