Abstract
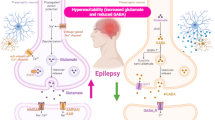
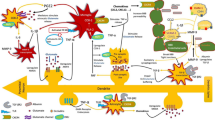
Recent evidence suggests that autophagy alterations are present in a variety of neurological disorders. These range from neurodegenerative diseases to acute neurological insults. Thus, despite a role of autophagy was investigated in a variety of neurological diseases, only recently these studies included epilepsy. This was fostered by the evidence that rapamycin, a powerful autophagy inducer, strongly modulates a variety of seizure models and epilepsies. These findings were originally interpreted as the results of the inhibition exerted by rapamycin on the molecular complex named “mammalian Target of Rapamycin” (mTOR). Recently, an increasing number of papers demonstrated that mTOR inhibition produces a strong activation of the autophagy machinery. In this way, it is now increasingly recognized that what was once defined as mTORpathy in epileptogenesis may be partially explained by abnormalities in the autophagy machinery. The present review features a brief introductory statement about the autophagy machinery and discusses the involvement of autophagy in seizures and epilepsies. An emphasis is posed on evidence addressing both pros and cons making it sometime puzzling and sometime evident, the role of autophagy in the epileptic brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado C, Sarkar S, Korolchuk VI, Criado O, Vernia S, Boya P, Sanz P, de Córdoba SR, Knecht E, Rubinsztein DC (2010) Laforin, the most common protein mutated in Lafora disease, regulates autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 19:2867–2876
Amiri A, Cho W, Zhou J, Birnbaum SG, Sinton CM, McKay RM, Parada LF (2012) Pten deletion in adult hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells causes cellular abnormalities and alters neurogenesis. J Neurosci 32:5880–5890
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Aronson LI, Davenport EL, Mirabella F, Morgan GJ, Davies FE (2013) Understanding the interplay between the proteasome pathway and autophagy in response to dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition in myeloma cells is essential for their effective clinical application. Leukemia 27:2397–2403
Baybis M, Yu J, Lee A, Golden JA, Weiner H, Mckhann G, Aronica E, Crino PB (2004) mTOR cascade activation distinguishes tubers from focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 56:478–487
Ben-Ari Y (1985) Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 14:375–403
Bernard A, Klionsky DJ (2014) Defining the membrane precursor supporting the nucleation of the phagophore. Autophagy 10:1–2
Buckmaster PS, Lew FH (2011) Rapamycin suppresses mossy fiber sprouting but not seizure frequency in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 31:2337–2347
Buckmaster PS, Wen X (2011) Rapamycin suppresses axon sprouting by somatostatin interneurons in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:2057–2064
Buckmaster PS, Ingram EA, Wen X (2009) Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway suppresses dentate granule cell axon sprouting in a rodent model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 29:8259–8269
Cabrera-López C, Martí T, Catalá V, Torres F, Mateu S, Ballarín J, Torra R (2012) Assessing the effectiveness of rapamycin on angiomyolipoma in tuberous sclerosis: a two years trial. Orphanet J Rare Dis 11(7):87
Calderó J, Brunet N, Tarabal O, Piedrafita L, Hereu M, Ayala V, Esquerda JE (2010) Lithium prevents excitotoxic cell death of motoneurons in organotypic slice cultures of spinal cord. Neuroscience 165:1353–1369
Cao L, Xu J, Lin Y, Zhao X, Liu X, Chi Z (2009) Autophagy is upregulated in rats with status epilepticus and partly inhibited by vitamin E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:949–953
Castino R, Lazzeri G, Lenzi P, Bellio N, Follo C, Ferrucci M, Fornai F, Isidoro C (2008) Suppression of autophagy precipitates neuronal cell death following low doses of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 106:1426–1439
Cecarini V, Bonfili L, Cuccioloni M, Mozzicafreddo M, Rossi G, Buizza L, Uberti D, Angeletti M, Eleuteri AM (2012) Crosstalk between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in a human cellular model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1741–1751
Chachua T, Poon KL, Yum MS, Nesheiwat L, DeSantis K, Velíšková J, Velíšek L (2012) Rapamycin has age-, treatment paradigm-, and model-specific anticonvulsant effects and modulates neuropeptide Y expression in rats. Epilepsia 53:2015–2025
Chen R, Jin R, Wu L, Ye X, Yang Y, Luo K, Wang W, Wu D, Ye X, Huang L, Huang T, Xiao G (2011) Reticulon 3 attenuates the clearance of cytosolic prion aggregates via inhibiting autophagy. Autophagy 7:205–216
Chen L, Hu L, Dong JY, Ye Q, Hua N, Wong M, Zeng LH (2012) Rapamycin has paradoxical effects on S6 phosphorylation in rats with and without seizures. Epilepsia 53:2026–2033
Criado O, Aguado C, Gayarre J, Duran-Trio L, Garcia-Cabrero AM, Vernia S, San Millán B, Heredia M, Romá-Mateo C, Mouron S, Juana-López L, Domínguez M, Navarro C, Serratosa JM, Sanchez M, Sanz P, Bovolenta P, Knecht E, Rodriguez de Cordoba S (2012) Lafora bodies and neurological defects in malin-deficient mice correlate with impaired autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 21:1521–1533
Crino PB, Miyata H, Vinters HV (2002) Neurodevelopmental disorders as a cause of seizures: neuropathologic, genetic, and mechanistic considerations. Brain Pathol 12:212–233
de Lanerolle NC, Lee TS, Spencer DD (2010) Astrocytes and epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics 7:424–438
Dengjel J, Høyer-Hansen M, Nielsen MO, Eisenberg T, Harder LM, Schandorff S, Farkas T, Kirkegaard T, Becker AC, Schroeder S, Vanselow K, Lundberg E, Nielsen MM, Kristensen AR, Akimov V, Bunkenborg J, Madeo F, Jäättelä M, Andersen JS (2012) Identification of autophagosome-associated proteins and regulators by quantitative proteomic analysis and genetic screens. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(M111):014035
Dudek FE, Clark S, Williams PA, Grabenstatter HL (2006) Kainate-induced status epilepticus: a chronic model of acquired epilepsy. In: Pitkänen A, Schwartzkroin PA, Moshé SL (eds) Models of seizures and epilepsy. Elsevier Academic, Amsterdam (ISBN: 978-0-12-088554-1)
Duran J, Gruart A, García-Rocha M, Delgado-García JM, Guinovart JJ (2014) Glycogen accumulation underlies neurodegeneration and autophagy impairment in Lafora disease. Hum Mol Genet 23:3147–3156
Ebrahimi-Fakhari D, McLean PJ, Unni VK (2012) Alpha-synuclein’s degradation in vivo: opening a new (cranial) window on the roles of degradation pathways in Parkinson disease. Autophagy 8:281–283
Engelender S (2012) α-Synuclein fate: proteasome or autophagy? Autophagy 8:418–420
Ferrucci M, Pasquali L, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008) Alpha-synuclein and autophagy as common steps in neurodegeneration. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(Suppl 2):S180–S184
Ferrucci M, Fulceri F, Toti L, Soldani P, Siciliano G, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2011) Protein clearing pathways in ALS. Arch Ital Biol 149:121–149
Fisher RS, van Emde Boas W, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, Engel J Jr (2005) Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46:470–472
Fornai F, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Busceti CL, Ruffoli R, Soldani P, Ruggieri S, Alessandri MG, Paparelli A (2003) Fine structure and biochemical mechanisms underlying nigrostriatal inclusions and cell death after proteasome inhibition. J Neurosci 23:8955–8966
Fornai F, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Capobianco L, de Blasi A, Battaglia G, Nicoletti F, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A (2004) Similarities between methamphetamine toxicity and proteasome inhibition. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:162–170
Fornai F, Soldani P, Lazzeri G, di Poggio AB, Biagioni F, Fulceri F, Batini S, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A (2005a) Neuronal inclusions in degenerative disorders. Do they represent static features or a key to understand the dynamics of the disease? Brain Res Bull 65:275–290
Fornai F, Schlüter OM, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Ruffoli R, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Busceti CL, Pontarelli F, Battaglia G, Pellegrini A, Nicoletti F, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Südhof TC (2005b) Parkinson-like syndrome induced by continuous MPTP infusion: convergent roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3413–3418
Fornai F, Lazzeri G, Bandettini Di Poggio A, Soldani P, De Blasi A, Nicoletti F, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A (2006a) Convergent roles of alpha-synuclein, DA metabolism, and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in nigrostriatal toxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1074:84–89
Fornai F, Ferrucci M, Gesi M, Bandettini di Poggio A, Giorgi FS, Biagioni F, Paparelli A (2006b) A hypothesis on prion disorders: are infectious, inherited, and sporadic causes so distinct? Brain Res Bull 69:95–100
Fornai F, Longone P, Cafaro L, Kastsiuchenka O, Ferrucci M, Manca ML, Lazzeri G, Spalloni A, Bellio N, Lenzi P, Modugno N, Siciliano G, Isidoro C, Murri L, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A (2008a) Lithium delays progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2052–2057
Fornai F, Longone P, Ferrucci M, Lenzi P, Isidoro C, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A (2008b) Autophagy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the multiple roles of lithium. Autophagy 4:527–530
Franz DN, Belousova E, Sparagana S, Bebin EM, Frost M, Kuperman R, Witt O, Kohrman MH, Flamini JR, Wu JY, Curatolo P, de Vries PJ, Whittemore VH, Thiele EA, Ford JP, Shah G, Cauwel H, Lebwohl D, Sahmoud T, Jozwiak S (2013) Efficacy and safety of everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytomas associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (EXIST-1): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 381:125–132
Fulceri F, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Paparelli S, Bartalucci A, Tamburini I, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2011) Autophagy activation in glutamate-induced motor neuron loss. Arch Ital Biol 149:101–111
Gaitanis JN, Donahue J (2013) Focal cortical dysplasia. Pediatr Neurol 49:79–87
Galanopoulou AS, Gorter JA, Cepeda C (2012) Finding a better drug for epilepsy: the mTOR pathway as an antiepileptogenic target. Epilepsia 53:1119–1130
Ganesh S, Delgado-Escueta AV, Sakamoto T, Avila MR, Machado-Salas J, Hoshii Y, Akagi T, Gomi H, Suzuki T, Amano K, Agarwala KL, Hasegawa Y, Bai DS, Ishihara T, Hashikawa T, Itohara S, Cornford EM, Niki H, Yamakawa K (2002) Targeted disruption of the Epm2a gene causes formation of Lafora inclusion bodies, neurodegeneration, ataxia, myoclonus epilepsy and impaired behavioral response in mice. Hum Mol Genet 11:1251–1262
García-Cabrero AM, Marinas A, Guerrero R, de Córdoba SR, Serratosa JM, Sánchez MP (2012) Laforin and malin deletions in mice produce similar neurologic impairments. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:413–421
Garyali P, Siwach P, Singh PK, Puri R, Mittal S, Sengupta S, Parihar R, Ganesh S (2009) The malin–laforin complex suppresses the cellular toxicity of misfolded proteins by promoting their degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Hum Mol Genet 18:688–700
Garyali P, Segvich DM, DePaoli-Roach AA, Roach PJ (2014) Protein degradation and quality control in cells from Laforin and Malin knockout mice. J Biol Chem 289:20606–20614
Giorgi FS, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Pizzanelli C, Lenzi P, Alessandrl MG, Murri L, Fornai F (2003) A damage to locus coeruleus neurons converts sporadic seizures into self-sustaining limbic status epilepticus. Eur J Neurosci 17:2593–2601
Giorgi FS, Bandettini di Poggio A, Battaglia G, Pellegrini A, Murri L, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2006) A short overview on the role of alpha-synuclein and proteasome in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:105–109 (review)
Hartman AL, Santos P, Dolce A, Hardwick JM (2012) The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin has limited acute anticonvulsant effects in mice. PLoS ONE 7:e45156
Heng K, Haney MM, Buckmaster PS (2013) High-dose rapamycin blocks mossy fiber sprouting but not seizures in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 54:1535–1541
Huang XL, Zhang H, Yang J, Wu J, McMahon J, Lin Y, Cao Z, Gruenthal M, Huang Y (2010) Pharmacological inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppresses acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 40:193–199
Jansen LA, Uhlmann EJ, Crino PB, Gutmann DH, Wong M (2005) Epileptogenesis and reduced inward rectifier potassium current in tuberous sclerosis complex-1-deficient astrocytes. Epilepsia 46:1871–1880
Jellinger KA, Stadelmann C (2000) Mechanisms of cell death in neurodegenerative disorders. J Neural Transm Suppl 59:95–114
Klionsky DJ, Eskelinen EL, Deretic V (2014) Autophagosomes, phagosomes, autolysosomes, phagolysosomes, autophagolysosomes… wait, I’m confused. Autophagy 10:549–551
Kraft C, Peter M, Hofmann K (2010) Selective autophagy: ubiquitin-mediated recognition and beyond. Nat Cell Biol 12:836–841
Lasarge CL, Danzer SC (2014) Mechanisms regulating neuronal excitability and seizure development following mTOR pathway hyperactivation. Front Mol Neurosci 14(7):18
Lenzi P, Marongiu R, Falleni A, Gelmetti V, Busceti CL, Michiorri S, Valente EM, Fornai F (2012) A subcellular analysis of genetic modulation of PINK1 on mitochondrial alterations, autophagy and cell death. Arch Ital Biol 150:194–217
Liberski PP, Sikorska B, Bratosiewicz-Wasik J, Gajdusek DC, Brown P (2004) Neuronal cell death in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases) revisited: from apoptosis to autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2473–2490 (review)
Macias M, Blazejczyk M, Kazmierska P, Caban B, Skalecka A, Tarkowski B, Rodo A, Konopacki J, Jaworski J (2013) Spatiotemporal characterization of mTOR kinase activity following kainic acid induced status epilepticus and analysis of rat brain response to chronic rapamycin treatment. PLoS ONE 8:e64455
Madeo F, Eisenberg T, Kroemer G (2009) Autophagy for the avoidance of neurodegeneration. Genes Dev 23:2253–2259
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2003) Rheb fills a GAP between TSC and TOR. Trends Biochem Sci 28:573–576
Mazarati A, Bragin A, Baldwin R, Shin D, Wilson C, Sankar R, Naylor D, Engel J, Wasterlain CG (2002) Epileptogenesis after self-sustaining status epilepticus. Epilepsia 43 Suppl 5:74–80
McMahon J, Huang X, Yang J, Komatsu M, Yue Z, Qian J, Zhu X, Huang Y (2012) Impaired autophagy in neurons after disinhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin and its contribution to epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 32:15704–15714
Miyahara H, Natsumeda M, Shiga A, Aoki H, Toyoshima Y, Zheng Y, Takeuchi R, Murakami H, Masuda H, Kameyama S, Izumi T, Fujii Y, Takahashi H, Kakita A (2013) Suppressed expression of autophagosomal protein LC3 in cortical tubers of tuberous sclerosis complex. Brain Pathol 23:254–262
Natale G, Pasquali L, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008) Parkinson’s disease and the gut: a well known clinical association in need of an effective cure and explanation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:741–749
Nixon RA (2013) The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med 19:983–997
Ortolano S, Vieitez I, Agis-Balboa RC, Spuch C (2014) Loss of GABAergic cortical neurons underlies the neuropathology of Lafora disease. Mol Brain 7:7
Orzi F, Casolla B, Rocchi R, Fornai F (2012) Prion-like mechanisms in epileptogenesis. Neurol Sci 34:1035–1108
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 8):1969–1978
Pasquali L, Longone P, Isidoro C, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2009) Autophagy, lithium, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 40:173–194
Pasquali L, Ruffoli R, Fulceri F, Pietracupa S, Siciliano G, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2010) The role of autophagy: what can be learned from the genetic forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Target 9:268–278 (review)
Petroi D, Popova B, Taheri-Talesh N, Irniger S, Shahpasandzadeh H, Zweckstetter M, Outeiro TF, Braus GH (2012) Aggregate clearance of α-synuclein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends more on autophagosome and vacuole function than on the proteasome. J Biol Chem 287:27567–27579
Piredda S, Gale K (1985) A crucial epileptogenic site in the deep prepiriform cortex. Nature 317:623–625
Polajnar ML, Zerovnik E (2011) Impaired autophagy: a link between neurodegenerative diseases and progressive myoclonus epilepsies. Trends Mol Med 17:293–300
Puri R, Suzuki T, Yamakawa K, Ganesh S (2012) Dysfunctions in endosomal–lysosomal and autophagy pathways underlie neuropathology in a mouse model for Lafora disease. Hum Mol Genet 21:175–184
Qiao L, Zhang J (2009) Inhibition of lysosomal functions reduces proteasomal activity. Neurosci Lett 456:15–19
Raab-Graham KF, Haddick PC, Jan YN, Jan LY (2006) Activity- and mTOR-dependent suppression of Kv1.1 channel mRNA translation in dendrites. Science 314:144–148
Raffo E, Coppola A, Ono T, Briggs SW, Galanopoulou AS (2011) A pulse rapamycin therapy for infantile spasms and associated cognitive decline. Neurobiol Dis 43:322–329
Ramachandran N, Girard JM, Turnbull J, Minassian BA (2009) The autosomal recessively inherited progressive myoclonus epilepsies and their genes. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 5):29–36
Rattka M, Brandt C, Löscher W (2013) The intrahippocampal kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy revisited: epileptogenesis, behavioral and cognitive alterations, pharmacological response, and hippocampal damage in epileptic rats. Epilepsy Res 103(2–3):135–152
Ravikumar B, Duden R, Rubinsztein DC (2002) Aggregate-prone proteins with polyglutamine and polyalanine expansions are degraded by autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 11:1107–1117
Riikonen R (2014) Recent advances in the pharmacotherapy of infantile spasms. CNS Drugs 28:279–290
Ryu HJ, Kim JE, Yeo SI, Kim DW, Kwon OS, Choi SY, Kang TC (2011a) F-actin depolymerization accelerates clasmatodendrosis via activation of lysosome-derived autophagic astroglial death. Brain Res Bull 85:368–373
Ryu HJ, Kim JE, Yeo SI, Kang TC (2011b) p65/RelA-Ser529 NF-κB subunit phosphorylation induces autophagic astroglial death (Clasmatodendrosis) following status epilepticus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31:1071–1078
Sadler RM (2006) The syndrome of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis: clinical features and differential diagnosis. Adv Neurol 97:27–37
Saitsu H, Nishimura T, Muramatsu K, Kodera H, Kumada S, Sugai K, Kasai-Yoshida E, Sawaura N, Nishida H, Hoshino A, Ryujin F, Yoshioka S, Nishiyama K, Kondo Y, Tsurusaki Y, Nakashima M, Miyake N, Arakawa H, Kato M, Mizushima N, Matsumoto N (2013) De novo mutations in the autophagy gene WDR45 cause static encephalopathy of childhood with neurodegeneration in adulthood. Nat Genet 45:445–449
Scantlebury MH, Galanopoulou AS, Chudomelova L, Raffo E, Betancourth D, Moshé SL (2010) A model of symptomatic infantile spasms syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 37:604–612
Seifert G, Steinhäuser C (2013) Neuron-astrocyte signaling and epilepsy. Exp Neurol 244:4–10
Sha LZ, Xing XL, Zhang D, Yao Y, Dou WC, Jin LR, Wu LW, Xu Q (2012) Mapping the spatio-temporal pattern of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation in temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS ONE 7:e39152
Shacka JJ, Lu J, Xie ZL, Uchiyama Y, Roth KA, Zhang J (2007) Kainic acid induces early and transient autophagic stress in mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 414:57–60
Silva JG, Mello LE (2000) The role of mossy cell death and activation of protein synthesis in the sprouting of dentate mossy fibers: evidence from calretinin and neo-timm staining in pilocarpine-epileptic mice. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 6):S18–S23
Singh PK, Singh S, Ganesh S (2012) The laforin–malin complex negatively regulates glycogen synthesis by modulating cellular glucose uptake via glucose transporters. Mol Cell Biol 32:652–663
Sisodiya SML, Fauser S, Cross JH, Thom M (2009) Focal cortical dysplasia type II: biological features and clinical perspectives. Lancet Neurol 8:830–843
Sloviter RS (2005) The neurobiology of temporal lobe epilepsy: too much information, not enough knowledge. C R Biol 328:143–153
Sloviter RS (2008) Hippocampal epileptogenesis in animal models of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis: the importance of the “latent period” and other concepts. Epilepsia 49 Suppl 9:85–92
Sosunov AA, Wu X, McGovern RA, Coughlin DG, Mikell CB, Goodman RR, McKhann GM 2nd (2012) The mTOR pathway is activated in glial cells in mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia 53 Suppl 1:78–86
Tee AR, Manning BD, Roux PP, Cantley LC, Blenis J (2003) Tuberous sclerosis complex gene products, tuberin and hamartin, control mTOR signaling by acting as a GTPase activating protein complex toward Rheb. Curr Biol 13:1259–1268
Turnbull J, Epp JR, Goldsmith D, Zhao X, Pencea N, Wang P, Frankland PW, Ackerley CA, Minassian BA (2014) PTG protein depletion rescues malin-deficient Lafora disease in mouse. Ann Neurol 75:442–446
Turski L, Ikonomidou C, Turski WA, Bortolotto ZA, Cavalheiro EA (1989) Review: cholinergic mechanisms and epileptogenesis. The seizures induced by pilocarpine: a novel experimental model of intractable epilepsy. Synapse 3:154–171
Urushitani M, Kurisu J, Tsukita K, Takahashi R (2002) Proteasomal inhibition by misfolded mutant superoxide dismutase 1 induces selective motor neuron death in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 83:1030–1042
Valles-Ortega JL, Duran J, Garcia-Rocha M, Bosch C, Saez I, Pujadas L, Serafin A, Cañas X, Soriano E, Delgado-García JM, Gruart A, Guinovart JJ (2011) Neurodegeneration and functional impairments associated with glycogen synthase accumulation in a mouse model of Lafora disease. EMBO Mol Med 3:667–681
Velísek L, Jehle K, Asche S, Velísková J (2007) Model of infantile spasms induced by N-methyl-d-aspartic acid in prenatally impaired brain. Ann Neurol 61:109–119
Viiri J, Amadio M, Marchesi N, Hyttinen JM, Kivinen N, Sironen R, Rilla K, Akhtar S, Provenzani A, D’Agostino VG, Govoni S, Pascale A, Agostini H, Petrovski G, Salminen A, Kaarniranta K (2013) Autophagy activation clears ELAVL1/HuR-mediated accumulation of SQSTM1/p62 during proteasomal inhibition in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 8:e69563
Weston MC, Chen H, Swann JW (2012) Multiple roles for mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in both glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 32:11441–11452
Wyttenbach A, Carmichael J, Swartz J, Furlong RA, Narain Y, Rankin J, Rubinsztein DC (2000) Effects of heat shock, heat shock protein 40 (HDJ-2), and proteasome inhibition on protein aggregation in cellular models of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2898–2903
Xilouri M, Brekk OR, Stefanis L (2013) α-Synuclein and protein degradation systems: a reciprocal relationship. Mol Neurobiol 47:537–551
Yang F, Yang YP, Mao CJ, Liu L, Zheng HF, Hu LF, Liu CF (2013) Crosstalk between the proteasome system and autophagy in the clearance of α-synuclein. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:674–680
Yasin SA, Ali AM, Tata M, Picker SR, Anderson GW, Latimer-Bowman E, Nicholson SL, Harkness W, Cross JH, Paine SM, Jacques TS (2013) mTOR-dependent abnormalities in autophagy characterize human malformations of cortical development: evidence from focal cortical dysplasia and tuberous sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 126:207–218
Yuen AW, Sander JW (2014) Rationale for using intermittent calorie restriction as a dietary treatment for drug resistant epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 33C:110–114
Zeng LH, Rensing NR, Wong M (2009) The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway mediates epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 29:6964–6972
Zhao W, Chuang SC, Bianchi R, Wong RK (2011) Dual regulation of fragile X mental retardation protein by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors controls translation-dependent epileptogenesis in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 31:725–734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giorgi, F.S., Biagioni, F., Lenzi, P. et al. The role of autophagy in epileptogenesis and in epilepsy-induced neuronal alterations. J Neural Transm 122, 849–862 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1312-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1312-1