Abstract
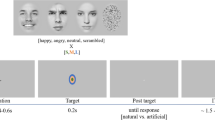
The objective is to study the change detection of emotion expression by electroencephalography (EEG). A visual letter task was combined with two neutral faces. After a short break another letter task occurred whilst the peripheral faces remained or randomly changed to joy, anger or disgust. Study participants responded whether they had perceived a change in emotion expression or not. Explicit change detection elicited more positive-going EEG amplitudes than change blindness between 750 and 900 ms. A change to disgust elicited largest effects. Furthermore, evidence for implicit change detection occurred.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austen EL, Enns JT (2003) Change detection in an attended face depends on the expectation of the observer. J Vis 3:64–74
Beck DM, Rees G, Frith CD, Lavie N (2001) Neural correlates of change detection and change blindness. Nat Neurosci 4(6):645–650
Dimberg U, Petterson M (2000) Facial reactions to happy and angry facial expressions: evidence for right hemnispere dominance. Psychophysiology 37:693–696
Dimberg U, Thunberg M, Elmehed K (2000) Uncounscious facial reactions to emotional facial expressions. Psychol Sci 11(1):86–89
Downing P, Liu J, Kanwisher N (2001) Testing cognitive models of visual attention with fMRI and MEG. Neuropsychologia 39:1329–1342
Eimer M, Holmes A (2003) The role of spatial attention in the processing of facial expression: an ERP study of rapid brain responses to six basic emotions. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3(2):97–110
Hoshiyama M, Kakigi R, Watanabe S, Miki K, Takeshima Y (2003) Brain responses for the subconscious recognition of faces. Neurosci Res 46:435–442
Jasper HH (1958) The ten twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 10:371–375
Kanwisher N, McDermott J, Chun MM (1997) The fusiform face area: a module in human extrastriate cortex specialized for face perception. J Neurosci 17(11):4302–4311
Koivisto M, Revonsuo A (2003) An ERP study of change detection, change blindness, and visual awareness. Psychophysiology 40(3):423–429
Niedeggen M, Wichman P, Stoerig P (2001) Change blindness and time to consciousness. Eur J Neurosci 14:1719
Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1994) Low resolution electromagnetic tomography: a new method for localizing electrical activity in the brain. Int J Psychophysiol 18:49–65
Pizzagalli DA, Lehmann D, Hendrick AM, Regard M, Pascual-Marqui RD, Davidson RJ (2002) Affective judgements of faces modulate early activity (160 ms) within the fusiform gyri. Neuroimage 16:663–677
Resink RA, O'Reagan JK, Clark JJ (1997) To see or not to see: the need for attention to perceive changes in scenes. Psychol Sci 8:368–373
Ro T, Russell C, Lavie N (2001) Changing faces: a detection advantage in the Flicker paradigm. Psychol Sci 12(1):94–99
Turatto M, Angrilli A, Mazza V, Umilta C, Driver J (2002) Looking without seeing the background change: electrophysical correlates of change detection versus change blindness. Cognition 84:B1–B10
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the professional actor who supported this study by being at our disposal for demonstrating his wonderful ability to change his facial expression whilst being photographed. Thank you very much for your time! We also want to thank Florian Ph.S. Fischmeister for his support related to statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khittl, B., Bauer, H. & Walla, P. Change detection related to peripheral facial expression: an electroencephalography study. J Neural Transm 116, 67–70 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-008-0125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-008-0125-5