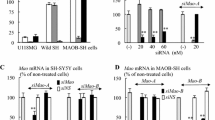
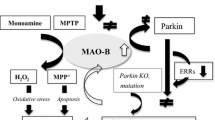
Abstract
Type A and B monoamine oxidases (MAO-A, -B) mediate and modulate intracellular signal pathways for survival or death of neuronal cells. MAO-A is associated with development of neuronal architecture, synaptic activity, and onset of psychiatric disorders, including depression, and antisocial aggressive impulsive behaviors. MAO-B produces hydrogen peroxide and plays a vital role in neuronal loss of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. This review presents a novel role of MAO-A and B, their substrates and inhibitors, and hydrogen peroxide in brain function and neuronal survival and death. MAO-A activity is regulated not only by genetic factor, but also by environmental factors, including stress, hormonal deregulation, and food factors. MAO-A activity fluctuates by genetic–environmental factors, modulates the neuronal response to the stimuli, and affects behavior and emotional activities. MAO-B inhibitors selegiline and rasagiline protect neurons via increase expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and pro-survival neurotrophic factors in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y and glioblastoma U118MG cell lines. MAO-A knockdown suppressed the rasagiline-induced gene expression in SH-SY5Y cells, whereas MAO-B silencing enhanced the basal- and selegiline-induced gene expression in U118MG cells. MAO-A and B were shown to function as a mediator or repressor of gene expression, respectively. Further study on cellular mechanism underlying regulation of signal pathways by MAO-A and B may bring us a new insight on the role of MAOs in decision of neuronal fate and the development of novel therapeutic strategy may be expected for neuropsychiatric disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- ETC:
-
Electron transfer chain
- KLF:
-
Krüppel-like factor
- MAO-A and MAO-B:
-
Type A and B monoamine oxidase
- mao-A and mao-B KD, KO:
-
MAO-A and MAO-B knockdown, knockout
- NHLH2:
-
Nescient helix-loop-helix 2
- NTF:
-
Neurotrophic factor
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinisitol-3 kinase
- siMao-A, siMao-B, siNS :
-
siRNA against mao-A and mao-B, and non-specific
- Sp1:
-
Specificity protein 1
References
Akao Y, Maruyama W, Yi H, Shamoto-Nagai M, Youdim MB, Naoi M (2002) An anti-Parkinson’s disease drug, N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan (rasagiline) enhances expression of antiapoptotic bcl-2 in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett 326(2):105–108
Alemany R, Olmos G, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1995) The effects of phenelzine and other monoamine oxidase inhibitor anti-depressants on brain and liver I2 imidazoline-preferring receptors. Br J Pharmacol 114(4):837–845
Badinter F, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim BH, Weinreb O (2015) Beneficial behavioral, neurochemical and molecular effects of 1-(R)-aminoindan in aged mice. Neuropharmacology 99:264–272
Balciuniene J, Emiilsson L, Oreland L, Pettersson U, Jazin E (2002) Investigation of the functional effect of monoamine oxidase polymorphisms in human brain. Hum Genet 110(1):1–7
Barac YD, Bar-Am O, Liani E, Amit T, Frolov L, Ovcharenko W, Angel O, Youdim MBH, Binah O (2012) I1 imidazoline receptor: novel potential cytoprotective target of TV1022, the S-enantiomer of rasagiline. PLoS ONE 7(11):e47890
Bar-Am O, Amit T, Youdim MB, Weinreb O (2016) Neuroprotective and neurorestorative potential of propargylamine derivatives in ageing: focus on mitochondrial targets. J Neural Transm 123(2):125–135
Bartl J, Müler T, Grünblatt E, Gerlach M, Riederer P (2014) Chronic monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor treatment blocks monoamine oxidase-A enzyme activity. J Neural Transm 121(4):379–383
Buckholtz JW, Mayer-Lindenberg A (2008) MAOA and the neurogenic architecture of human aggression. Trends Neurosci 31(3):120–129
Byrd AL, Manuck SB (2014) MAOA, childhood maltreatment, and antisocial behavior: meta-analysis of a gene–environmental interaction. Biol Psychiatry 75(1):9–17
Cao X, Wei Z, Gabriel GG, Li XM, Mousseau DD (2007) Calcium-sensitive regulation of monoamine oxidase-A contributes to the production of peroxyradicals in hippocampal cultures: implications for Alzheimer disease-related pathology. BMC Neurosci 8:73
Cao X, Rui L, Pennington PR et al (2009) Serine 209 resides with a putative p38(MAPK) consensus motif and regulates monoamine oxidase-A activity. J Neurochem 111(1):101–110
Catarzi S, Biagioni C, Favilli F, Marcucci T, Iantomasi T, Vincenzini MT (2005) Redox regulation of platelet-derived-growth-factor-receptor: role of NADPH-oxidase and c-Src tyrosine kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1745:166–175
Chaudhuri AD, Yelamanchili SV, Fox HS (2013) MicroRNA-142 reduces monoamine oxidase A expression and activity in neuronal cells by downregulating SIRT1. PLoS ONE 8(1):e79579
Checknita D, Maussion G, Labonte B et al (2015) Monoamine oxidase A gene promoter methylation and transcriptional downregulation in an offender population with antisocial personality disorder. Br J Psychiatry 206(3):216–222
Chen J, Zhou Y, Müler-Steiner S et al (2005) SIRT1 protects against microglia- dependent amyloid-β toxicity through inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J Biol Chem 280(48):40364–40374
Chen PS, Peng GS, Li G et al (2006) Valproate protects dopaminergic neurons in midbrain neuron/glia culture by stimulating the release of neurotrophic factors from astrocytes. Mol Psychiatry 11(12):1116–1125
Chen MJ, Nguyen TV, Pike CJ, Rosso-Neustadt AA (2007) Norepinephrine induces BDNF and activates the PI-3K and MAPK cascades in embryonic hippocampal neurons. Cell Signal 19(1):114–128
Chen K, Ou XM, Wu JB, Shih JC (2011) Transcription factor E2F-associated phosphoprotein (EAPP), RAM2/CDCA7L/JPO2 (R1), and Simian virus 40 promoter factor 1 (Sp1) cooperatively regulate glucocorticoid activation of monoamine oxidase B. Mol Pharmacol 79(2):308–317
Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhang L, Shen Y, Xu Q (2012) Effects of MAOA promoter methylation on susceptibility to paranoid schizophrenia. Hum Genet 131(7):1081–1087
Costa-Mallen P, Kelada SN, Costa LG, Checkoway H (2005) Characterization of the in vitro transcriptional activity of polymorphic allele of the human monoamine oxidase-B gene. Neurosci Lett 283(1–2):171–175
Costantini P, Chernyak BV, Petronilli V, Bernardi P (1996) Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore by pyrimidine nucleotides and dithiol oxidation at two separate sites. J Biol Chem 271(12):6746–6751
De Zutter GS, Davis RJ (2001) Pro-apoptotic gene expression mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(11):6168–6173
Dlugos AM, Palmer AA, de Wit H (2009) Negative emotionality: monoamine oxidase B gene variants modulate personality traits in healthy humans. J Neural Transm 116(10):1323–1334
Dolle F, Valette H, Bramoulle Y et al (2003) Synthesis and in vivo imaging properties of [11C]befloxatone: a novel highly potent position emission tomography ligand for mono-amine oxidase-A. Bioorg Med Chem 13(10):1771–1775
Domschke K, Tidow N, Kuithan H et al (2012) Monoamine oxidase A gene DNA hypomethylation—a risk factor for panic disorder? Int J Neuropychopharmacol 15(9):1217–1228
Ducci F, Enoch MA, Hodgkinson C, Xu K, Catena M, Robin RW, Goldman D (2008) Interaction between a functional MAOA locus and childhood sexual abuse predicts alcoholism and antisocial personal disorder in adult women. Mol Psychiatry 13(3):334–347
Duncan JW, Zhang X, Wang N et al (2016) Binge ethanol exposure the Krüppel-like factor 11-monoamine oxidase (MAO) pathway in rats: examining the use of MAO inhibitors to prevent ethanol-induced brain injury. Neuropharmacology 105:329–340
Egashira T, Sakai K, Sakurai M, Takayama F (2003) Calcium disodium edetate enhances type A monoamine oxidase activity in monkey brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 94(3):203–211
Ekblom J, Oreland L, Chen K, Shih JC (1998) Is there a “non-MAO” macromolecular target for l-deprenyl?: Studies on MAOB mutant mice. Life Sci 63(12):PL161–PL186
Erjavec GN, Sviglin KN, Perkovic MN, Muck-Seler D, Jovanovic T, Pivac N (2014) Association of gene polymorphisms encoding dopaminergic system components and platelet MAO-B activity with alcohol dependence and alcohol dependence-related phenotypes. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 54:321–327
Fergusson DM, Boden JM, Honwood LJ, Miller AL, Kennedy MA (2011) MAOA, abuse exposure and antisocial behaviour: 30-year longitudinal study. Br J Psychiatry 198(6):457–463
Finberg JPM, Rabey JM (2016) Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B in psychiatry and neurology. Front Pharmacol 7:340
Fitzgerald JC, Ufer C, De Girolamo LA, Kuhn H, Billett EE (2007) Monoamine oxidase-A modulates apoptosis cell death induced by staurosporine in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 103(6):2189–2199
Fitzgerald KC, Ugun-Klusek A, Allen G, De Girolamo LA, Hargreaves I, Ufer C, Abramov AY, Billett WW (2014) Monoamine oxidase-A knockdown in human neuroblastoma cells reveals protection against mitochondrial toxins. FASEB J 28(1):218–229
Fonseca CP, Gama S, Saavedra A, Baltazar G (2014) H2O2- or l-DOPA-injured dopaminergic neurons trigger the release of double mediators that up-regulate striatal GDNF through different signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(7):927–934
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Logan J, Pappas N, Shea C, MacGregor R (1997) Age-related increases in brain monoamine oxidase B in living healthy human subjects. Neurobiol Aging 18(4):431–435
Fowler JS, Logan J, Volkow ND, Wang GJ (2005) Translational neuroimaging: positron emission tomography studies of monoamine oxidase. Mol Imaging Biol 7:377–387
Fowler JS, Alia-Klein N, Kriplani A et al (2007) Evidence that brain MAO A activity does not correspond to MAO genotype in healthy male subjects. Biol Psychiatry 62(4):355–358
Fowler JS, Logan J, Volkow ND et al (2015) Evidence that formulation of the elective MAO-B inhibitor, selegiline, which bypass first-pass metabolism, also inhibit MAO-A in the human brain. Neuropharmacology 40(3):650–657
Freedman NMT, Mishani E, Krausz Y, Weininger J, Lester H, Blaugrund E, Ehrlich D, Chisin R (2005) In vivo measurement of rain monoamine oxidase B occupancy by rasagiline, using 11C-l-deprenyl and PET. J Nucl Med 46(10):1618–1624
Gan L, Johnson JA (2014) Oxidative damage and the Nrf2–ARE pathway in neurodegenerative disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(8):1208–1218
Gasso P, Bernardo M, Mas S, Crescenti A, Garcia C, Parellada E, Lafuente A (2008) Association of A/G polymorphism in intron 13 of the monoamine oxidase B gene with schizophrenia in a Spanish population. Neuropsychobiology 58(2):65–70
Giorgio M, Trinei M, Migliaccio E, Pelicci PG (2007) Hydrogen peroxide: a metabolic by-product or a common mediator of ageing signals? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(9):722–728
Glover V, Sandler M, Owen F, Riley GJ (1977) Dopamine is a monoamine oxidase B substrate in man. Nature 265(5589):80–81
Godar SC, Fite PJ, McFarlin KM, Bortolato M (2016) The role of monoamine oxidase A in aggression: current translational developments and future challenges. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 69:90–100
Götz ME, Fischer P, Gsell W, Riederer P, Streifler M, Simanyi M, Müller F, Danielczyk W (1998) Platelet monoamine oxidase B activity in dementia. A 4-year follow-up. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 9(2):74–77
Grimsby J, Chen K, Wang LJ, Lan NC, Shih JC (1991) Human monoamine oxidase A and B genes exhibit identical exon-intron organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(9):3637–3641
Grunewald M, Johnson S, Lu D et al (2012) Mechanistic role of a novel gluocorticoid-KLF11 (TIEG2) protein pathway in stress-induced monoamine oxidase A expression. J Biol Chem 287(29):24195–24206
Gulyas B, Pavlova E, Kasa P et al (2011) Activated MAO-B in the brain of Alzheimer patients, demonstrated by [11C]-l-deprenyl using whole hemisphere autoradiography. Neurochem Int 58(1):60–68
Gyarfas T, Knuuttila J, Lindholm P, Rantamäki T, Castren E (2010) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor (CDNF) by anti-parkinsonian drug therapy in vivo. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30(3):361–369
Halliday GM, Stevens CH (2011) Glia: initiators and progressors of pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(1):6–17
Haneka MT, Rodriguez JJ, Verkharatsky A (2010) Neuroglia in neurodegeneration. Br Res Rev 63(1–2):189–211
Harris S, Johnson S, Duncan JW et al (2015) Evidence revealing deregulation of the KLF11–MAO A pathway in association with chronic stress and depressive disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:1373–1382
Hauptman N, Grmsby J, Shi JC, Cadenas E (1996) The metabolism of tyramine by monoamine oxidase A/B causes oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA. Arch Biochem Biophys 335(2):295–304
Heikkila RE, Manzino L, Cabbat FS, Duvoisin RC (1984) Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) by monoamine inhibitors. Nature 311(5985):467–469
Hisaoka K, Nishida A, Takebayashi M, Koda T, Yamawaki S, Nakata Y (2004) Serotonin increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor release in rat C6 glioblastoma cells. Br Res 1002:167–170
Hisaoka K, Maeda N, Tsuchioka M, Takebayashi M (2008) Antidepressants induce acute CREB phosphorylation and CRE-mediated gene expression in glial cells: a possible contribution to GDNF production. Br Res 1196:53–58
Holschneider DP, Scremin QU, Huynh L, Chen K, Shih JC (1999a) Lack of protection from ischemic injury of monoamine oxidase B-deficient mice following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci Lett 259(3):161–164
Holschneider DP, Scremin QU, Chen K, Shih JC (1999b) Lack of protection of monoamine oxidase B-deficient mice from age-related spatial learning deficits in the Morris water maze. Life Sci 65(17):1757–1763
Holschneider DP, Chen K, Shi JC (2001) Biochemical, behavioral, physiologic, and neurodevelopmental changes in mice deficient in monoamine oxidase A or B. Brain Res Bull 56(5):453–462
Holt A, Berry MD, Boulton AA (2004) On the binding of monoamine oxidase inhibitors to some sites distinct from the MAO active site, and effects thereby elicited. Neurotoxicology 25(1–2):251–266
Huang Y, Cate SP, Battistuzz C, Oquendo MA, Brent D, Man JJ (2004) An association between a functional polymorphism in the monoamine oxidase A gene promoter, impulsive traits and early abuse experiences. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(8):1498–1505
Inaba-Hasegawa K, Akao Y, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2012) Type A monoamine oxidase is associated with induction of neuroprotective Bcl-2 by rasagiline, an inhibitor of type B monoamine oxidase. J Neural Transm 119(4):405–414
Inaba-Hasegawa K, Akao Y, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2013) Rasagiline and selegiline, inhibitors of type B monoamine oxidase, induce type A monoamine oxidase in human SH-SY5Y cells. J Neural Transm 120(3):435–444
Inaba-Hasegawa K, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2017a) Type B and A monoamine oxidase and their inhibitors regulate the gene expression of Bcl-2 and neurotrophic factors in human glioblastoma U118MG cells: different signal pathways for neuroprotection by selegiline and rasagiline. J Neural Transm 124(9):1055–1066
Inaba-Hasegawa K, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2017b) Phytochemicals induce genes coding Bcl-2 and neurotrophic factors in human glioblastoma U118MG cells: suppression by type B monoamine oxidase (in preparation)
Ivy AS, Rodriguez FG, Garcia C, Chen MJ, Russo-Neustadt AA (2003) Noradrenergic and serotonergic blockage inhibits BDNF mRNA activation following exercise and antidepressant. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75(1):81–88
Jakubauskiene E, Janaviciute V, Peciuliene I, Söderkvist P, Kanopka A (2012) G/A polymorphism in intronic sequence affects the processing of MAO-B in patients with Parkinson disease. FEBS Lett 586(20):3698–3704
Jiang H, Jiang Q, Liu W, Feng J (2006) Parkin suppresses the expression of monoamine oxidases. J Biol Chem 281(13):8591–8599
Johnson S, Stockmeyer CA, Meyer JH et al (2011) The reduction of R1, a novel repressor protein for monoamine oxidase A, in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(10):2139–2148
Juric DM, Miklic S, Carman-Krzan M (2006) Monoaminergic neuronal activity up-regulates BDNF synthesis in cultured neonatal rat astrocytes. Brain Res 1108:54–62
Juric DM, Loncar D, Carman-Lrzan M (2008) Noradrenergic stimulation of BDNF synthesis in astrocytes: mediation via α1- and β1/β2-adrenergic receptors. Neurochem Int 52(1–2):297–306
Kabayama M, Swkoori K, Yamada K, Ornthanalai VG, Ota M, Morimura N, Katayama K, Murphy NP, Aruga J (2013) Rines E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates MAO-A levels and emotional responses. J Neurosci 33(32):12940–12953
Kang SJ, Scott WK, Li YJ et al (2006) Family-based case-control study of MAOA and MAOB polymorphisms in Parkinson disease. Mov Dis 21(12):2175–2180
Kersemans K, Laeken NV, de Vos F (2013) Padiochemistry devoted to the production monoamine oxidase (MAO-A and MAO-B) ligands for brain imaging with positron emission tomography. Label Compd Radiopharm 56(3–4):78–88
Kim D, Nguyen MD, Dobbin MM et al (2007) SIRT1 deacetylase protects against neurodegeneration in models for Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J 26(13):3169–3179
Kinor N, Geffen R, Golomb E, Zinman T, Yadid G (2001) Dopamine increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in human fetal astrocytes. Glia 33(2):143–150
Klegeris A, McGeer PL (2000) R-(−)-Deprenyl inhibits monocytic THP-1 cell neurotoxicity independently of monoamine oxidase inhibition. Exp Neurol 166(2):658–664
Ledreux A, Boger HA, Hinson VK, Cantwell K, Granholm AC (2016) BDNF levels are increased by aminoindan and rasagiline in a double lesion model of Parkinson’s disease. Br Res 1631:34–45
Leroy C, Bragulat V, Berlin I et al (2009) Cerebral monoamine oxidase A inhibition in tobacco smokers confirmed with PET and [11C]befloxatone. J Clin Psychopharmacol 29(1):86–88
Levant B, Morgan KA, Ahlgren-Beckendorf JA, Grandy DK, Chen K, Shih JC, Self I (2010) Modulation of [3H]quinopirole binding at striatal D2 dopamine receptor by a monoamine oxidaseA-like site: evidence from radioligand studies and D2-receptor- and MAO(A)-deficient mice. Life Sci 70(2):229–241
Libert S, Pointer K, Bell EL et al (2011) SIRT1 activates MAO-A in the brain to mediate anxiety and exploratory drive. Cell 147(7):1459–1472
Liu CA, Chinta SJ, Rane A, Andersen JK (2013) Age-related behavioral phenotype of astrocytic monoamine oxidase-B transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54200
Liu W, Rabinpvich A, Nash Y, Frenkel D, Wang Y, Youdim MBH, Weinreb O (2017) Anti-inflammatory and protective effects of MT-031, a novel multitarget MAO-A and AChE/BuChE inhibitor in scopolamine mouse model and inflammatory cells. Neuropharmacology 113(Pt A):445–456
Lu D, Johnson C, Johnson S, Tazil S, Ou XM (2008) The neuroprotective effect of antidepressant drug via inhibition of TIEG2–MAO B mediated cell death. Dug Disc Ther 2(5):289–295
Ludwig B, Dwivedi Y (2016) Dissecting bipolar disorder complexity through epigenomic approach. Mol Psychiatry 21(11):1490–1498
MacInnes N, Handley SL (2002) Characterization of the discriminable stimulus produced by 2-BFI: effects of imidazoline I2-site ligands, MAOIs, β-carbolines, agmatine and ibogaine. Br J Pharm 135(5):1227–1234
Mandel S, Sagi Y, Amit T (2007) Rasagiline promotes regeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in post-MPTP-induced parkinsonism via activation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 32(10):1694–1699
Manoli I, Le H, Alesci S, McFann KK, Su YA, Kino T, Chrousos GP, Blackman MR (2005) Monoamine oxidase-A is a major target for glucocorticoids in human skeletal muscle cells. FASEB J 19(10):1359–1361
Marcocci L, De March U, Salvi M, Nocera S, Agostinelli E, Mondovi B, Toninelllo A (2002) Tyramine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors as modulators of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition. J Membr Biol 188(1):23–32
Marinho HS, Reak C, Cyrne L, Soares H, Antunes F (2014) Hydrogen peroxide sensing, signaling and regulation of transcription factors. Redox Biol 2:535–562
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192(1):1–15
Maruyama W, Naoi M (2013) “70th Birthday Professor Riederer” Induction of glial cell line-derived and brain-derived neurotrophic factors by rasagiline and (−)deprenyl: a way to a disease-modifying therapy? J Neural Transm 120(1):83–89
Maruyama W, Nitta A, Shamoto-Nagai M, Hirata Y, Akao Y, Youdim M, Furukawa S, Nabeshima T, Naoi M (2004) N-Propargyl-1-(R)-aminoindan, rasagiline, increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells through activation of NF-κB transcription factor. Neurochem Int 44(6):293–400
Maschauer S, Haller A, Riss PJ, Kuwert T, Prante O, Cumming P (2015) Specific binding of [18F]fluoroethyl-harmol to monoamine oxidase A in rat brain cytostat sections, and compartmental analysis of binding in living brain. J Neurochem 135(5):908–917
Mattson MP, Chan SL, Duan W (2002) Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol Rev 82:637–672
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B (2004) BDNF and 5-HT: a dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 27(10):588–594
McCarthy D, Lueras P, Bhide P (2007) Elevated dopamine levels during gestation reduced region-specific decreases in neurogenesis and subtle deficits in neuronal numbers. Br Res 1182:11–25
Melas PA, Forsell Y (2015) Hypomethylation of MAOA’s first exon region in depression: a replication study. Psychiatry Res 226(1):389–391
Mele T, Carman-Krzan M, Juric DM (2010) Regulatory role of monoamine transmitters in astrocytic NT-3 synthesis. Int J Dev Neurosci 28(1):13–19
Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A et al (2006) Elevated monoamine oxidase A levels in the brain. An explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(11):1209–1216
Michan S, Li Y, Chou MMH et al (2010) SIRT1 is essential for normal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 30(29):9695–9707
Michel TM, Frangou S, Camara S, Thiemeyer D, Jecel J, Tatschner T, Zoechling R, Gruunblatt E (2008) Altered glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) concentrations in the brain of patients with depressive disorder: a comprehensive post-mortem study. Eur Psychiatry 23(6):413–420
Miklic S, Juric DM, Caman-Krzan M (2004) Differences in the regulation of BDNF and NGF synthesis in cultured neonatal rat astrocytes. Int J Dev Neurosci 22(3):119–130
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163(3):1450–1455
Mizuta I, Ohta M, Ohta K, Nishimura M, Mizuta E, Hayashi K, Kuno S (2000) Selegiline and desmethylselegiline stimulate NGF, BDNF, and GDNF synthesis in cultured mouse astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279(3):751–755
Mousseau DD, Baker GB (2012) Recent developments in the regulation of monoamine oxidase form and function: is the current model restricting our understanding of the breath of contribution of monoamine oxidase to brain dysfunction? Curr Topics Med Chem 12(20):2163–2176
Nag S, Lehmann L, Kettschau G, Heinrich T, Thiele A, Varrone A, Gulyas B, Halldin C (2012) Synthesis and evaluation of [18F]fluororasagiline, a novel position emission tomography (PET) radioligand for monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). Bioorg Med Chem 20(9):3065–3071
Nakamura S, Kawamata T, Akiguchi I, Kameyama M, Nakamura N, Kimura H (1990) Expression of monoamine oxidase B activity in astrocytes of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol 80(4):419–425
Nakaso K, Nakamura C, Sato H, Imamura K, Takeshima T, Nakashima K (2006) Novel cytoprotective mechanism of anti-parkinsonian drug deprenyl: pIK3 and Nrf2-derived induction of antioxidant proteins. Biochim Biophys Res Acta 339(3):915–922
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Inaba-Hasegawa K (2012) Type A and B monoamine oxidase in age-related neurodegenerative disorders: their distinct roles in neuronal death and survival. Curr Top Med Chem 12(20):2177–2188
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Inaba-Hasegawa K (2013) Revelation in the neuroprotective functions of rasagiline and selegiline: the induction of distinct genes by different mechanisms. Expert Rev Neurother 13(6):1233–1250
Naoi M, Riederer P, Maruyama W (2016) Modulation of monoamine oxidase (MAO) expression in neuropsychiatric disorders: genetic and environmental factors involved in type A MAO expression. J Neural Transm 123(2):91–106
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Shamoto-Nagai M (2017a) Type A monoamine oxidase and serotonin are coordinately involved in depressive disorders: from neurotransmitter imbalance to impaired neurogenesis. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1709-8
Naoi M, Inaba-Hasegawa K, Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W (2017b) Neurotrophic function of phytochemicals for neuroprotection in aging and neurodegenerative disorders: modulation of intracellular signaling and gene expression. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-1797-5
Ohta K, Kuno S, Inoue S, Ikeda E, Fujinami A, Ohta M (2010) The effect of dopamine agonists: the expression of GDNF, NGF, and BDNF in cultured mouse astrocytes. J Neurol Sci 291(1–2):12–16
Ossola B, Schendzielorz N, Chen SH, Bird GS, Tuominen RK, Manniströ PT, Hong JS (2011) Amantadine protects dopamine neurons from a dual action: reducing activation of microglia and inducing expression of GDNF in astroglia. Neuropharmacology 61(4):574–582
Ou XM, Chen K, Shih JC (2006a) Monoamine oxidase A and repressor R1 are involved in apoptotic signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(29):10923–10928
Ou XM, Chen K, Shih JC (2006b) Glucocorticoid and androgen activation of monoamine oxidase A is regulated by R1 and Sp1. J Biol Chem 281(30):21512–21525
Patel NJ, Chen MJ, Russo-Neustadt AA (2010) Norepinephrine and nitric oxide promote cell survival signaling in hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 633(1–3):1–9
Pav M, Kovaru H, Fiserova A, Havrdova E, Lisa V (2008) Neurobiological aspects of depressive disorder and antidepressant treatment: role of glia. Physiol Res 57(2):151–164
Pennington PR, Wei Z, Rui L, Doing JA, Graham B, Kuski K, Gabriel GG, Mousseau DD (2011) Alzheimer disease-related presenilin-1 variants exert distinct effects on monoamine oxidase-A activity in vitro. J Neural Transm 118(7):987–995
Perkovic MN, Strac DS, Erjavec GN, Uzun S, Podobnik J, Kozumplik O, Vlatkovic S, Pivac N (2016) Monoamine oxidase and agitation in psychiatric patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 69:131–146
Philibert RA, Gunter TD, Beach SRH, Brody GH, Madan A (2008) MAOA methylation is associated with nicotine and alcohol dependence in women. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(5):565–570
Pizzinat N, Marchal-Victorion S, Maurel A, Ordener C, Bompart G, Parini A (2003) Substrate-dependent regulation of MAO-A in rat mesangial cells: involvement of dopamine D2-like receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284(1):F167–F174
Rekkas PV, Wilson AA, Lee VWH et al (2014) Greater monoamine oxidase A binding in perimenopausal age as measured with carbon 11-labelled harmine position emission tomography. JAMA Psychiatry 71(8):873–879
Ren Y, Jiang H, Ma D, Nakaso K, Feng J (2011) Parkin degrades estrogen-related receptors to limit the expression of monoamine oxidases. Hum Mol Genet 20(6):1074–1083
Riederer P, Laux G (2011) MAO-inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 20(1):1–17
Riederer P, Konradi C, Habenstreit G, Youdim MBH (1989) Neurochemical perspectives to the function of monoamine oxidase. Acta Neurol Scand 126(1):41–45
Roth TL, Sweatt JD (2011) Annual research review: Epigenetic mechanisms and environmental shaping of the brain during sensitive periods of development. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 52(4):398–408
Ryu H, Lee J, Zaman K, Kubilis J, Ross BD, Neve R, Ratan RR (2003) Sp1 and Sp3 are oxidative stress-inducible, antideath transcription factors in cortical neurons. J Neurosci 23(9):3597–3606
Saavedra A, Baltazar G, Santos P, Carvalhp CM, Duarte EP (2006) Selective injury to dopaminergic neurons up-regulates GDNF in substantia nigra postnatal cell cultures: role of neuron-glia crosstalk. Neurobiol Dis 23(3):533–542
Sacher J, Wilson AA, Houle S, Rusjan P, Hassan S, Bloomfield PM, Stewart DE, Maeyer JH (2010) Elevated brain monoamine oxidase A binding in the early postpartum period. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(5):468–474
Sacher J, Rabiner EA, Clark M et al (2012) Dynamic, adaptive changes in MAO-A binding after alterations in substrate availability: an in vivo [11C]-harmine position emission tomography study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(3):443–446
Sacher J, Rekkas PV, Wilson AA et al (2015) Relationship of monoamine oxidase-A distribution volume to postpartum depression and postpartum crying. Neuropsychopharmacology 40(2):427–435
Samantaray S, Chandra G, Mohanakumar KP (2003) Calcium channel agonist, (±)-Bay K8644, causes a transient increase in striatal monoamine oxidase activity in Balb/c mice. Neurosci Lett 342(1–2):73–76
Saura J, Bleuel Z, Ulrich J et al (1996) Molecular neuroanatomy of human monoamine oxidases A and B revealed by quantitative enzyme radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 70(3):755–774
Schedin-Weiss S, Inoue M, Hromadkova L et al (2017) Monoamine oxidase B in elevated in Alzheimer disease neurons, is associated with γ-secretase and regulates neuronal amyloid β-peptide levels. Alzheimers Res Ther 9(1):57
Shih JC, Chen K, Ridd MJ (1999) Monoamine oxidase: from genes to behavior. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:197–217
Shih JC, Boyang J, Chen K (2011) Transcriptional regulation and multiple functions of MAO genes. J Neural Transm 118(7):979–986
Shumay E, Logan J, Volkow ND, Fowler JS (2012) Evidence that the methylation state of the monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) gene predicts brain activity of MAOA enzyme in healthy men. Epigenetics 7(10):1151–1160
Sies H (2014) Role of metabolic H2O2 generation, redox signaling and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 289(13):8735–8741
Sies H (2017) Hydrogen peroxide as central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: oxidative eustress. Redox Biol 11:613–619
Sjöberg RL, Ducci F, Barr CS, Newman T, Dell’Osso L, Virkkunen M, Foldman D (2008) A non-additive interaction of a functional MAO-A VNTR and testosterone predicts antisocial behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(2):425–430
Soliman A, Udemgba C, Fan I et al (2012) Convergent effects of acute stress and glucocorticoid exposure upon MAO-A in humans. J Neurosci 32(48):17120–17127
Strac DS, Petrovic ZK, Perkovic MN, Molac D, Erjavec GN, Pivac N (2016) Platelet monoamine oxidase type B, MAOB intron 13 and MAOA-uVNTR polymorphism and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorders. Stress 29(4):362–373
Su C, Sun F, Cunningham RL, Rybalchenko N, Sigh M (2014) ERK5/KLF4 signaling as a common mediator of the neuroprotective effects of both nerve growth factor and hydrogen peroxide preconditioning. Age (Dordr) 36(4):9685
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman RME, Ju WJ, Mammen M, Carlile GW, Pong AW, Tatton NA (2002) Propargylamines induce antiapoptotic new protein synthesis in serum- and nerve growth factor (NGF)-withdrawn, NGF-differentiated PC-12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301(12):753–764
Truong TH, Carroll KS (2012) Redox regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through cysteine oxidation. Biochemistry 51(50):9954–9965
Tsuchioka M, Takebayashi M, Hisaoka K, Maeda N, Nakata Y (2008) Serotonin (5-HT) induces glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) mRNA expression via the transactivation of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGR2) in rat C6 glioma cells. J Neurochem 106(1):244–257
Udemgba C, Johnson S, Stockmeier CA et al (2014) The expression of KLF11(TIEG2), a monoamine oxidase B transcription activator in the prefrontal cortex of human alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(1):144–151
Vaarmann A, Gandhi S, Abramov AY (2010) Dopamine induces Ca2+ signaling in astrocytes through reactive oxygen species generated by monoamine oxidase. J Biol Chem 85(32):25018–25023
Valla J, Schneider L, Niedzielko T et al (2006) Impaired platelet mitochondrial activity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Mitochondrion 6(6):323–330
Vina D, Serra S, Lamela M, Delogu G (2012) Herbal natural products as a source of monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a review. Curr Topics Ned Chem 12(20):2131–2144
Wang CC, Borchert A, Ugun-Klusek A et al (2011) Monoamine oxidase A expression is vital for embryonic brain development by modulating developmental apoptosis. J Biol Chem 286(32):28322–28330
Wei Z, Gabriel GG, Rui L, Cao X, Pennington PR, Chlan-Fourney J, Nazaralli A, Baker GB, Mousseau DD (2012a) Monoamine oxidase-A physically interacts with presenilin-1 (M146V) in the mouse cortex. J Alzheimer’s Dis 28(2):403–422
Wei Z, Satram-Maharaj T, Chaharyn B, Kuski K, Pennington PR, Cao X, Chlan J, Mousseau DD (2012b) Aspartic acid substitution in monoamine oxidase-A reveal both catalytic-dependent and -independent influences on cell viability and proliferation. J Neural Transm 119(11):1285–1294
Weinreb O, Bar-Am O, Amit T, Chillag-Talmor O, Youdim MBH (2004) Neuroprotection via pro-survival protein kinase C isoforms associated with Bcl-2 family members. FASEB J 18(12):1471–1473
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB (2010) Rasagiline: a novel anti-Parkinsonian monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor with neuroprotective activity. Prog Neurobiol 92(3):330–344
Wong WK, Chen K, Shih JC (2001) Regulation of human monoamine oxidase B gene by Sp1 and Sp3. Mol Psychiatry 59(4):852–859
Wong WK, Chen K, Shih JC (2002) Activation of human monoamine oxidase B gene expression by a protein kinase C MAP signal transduction pathway involves c-Jun and Egr-1. J Biol Chem 277(25):22222–22230
Wong WK, Ou XM, Chen K, Shih JC (2003) Decreased methylation and transcription repressor Sp3 up-regulated human monoamine oxidase (MAO) B expression during Caco-2 differentiation. J Biol Chem 278(38):36227–36235
Wu JB, Chen K, Ou XM, Shi JC (2009a) Retinoic acid activates monoamine oxidase-B promoter in human neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 284(25):16723–16735
Wu HM, Tzeng NS, Qian L et al (2009b) Novel neuroprotective mechanisms of memantine: increase in neurotrophic factor release from astroglia and anti-inflammation by preventing microglia activation. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(10):2344–2357
Wu Y, Kazumura K, Maruyama W, Osawa T, Naoi M (2015) Rasagiline and selegiline suppress calcium efflux from mitochondria by PK11195-induced opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore: a novel antiapoptotic function for neuroprotection. J Neural Transm 122(10):1399–1407
Yang CS, Fang M, Lambert JD, Yan P, Huang HM (2008) Reversal of hypomethylation and reactivation of genes by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Nutr Res 66(Suppl 1):S18–S20
Yi H, Akao Y, Maruyama W, Chen K, Shih Naoi M (2006a) Type A monoamine oxidase is the target of an endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, leading to apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 96(2):541–549
Yi H, Maruyama W, Akao Y, Takahashi T, Iwasa K, Youdim MB, Naoi M (2006b) N-Propargylamine protects SH-SY5Y cells from apoptosis induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, through stabilization of mitochondrial membrane and induction of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2. J Neural Transm 113(1):21–32
Youdim MBH, Bakhle YS (2006) Monoamine oxidase: isoforms and inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease and depressive illness. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S287–S296
Yu Q, Teixeira CM, Mahadevia D, Huang Y, Balsam D, Mann JJ, Gingrich JA, Ansorge MS (2014) Dopamine and serotonin signaling during two sensitive developmental periods differentially impact adult aggressive and affective behaviors in mice. Mol Psychiatry 19(6):688–698
Zellner M, Baureder M, Rappold E et al (2012) Comparative platelet proteome analysis reveals an increase of monoamine oxidase-B protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease but not in non-demented Parkinson’s disease patients. J Proteom 75(7):2080–2092
Zhou G, Miura Y, Shoji H, Yamada S, Matsuishi T (2001) Platelet monoamine oxidase B and plasma β-phenylethanolamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70(2):229–231
Ziegler C, Richter J, Mahr M et al (2016) MAOA gene hypomethylation in panic disorder-reversibility of an epigenetic risk pattern by psychotherapy. Transl Psychiatry 6:e773
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W. & Shamoto-Nagai, M. Type A and B monoamine oxidases distinctly modulate signal transduction pathway and gene expression to regulate brain function and survival of neurons. J Neural Transm 125, 1635–1650 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1832-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1832-6