Abstract
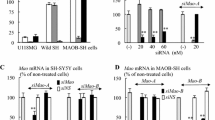
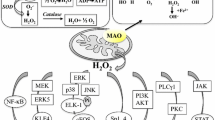
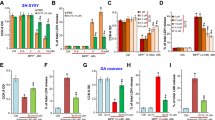
Type B monoamine oxidase (MAO-B) is proposed to be involved in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, through oxidative stress and synthesis of neurotoxins. MAO-B inhibitors, rasagiline and selegiline [(−)deprenyl], protect neuronal cells by direct intervention in mitochondrial death signaling and induction of pro-survival Bcl-2 and neurotrophic factors. Recently, type A MAO (MAO-A) was found to mediate the induction of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 by rasagiline, whereas MAO-A increases in neuronal death and also serves as a target of neurotoxins. These controversial results suggest that MAO-A may play a decisive role in neuronal survival and death. This paper reports that rasagiline and selegiline increased the mRNA, protein and catalytic activity of MAO-A in SH-SY5Y cells. Silencing MAO-A expression with small interfering (si)RNA suppressed rasagiline-dependent MAO-A expression, but MAO-B overexpression in SH-SY5Y cells did not affect, suggesting that MAO-A, not MAO-B, might be associated with MAO-A upregulation. Rasagiline reduced R1, a MAO-A specific repressor, but selegiline did not. Mithramycin-A, an inhibitor of Sp1 binding, and actinomycin-D, a transcriptional inhibitor, reduced the rasagiline-dependent upregulation of MAO-A mRNA, indicating that rasagiline induced MAO-A transcriptionally through R1-Sp1 pathway, whereas selegiline by another non-defined pathway. These results are discussed in relation to the role of MAO-A and these MAO-B inhibitors in neuronal death and neuroprotection.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MAO:
-
Monoamine oxidase
- MAO-A and MAO-B:
-
Type A and B MAO
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SiRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
References
Abu-Raya S, Tabakman R, Blaugrund E, Trembovler V, Lazarovici P (2002) Neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors and derived metabolites under ischemia in PC12 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 434:109–116
Akao Y, Maruyama W, Shimizu S, Yi H, Shamoto-Nagai M, Youdim MB, Tsujimoto Y, Naoi M (2002) Mitochondrial permeability transition mediates apoptosis induced by N-methyl(R)salsolinol, an endogenous neurotoxin, and its inhibited by Bcl-2 and rasagiline, N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan. J Neurochem 82:913–923
Bar Am O, Amit T, Youdim MBH (2004) Contracting neuroprotective and neurotoxic action of respective metabolites of anti-Parkinson drugs rasagiline and selegiline. Neurosci Lett 355:169–172
Bar-Am O, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MBH (2010) The neuroprotective mechanism of 1-(R)-aminoindan, the major metabolite of anti-parkinsonian drug rasagiline. J Neurochem 112:1131–1137
Bortolato M, Chen K, Shih JC (2008) Monoamine oxidase inactivation: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 60:1527–1533
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cao X, Li X-M, Mousseau DD (2009) Calcium alters monoamine oxidase-A parameters in human cerebellar and rat glial C6 cell extracts: possible influence by distinct signal pathways. Life Sci 85:262–268
Chen K, Ou X-M, Chen G, Choi SH, Shih JC (2005) R1, a novel repressor of the human monoamine oxidase A. J Biol Chem 280:11552–11559
De Girolamo LA, Hargreaves AJ, Billett EE (2001) Protection from MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in differentiating N2a neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 76:650–660
De Zutter GS, Davis RJ (2001) Pro-apoptotic gene expression mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6168–6173
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Nichols A et al (1999) Bid-induced conformational changes of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 144:891–901
Ebadi M, Brown-Borg H, Ren J, Sharma S, Shavali S, ReFaey HE, Carlson EC (2006) Therapeutic efficiency of selegiline in neurodegenerative disorders and neurological diseases. Curr Drug Targets 7:1513–1529
Edmondson DE, Binda C, Mattevi A (2007) Structural insights into the mechanism of amine oxidation by monoamine oxidases A and B. Arch Biochem Biophys 464:269–276
Egashira T, Sakai K, Sakurai M, Takayama F (2003) Calcium disodium edetate enhances type A monoamine oxidase activity in monkey brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 94:203–211
Finberg JPM, Youdim MBH (2002) Pharmacological properties of the anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline; modification of endogenous brain amines, reserpine reversal, serotonergic and dopaminergic behaviours. Neuropharmacology 43:1110–1118
Fitzgerald JC, Ufer C, De Girolamo LA, Kuhn H, Billet EE (2007) Monoamine oxidase-A modulates apoptotic cell death induced by staurosporine in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 103:2189–2199
Heikkila RE, Manzino L, Cabbat FS, Duvoisin RN (1985) Studies on the oxidation of the dopaminergic neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine oxidase B. J Neurochem 45:1049–1054
Hirano F, Tanaka H, Hirano Y, Hiramoto M, Handa H, Makino I, Scheidereit C (1998) Functional interference of Sp1 and NF-κB through the same DNA binding site. Mol Cell Biol 18:1266–1274
Hubalek F, Binda C, Ki M, Herzig Y, Sterling J, Youdim MBH, Mattevi A, Edmondson DE (2004) Inactivation of purified human recombinant monoamine oxidase A and B by rasagiline and its analogues. J Med Chem 47:1760–1768
Hynson RMG, Kelly SM, Price NC, Ramsay RR (2004) Conformational changes in monoamine oxidase A in response to ligand binding or reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1672:60–66
Inaba-Hasegawa K, Akao Y, Maruyama W, Naoi M (2012) Type A monoamine oxidase is associated with induction of neuroprotective Bcl-2 by rasagiline, an inhibitor of type B monoamine oxidase. J Neural Transm 119:405–414
Konradi C, Riederer P, Youdim MB (1986) Hydrogen peroxide enhances the activity of monoamine oxidase type B but not of type-A: a pilot study. J Neural Transm Suppl 22:61–63
Kraml M (1965) A rapid microfluorometric determination of monoamine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol 14:1684–1686
Lamensdorf I, Youdim MBH, Finberg JPM (1996) Effect of long-term treatment with selective monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors on dopamine release from rat striatum in vivo. J Neurochem 67:1532–1539
Maruyama W, Naoi M (2012) Induction of glial cell line-derived and brain-derived neurotrophic factors by rasagiline and (−)deprenyl: a way to disease-modifying therapy? J Neural Transm. doi:10.1007/s00702-0876-x
Maruyama W, Nitta A, Shamoto-Nagai M, Hirata Y, Akao Y, Youdim M, Furukawa S, Nabeshima T, Naoi M (2004) N-Propargyl-1-(R)-aminoindan, rasagiline, increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells through activation of NF-κB transcription factor. Neurochem Int 44:293–400
Naoi M, Maruyama W (2010) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors as neuroprotective agents in age-dependent neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Pharmaceut Des 16:2799–2817
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Yi H, Akao Y, Yamaoka Y, Shamoto-Nagai M (2007) Neuroprotection by propargylamines in Parkinson’s disease: intracellular mechanism underlying the anti-apoptotic function and search for clinical markers. J Neural Transm Suppl 72:121–131
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Inaba-Hasegawa K, Akao Y (2011) Type A monoamine oxidase regulates life and death of neurons in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Inter Rev Neurobiol 100:85–106
Ou X-M, Chen K, Shih JC (2006a) Monoamine oxidase A and repressor R1 are involved in apoptotic signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10923–10928
Ou X-M, Chen K, Shih JC (2006b) Glucocorticoid and androgen activation of monoamine oxidase A is regulated differently by R1 and Sp1. J Biol Chem 281:21512–21525
Ou X-M, Lu D, Johnson C, Chen K, Youdim MBH, Rajkowska G, Shih JC (2009) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-monoamine oxidase B-mediated cell death-induced by ethanol is prevented by rasagiline and 1-R-aminoindan. Neurotox Res 16:148–159
Parkinson Study Group (2002) A controlled trial of rasagiline in early Parkinson disease: the TEMPO study. Arch Neurol 59:1937–1943
Pizzinat N, Marchal-Victorion S, Maurel A, Ordener C, Bompart G, Parini A (2003) Substrate-dependent regulation of MAO-A in rat mesangial cells: involvement of dopamine D2-like receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F167–F174
Riederer P, Lachenmayer L, Laux G (2004) Clinical applications of MAO-inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 11:2033–2043
Shih JC, Chen K, Ridd MJ (1999) Monoamine oxidase: from genes to behavior. Ann Rev Neurosci 22:197–217
Shih JC, Boyang J, Chen K (2011) Transcriptional regulation and multiple functions of MAO genes. J Neural Transm 118:979–986
Tazik S, Johnson S, Lu D, Johnson C, Youdim MBH, Stockmeier OuX-M (2009) Comparative neuroprotective effects of rasagiline and aminoindan with selegiline on dexamethasone-induced brain cell apoptosis. Neurosci Res 15:284–290
Wang J, Edmondson DE (2011) Topological probes of monoamine oxidases A and B in rat liver mitochondria: inhibition by TEMPO-substituted pargyline analogues and inactivation by proteolysis. Biochemistry 50:2499–2505
Wong WK, Ou XM, Chen K, Shih JC (2002) Activation of human monoamine oxidase B gene expression by a protein kinase C MAPK signal transduction pathway involves c-Jun and Egr-1. J Biol Chem 277:22222–22230
Wu JB, Shih JC (2011) Valproic acid induces monoamine oxidase A via Akt/Forkhead Box O1 activation. Mol Pharmacol 80:714–723
Yi H, Akao Y, Maruyama W, Chen K, Shih J, Naoi M (2006) Type A monoamine oxidase is the target of an endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, leading to apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 96:541–549
Youdim MBH, Bakhle YS (2006) Monoamine oxidase: isoforms and inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease and depressive illness. Br J Pharmacol 147:S287–S296
Youdim MBH, Edmondson D, Tipton KF (2006) The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:295–309
Zhu W, Xie W, Pan T, Jankovic J, Youdim MBH, Le W (2008) Comparison of neuroprotective and neurorestorative capacities of rasagiline and selegiline against lactacystin-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic degeneration. J Neurochem 105:1970–1978
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Grant for Longevity Sciences (21A-13, 23A-2) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (W. M., M. N).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inaba-Hasegawa, K., Akao, Y., Maruyama, W. et al. Rasagiline and selegiline, inhibitors of type B monoamine oxidase, induce type A monoamine oxidase in human SH-SY5Y cells. J Neural Transm 120, 435–444 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0899-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0899-3