Abstract
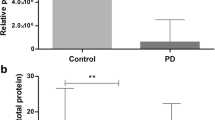
Chromogranin A (CgA) levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) have been reported to be significantly reduced in the later stages of Parkinson’s disease (PD). There are only limited data regarding its levels in the early stages, so its significance as a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of PD cannot be established. The aim of our study was to establish the level of CgA in a cohort of treatment-naïve patients with early stage PD. Ten patients (4 males, 6 females) and 10 gender- and age-matched controls were examined for CgA levels in the CSF. Control subjects were patients with low-back pain or tension-type headache. The mean CSF CgA level in PD patients was 74.8 (41.9–123.8) μg/l; in the control group it was 143.9 (116–181.3) μg/l. Statistical analysis showed a difference at the significance level P ≤ 0.05. Our pilot study shows that CSF CgA levels are reduced in the early stages of PD. CgA could therefore be a potential biomarker helpful in the diagnosis of PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks P, Helle K (1965) The release of protein from the stimulated adrenal medulla. Biochem J 97(3):40C–41C
Bartolomucci A, Pasinetti GM, Salton SR (2010) Granins as disease-biomarkers: translational potential for psychiatric and neurological disorders. Neuroscience 170(1):289–297
Blennow K, Davidsson P, Wallin A, Ekman R (1995) Chromogranin A in cerebrospinal fluid: a biochemical marker for synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease? Dementia 6(6):306–311
Conlon JM (2010) Granin-derived peptides as diagnostic and prognostic markers for endocrine tumors. Regul Pept 165(1):5–11
Eder U, Leitner B, Kirchmair R, Pohl P, Jobst KA, Smith AD, Málly J, Benzer A, Riederer P, Reichmann H, Saria A, Winkler H (1998) Levels and proteolytic processing of chromogranin A and B and secretogranin II in cerebrospinal fluid in neurological diseases. J Neural Transm 105(1):39–51
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51(6):745–752
Kim T, Loh YP (2005) Chromogranin A: a surprising link between granule biogenesis and hypertension. J Clin Invest 115(7):1711–1713
Loh YP, Cheng Y, Mahata SK, Corti A, Tota B (2012) Chromogranin A and derived peptides in health and disease. J Mol Neurosci 3
Mahapatra NR, O’Connor DT, Vaingankar SM, Hikim AP, Mahata M, Ray S, Staite E, Wu H, Gu Y, Dalton N, Kennedy BP, Ziegler MG, Ross J, Mahata SK (2005) Hypertension from targeted ablation of chromogranin A can be rescued by the human ortholog. J Clin Invest 115(7):1942–1952
Miller C, Kirchmair R, Troger J, Saria A, Fleischhacker WW, Fischer-Colbrie R, Benzer A, Winkler H (1996) CSF of neuroleptic-naive first-episode schizophrenic patients: levels of biogenic amines, substance P, and peptides derived from chromogranin A (GE-25) and secretogranin II (secretoneurin). Biol Psychiatry 39(11):911–918
Nishimura M, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Nakamura S, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Akiguchi I, Kimura J (1994) Synaptophysin and chromogranin A immunoreactivities of Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease brains. Brain Res 634(2):339–344
O’Connor DT, Cervenka JH, Stone RA, Parmer RJ, Franco-Bourland RE, Madrazo I, Langlais PJ (1993) Chromogranin A immunoreactivity in human cerebrospinal fluid: properties, relationship to noradrenergic neuronal activity, and variation in neurologic disease. Neuroscience 56(4):999–1007
O’Connor DT, Mahata SK, Taupenot L, Mahata M, Livsey Taylor CV, Kailasam MT, Ziegler MG, Parmer RJ (2000) Chromogranin A in human disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 482:377–388
Schrott-Fischer A, Bitsche M, Humpel C, Walcher C, Maier H, Jellinger K, Rabl W, Glueckert R, Marksteiner J (2009) Chromogranin peptides in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Regul Pept 152(1–3):13–21
Somogyi P, Hodgson AJ, DePotter RW, Fischer-Colbrie R, Schober M, Winkler H, Chubb IW (1984) Chromogranin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Immunochemical characterisation, distribution and relationship to catecholamine and enkephalin pathways. Brain Res 320(2–3):193–230
Takiyyuddin MA, Parmer RJ, Kailasam MT, Cervenka JH, Kennedy B, Ziegler MG, Lin MC, Li J, Grim CE, Wright FA et al (1995) Chromogranin A in human hypertension. Influence of heredity. Hypertension 26(1):213–220
Taupenot L, Harper KL, O’Connor DT (2003) The chromogranin-secretogranin family. N Engl J Med 348(12):1134–1149
Tinaz S, Courtney MG, Stern CE (2011) Focal cortical and subcortical atrophy in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(3):436–441
Weiler R, Lassmann H, Fischer P, Jellinger K, Winkler H (1990) A high ratio of chromogranin A to synaptin/synaptophysin is a common feature of brains in Alzheimer and Pick disease. FEBS Lett 263(2):337–339
Willis M, Leitner I, Jellinger KA, Marksteiner J (2011) Chromogranin peptides in brain diseases. J Neural Transm 118(5):727–735
Yasuhara O, Kawamata T, Aimi Y, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Expression of chromogranin A in lesions in the central nervous system from patients with neurological diseases. Neurosci Lett 170(1):13–16
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant projects IGA MZ CR NT-12221, IGA UP LF_2012_005 and IGA UP LF_2013_024.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiserová, M., Vranová, H.P., Stejskal, D. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of chromogranin A in the treatment-naïve early stage Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. J Neural Transm 120, 1559–1563 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1020-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1020-2