Abstract
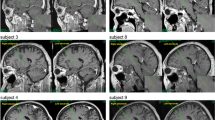
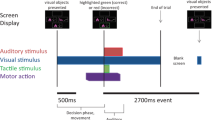
We studied the appearance of cognitive event-related potentials (ERPs) and event-related de/synchronizations (ERD/S) in the subthalamic nucleus (STN) and globus pallidus internus (GPi). We particularly focused on the rare non-target (distractor) stimuli processing. ERPs and ERD/S in the alpha and beta frequency range were analyzed in seven Parkinson’s disease patients and one primary dystonia patient with implanted deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes. A visual three-stimulus protocol was used (frequent stimulus, target stimulus, and distractor). The non-target and distractor-related waveforms manifested similar shapes. A specific positive ERP peak around 200 ms and a low alpha frequency ERS were detected from the STN as a response to the distractor stimuli in six of the patients with Parkinson’s disease and also in the primary dystonia patient’s GPi. This positivity probably reflects an attentional orienting response to the distractor stimuli. The STN and GPi are probably involved in attentional cerebral networks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay M (2000) Time frequency and wavelets in biomedical signal processing. Wiley, New York
Albin RL, Young AB, Penny JB (1989) The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12:366–375
Anderson VC, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, Favre J, Hammerstad JP (2005) Pallidal vs subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 62:554–560
Aron AR, Poldrack RA (2006) Cortical and subcortical contributions to stop signal response inhibition: role of the subthalamic nucleus. J Neurosci 26:2424–2433
Aron AR, Behrens TE, Smith S, Frank MJ, Poldrack RA (2007) Triangulating a cognitive control network using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and functional MRI. J Neurosci 27:3743–3752
Baláž M, Rektor I, Pulkrábek J (2008) Participation of the subthalamic nucleus in executive functions: an intracerebral recording study. Mov Disord 23:553–557
Baláž M, Srovnalová H, Rektorová I, Rektor I (2010) The effect of cortical repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on cognitive event-related potentials recorded in the subthalamic nucleus. Exp Brain Res 203:317–327
Ballanger B, van Eimeren T, Moro E, Lozano AM, Hamani C, Boulinguez P, Pellecchia G, Houle S, Poon YY, Lang AE, Strafella AP (2009) Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus and impulsivity: release your horses. Ann Neurol 66:817–824
Baudena P, Halgren E, Heit G, Clarke JM (1995) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. III. Frontal cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:251–264
Baunez C, Robbins TW (1997) Bilateral lesions of the subthalamic nucleus induce multiple deficits in an attentional task in rats. Eur J Neurosci 9:2086–2099
Baunez C, Robbins TW (1999a) Effects of dopamine depletion of the dorsal striatum and further interaction with subthalamic nucleus lesions in an attentional task in the rat. Neuroscience 92:1343–1356
Baunez C, Robbins TW (1999b) Effects of transient inactivation of the subthalamic nucleus by local muscimol and APV infusions on performance on the five-choice serial reaction time task in rats. Psychopharmacology 141:57–65
Baunez C, Amalric M, Robbins TW (2002) Enhanced food-related motivation after bilateral lesions of the subthalamic nucleus. J Neurosci 22:562–568
Baunez C, Dias C, Cador M, Amalric M (2005) The subthalamic nucleus exerts opposite control on cocaine and ‘natural’ rewards. Nat Neurosci 8:484–489
Baunez C, Christakou A, Chudasama Y, Forni C, Robbins TW (2007) Bilateral high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on attentional performance: transient deleterious effects and enhanced motivation in both intact and parkinsonian rats. Eur J Neurosci 25:1187–1194
Benarroch EE (2008) Subthalamic nucleus and its connections: anatomic substrate for the network effects of deep brain stimulation. Neurology 70:1991–1995
Bledowski C, Prvulovic D, Hoechstetter K, Scherg M, Wibral M, Goebel R, Linden DE (2004) Localizing P300 generators in visual target and distractor processing: a combined event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 24:9353–9360
Boiten F, Sergeant J, Geuze R (1992) Event-related desynchronization: the effects of energetic and computational demands. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:302–309
Brown P, Williams D (2005) Basal ganglia local field potential activity: character and functional significance in the human. Clin Neurophysiol 116:2510–2519
Christakou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2001) Functional disconnection of a prefrontal cortical-dorsal striatal system disrupts choice reaction time performance: implications for attentional function. Behav Neurosci 115:812–825
Conroy MA, Polich J (2007) Normative variation of P3a and P3b from a large sample (N = 120): gender, topography, and response time. J Psychophysiol 21:22–32
Courchesne E, Hillyard SA, Galambos R (1975) Stimulus novelty, task relevance, and visual evoked-potential in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 39:131–143
Coxon JP, Stinear CM, Byblow WD (2006) Intracortical inhibition during volitional inhibition of prepared action. J Neurophysiol 95:3371–3383
Daffner KR, Mesulam MM, Scinto LF, Acar D, Calvo V, Faust R, Chabrerie A, Kennedy B, Holcomb P (2000) The central role of the prefrontal cortex in directing attention to novel events. Brain 123:927–939
Desmedt JE (1981) Scalp-recorded event-related potentials in man as point of entry into the analysis of cognitive processing. In: Schmitt FO, Worden FG, Edelmann G, Dennis SD (eds) The organization of the cerebral cortex. MIT, Cambridge, MA, pp 441–473
Enriquez-Geppert S, Konrad C, Pantev C, Huster RJ (2010) Conflict and inhibition differentially affect the N200/P300 complex in a combined go/nogo and stop-signal task. Neuroimage 51(2):877–887
Friedman D, Cycowicz YM, Gaeta H (2001) The novelty P3: an event-related brain potential (ERP) sign of the brain’s evaluation of novelty. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:355–373
Graybiel AM (1997) The basal ganglia and cognitive pattern generators. Schizophr Bull 23:459–469
Grunwald T, Lehnertz K, Heinze HJ, Helmstaedter C, Elger CE (1998) Verbal novelty detection within the human hippocampus proper. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3193–3197
Halgren E, Baudena P, Clarke JM, Heit G, Liégeois C, Chauvel P, Musolino A (1995a) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. I. Superior temporal plane and parietal lobe. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:191–220
Halgren E, Baudena P, Clarke JM, Heit G, Marinkovic K, Devaux B, Vignal JP, Biraben A (1995b) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. II. Medial, lateral and posterior temporal lobe. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:229–250
Hamani C, Saint-Cyr JA, Fraser J, Kaplitt M, Lozano AM (2004) The subthalamic nucleus in the context of movement disorders. Brain 127:4–20
Herrmann CS, Knight RT (2001) Mechanisms of human attention: event-related potentials and oscillations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:465–476
Herzog J, Reiff J, Krack P, Witt K, Schrader B, Müller D, Deuschl G (2003) Manic episode with psychotic symptoms induced by subthalamic nucleus stimulation in a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:1382–1384
Intriligator J, Polich J (1995) On the relationship between EEG an P300 variability. Int J Psychophysiol 20:59–74
Kaipio ML, Cheour M, Ceponiene R, Ohman J, Alku P, Näätänen R (2000) Increased distractibility in closed head injury as revealed by event-related potentials. Neuroreport 11:1463–1468
Kiehl KA, Stevens MC, Laurens KR, Pearlson G, Calhoun VD, Liddle PF (2005) An adaptive reflexive processing model of neurocognitive function: supporting evidence from a large scale (n = 100) fMRI study of an auditory oddball task. Neuroimage 25:899–915
Klimesch W (1997) EEG-alpha rhythms and memory processes. Int J Psychophysiol 26:319–340
Knight RT (1984) Decreased response to novel stimuli after prefrontal lesions in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 59:9–20
Knight RT (1997) Distributed cortical networkfor visual attention. J Cogn Neurosci 9:75–91
Krack P, Batir A, Van Blercom N, Chabardes S, Fraix V, Ardouin C, Koudsie A, Limousin PD, Benazzouz A, LeBas JF, Benabid AL, Pollak P (2003) Five-year follow-up of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 349:1925–1934
Kutas M, McCarthy G, Donchin E (1997) Augmenting mental chronometry: the P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation tim. Science 197:792–795
Magliero A, Bashore TR, Coles MG, Donchin E (1984) On the dependence of P300 latency on stimulus evaluation processes. Psychophysiology 21:171–186
Mink JW (1996) The basal ganglia: focused selection and inhibition of competing motor programs. Prog Neurobiol 50:381–425
Nambu A, Tokuno H, Takada M (2002) Functional significance of the cortico-subthalamo-pallidal ‘hyperdirect’ pathway. Neurosci Res 43:111–117
Okun MS, Fernandez HH, Wu SS, Kirsch-Darrow L, Bowers D, Bova F, Suelter M, Jacobson CE 4th, Wang X, Gordon CW Jr, Zeilman P, Romrell J, Martin P, Ward H, Rodriguez RL, Foote KD (2009) Cognition and mood in Parkinson’s disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: the COMPARE trial. Ann Neurol 65:586–595
Parent A, Hazrati LN (1995) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. II. The place of subthalamic nucleus and external pallidum in basal ganglia circuitry. Brain Res Rev 20:128–154
Pfurtscheller G (2001) Functional brain imaging based on ERD/ERS. Vis Res 41:1257–1260
Pfurtscheller G, Aranibar A (1977) Event-related cortical desynchronization detected by power measurements of scalp EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 42:817–826
Pfurtscheller G, Klimesch W (1991) Event-related desynchronization during motor behavior and visual information processing. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 42:58–65
Pfurtscheller G, Klimesch W (1992) Functional topography during a visuoverbal judgment task studied with event-related desynchronization mapping. J Clin Neurophysiol 9:120–131
Polich J (1997) On the relationship between EEG and P300: individual differences, aging and ultradian rhythms. Int J Psychophysiol 26:299–317
Polich J (2007) Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin Neurophysiol 118:2128–2148
Rektor I, Kaňovský P, Bareš M, Brázdil M, Streitová H, Klajblová H, Kuba R, Daniel P (2003) A SEEG study of ERP in motor and premotor cortices and in the basal ganglia. Clin Neurophysiol 114:463–471
Rektor I, Bareš M, Brázdil M, Kaňovský P, Rektorová I, Sochůrková D, Kubová D, Kuba R, Daniel P (2005) Cognitive- and movement-related potentials recorded in the human basal ganglia. Mov Disord 20:62–568
Rektor I, Brázdil M, Nestrasil I, Bareš M, Daniel P (2007) Modifications of cognitive and motor tasks affect the occurrence of event-related potentials in the human cortex. Eur J Neurosci 26:1371–1380
Rogers RD, Baunez C, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2001) Lesions of the medial and lateral striatum in the rat produce differential deficits in attentional performance. Behav Neurosci 115:799–811
Saint-Cyr JA, Trépanier LL, Kumar R, Lozano AM, Lang AE (2000) Neuropsychological consequences of chronic bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 123:2091–2108
Schröger E, Wolff C (1998) Behavioral and electrophysiological effects of task-irrelevant sound change: a new distraction paradigm. Cogn Brain Res 7:71–87
Sergeant J, Geuze R, van Winsum W (1987) Event-related desynchronization and P300. Psychophysiology 24:272–277
Squires NK, Squires KC, Hillyard SA (1975) Two varieties of long-latency positive waves evoked by unpredictable auditory stimuli in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 38:387–401
Strobel A, Debener S, Sorger B, Peters JC, Kranczioch C, Hoechstetter K, Engel AK, Brocke B, Goebel R (2008) Novelty and target processing during an auditory novelty oddball: a simultaneous event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 40:869–883
Temel Y, Blokland A, Steinbusch HW, Visser-Vandewalle V (2005) The functional role of the subthalamic nucleus in cognitive and limbic circuits. Prog Neurobiol 76:393–413
Temel Y, Kessels A, Tan S, Topdag A, Boon P, Visser-Vandewalle V (2006) Behavioural changes after bilateral subthalamic stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12:265–272
Voon V, Kubu C, Krack P, Houeto JL, Tröster AI (2006) Deep brain stimulation: neuropsychological and neuropsychiatric issues. Mov Disord Suppl 14:S305–S327
Wennberg RA, Lozano AM (2003) Intracranial volume conduction of cortical spikes, sleep potentials recorded with deep brain stimulating electrodes. Clin Neurophysiol 114:1403–1418
Witt K, Daniels C, Reiff J, Krack P, Volkmann J, Pinsker MO, Krause M, Tronnier V, Kloss M, Schnitzler A, Wojtecki L, Bötzel K, Danek A, Hilker R, Sturm V, Kupsch A, Karner E, Deuschl G (2008) Neuropsychological and psychiatric changes after deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol 7:605–614
Yordanova J, Kolev V, Polich J (2001) P300 and alpha event-related desynchronization (ERD). Psychophysiology 38:143–152
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by MSMT CR research project: MSM0021622404. The technical part of this study was supported by grant GA AV IAA 200650801. The technical part of the study was also supported by project: Application laboratories of advanced microtechnologies and nanotechnologies, CZ.1.05/2.1.00/01.0017, co-funded by the Operational Programme ‘Research and Development for Innovations’, the European regional development fund and state budget. We wish to thank Drs Novak and Chrastina (neurosurgery).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bočková, M., Chládek, J., Jurák, P. et al. Involvement of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus in attention. J Neural Transm 118, 1235–1245 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0575-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0575-4