Summary.
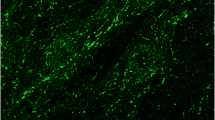
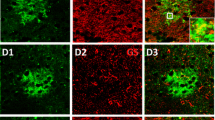
Astroglia-rich primary cultures from rat brain were used to investigate the presence in glial cells of Nɛ-(carboxymethyl)lysine (CML), an advanced glycation endproduct. Westernblot analysis of homogenates of rat brain as well as of astroglia-rich cultures demonstrated the presence of CML-modified proteins in these samples. Immunocytochemical staining of astroglia-rich cultures revealed that only a minority of the cells in these cultures were intensively stained for CML. The staining intensity of CML-positive cells was strongly reduced, if the cells were not permeabilized, indicating that intracellular proteins were CML-modified. The CML-positive cells were identified as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes by double-labelling immunocytochemical staining for CML and the cellular markers galactocerobroside, myelin basic protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein. In contrast to other glial cells, microglial cells in astroglia-rich cultures were CML-negative. The finding that only a minority of cells in astroglia-rich cultures contains high amounts of intracellular CML-modified proteins indicates that specific properties of these CML-positive cells are responsible for the CML-formation in these cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 28, 2003; accepted April 22, 2003 Published online June 30, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawlowski, P., Dringen, R. Identification of Nɛ-(carboxymethyl)lysine-positive cells in astroglia-rich primary cultures. J Neural Transm 110, 1077–1090 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0020-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0020-z