Summary.
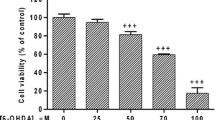
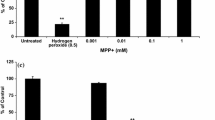
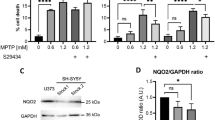
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is widely used to generate animal models of Parkinson's disease. However, little is known about the intracellular events leading to cell death of dopaminergic neurones. Here we correlate indices of energy production and cell viability in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells after exposure to 6-OHDA. The toxin induces a time and dose-dependent decrease in cell survival with an IC50 value of 25 μM after 24 h. In contrast to the mitochondrial complex I inhibitor 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), 6-OHDA-induced reduction of cell viability is not associated with a decrease of intracellular ATP content, intracellular ATP/ADP ratio or NAD+ content. In addition, preventing or forcing glycolysis do not alter 6-OHDA toxicity. The antioxidant D-α-tocopherol can attenuate cell death induced by 6-OHDA. These results suggest that cell death induced by 6-OHDA is not due to an inhibition of mitochondrial energy supply, but probably involves production of free radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received February 10, 1999; accepted August 18, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storch, A., Kaftan, A., Burkhardt, K. et al. 6-Hydroxydopamine toxicity towards human SH-SY5Y dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells: independent of mitochondrial energy metabolism. J Neural Transm 107, 281–293 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050023
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050023