Abstract
Background
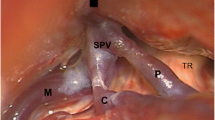
Implication of veins as neurovascular conflict (NVC) in the genesis of trigeminal neuralgia (TN) remains a matter of debate. Few reports dealing with venous NVC have been published. The objective of this study is to describe the outcome in a historical cohort of consecutive patients with classical TN due to venous compression.
Methods
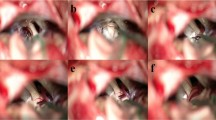
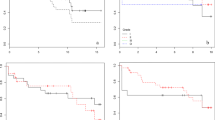
All patients with TN treated by microvascular decompression (MVD) from 2005 to 2013 were included if a marked venous compression was found at the surgery either alone or accompanied by an artery. Patients were evaluated for clinical presentation, operative findings and the long-term outcome. Outcome was considered favourable if patients were classed as BNI I or II (i.e. not requiring any medication). Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to determine probability of a favourable outcome at 10 years of follow-up.
Results
Out of the overall series of 313 patients having been treated by MVD and considered for the study, in 55 (17.5 %) a vein was the main compressive vessel; in 26 (8.3 %) it was the only compressive vessel. Probability of relief with no need for medication at 10 years was 70.6 %. The patients with focal arachnoiditis had a poor long-term outcome, i.e. BNI III-V, in 85.7 % compared with 20.8 % without arachnoiditis (p = 0.0037 Fisher’s exact test). No differences in outcome were found between patients presenting with purely venous compression and patients with mixed compression. Outcome was similarly good for patients with atypical neuralgia when compared to patients with typical clinical presentation.
Conclusions
Venous NVC as a cause of TN is far from rare. MVD with complete liberation of the entire root in cases with clear-cut venous compression on imaging studies gives a good probability of long-term pain relief, thus encouraging to propose surgery for such patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahgat D, Ray DK, Raslan AM, McCartney S, Burchiel KJ (2011) Trigeminal neuralgia in young adults. J Neurosurg 114:1306–1311
Barker FG, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334:1077–1083
Burchiel KJ (2003) A new classification for facial pain. Neurosurgery 53:1164–1166
Degn J, Brennum J (2010) Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Results from the use of glycerol injection, microvascular decompression, and rhizotomia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:2125–2132
Dumot C, Sindou M (2015) Trigeminal neuralgia due to neurovascular conflicts from venous origin: an anatomical-surgical study (consecutive series of 124 operated cases). Acta Neurochir (Wien) 157:455–466
Han PP, Shetter AG, Smith KA, Fiedler JA, Rogers CL, Speiser B, Feiz-Erfan I (1999) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: experience at the Barrow Neurological Institute. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 73:131–133
Han-Bing S, Wei-Guo Z, Jun Z, Ning L, Jian-Kang S, Yu C (2010) Predicting the outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia using magnetic resonance tomographic angiography. J Neuroimaging 20:345–349
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS): The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version) (2013). Cephalalgia Int J Headache 33:629–808
Hong W, Zheng X, Wu Z, Li X, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang W, Zhong J, Hua X, Li S (2011) Clinical features and surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:1037–1042
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26:159–162
Jo KW, Kong DS, Hong KS, Lee JA, Park K (2013) Long-term prognostic factors for microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci 20:440–445
Kuncz A, Vörös E, Barzó P, Tajti J, Milassin P, Mucsi Z, Elek P, Benedek K, Tarjányi J, Bodosi M (2006) Comparison of clinical symptoms and magnetic resonance angiographic (MRA) results in patients with trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain. Medium-term outcome after microvascular decompression of cases with positive MRA findings. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 26:266–276
Leal PRL, Hermier M, Froment JC, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M (2010) Preoperative demonstration of the neurovascular compression characteristics with special emphasis on the degree of compression, using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study, with comparison to surgical findings, in 100 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:817–825
Li GW, Zhang WC, Yang M, Ma QF, Zhong WX (2014) Clinical characteristics and surgical techniques of trigeminal neuralgia caused simply by venous compression. J Craniofac Surg 25:481–484
Matsushima T, Huynh-Le P, Miyazono M (2004) Trigeminal neuralgia caused by venous compression. Neurosurgery 55:334–339
Matsushima T, Rhoton AL, de Oliveira E, Peace D (1983) Microsurgical anatomy of the veins of the posterior fossa. J Neurosurg 59:63–105
Miller JP, Acar F, Burchiel KJ (2009) Classification of trigeminal neuralgia: clinical, therapeutic, and prognostic implications in a series of 144 patients undergoing microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 111:1231–1234
Oesman C, Mooij JJA (2011) Long-term follow-up of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Skull Base Al 21:313–322
Oishi M, Fukuda M, Noto Y, Kawaguchi T, Hiraishi T, Fujii Y (2011) Trigeminal neuralgia associated with the specific bridging pattern of transverse pontine vein: diagnostic value of three-dimensional multifusion volumetric imaging. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89:226–233
Sandell T, Eide PK (2008) Effect of microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia patients with or without constant pain. Neurosurgery 63:93–99, discussion 99–100
Sekula RF, Frederickson AM, Jannetta PJ, Bhatia S, Quigley MR, Abdel Aziz KM (2009) Microvascular decompression in patients with isolated maxillary division trigeminal neuralgia, with particular attention to venous pathology. Neurosurg Focus 27:E10
Sweet WH (1989) Characteristics of atypical trigeminal neuralgia. In: Gybels JM, Sweet WH (eds) Neurosurgical treatment of persistent pain. Karger, Basel, pp 41–42
Sweet WH (1969) Characteristics of atypical facial pain. In: White JC, Sweet WH (eds) Pain and the neurosurgeon: a forty year experience. CC Thomas, Springfield, pp 408–409
Sindou M, Leston J, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2008) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: the importance of a non-compressive technique. Kaplan-Meyer analysis in a consecutive series of 330 patients. Neurosurg Operative Neurosurg 63:341–351
Sindou M, Howeidy T, Acevedo G (2002) Anatomical observations during microvascular decompression for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (with correlations between topography of pain and site of the neurovascular conflict). Prospective study in a series of 579 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:1–12
Sindou M, Leston J, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2007) Microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia: long-term effectiveness and prognostic factors in a series of 362 consecutive patients with clear-cut neurovascular conflicts who underwent pure decompression. J Neurosurg 107:1144–1153
Sindou M, Leston J, Howeidy T, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2005) Microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia (typical or atypical). Long term effectiveness on pain; prospective study with survival analysis in a consecutive series of 362 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wein) 148:1235–1245
Szapiro J, Sindou M, Szapiro J (1985) Prognostic factors in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 17:920–929
Tatli M, Satici O, Kanpolat Y, Sindou M (2008) Various surgical modalities for trigeminal neuralgia: literature study of respective long-term outcomes. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:243–255
Tyler-Kabara EC, Kassam AB, Horowitz MH, Urgo L, Hadjipanayis C, Levy EI, Chang YF (2002) Predictors of outcome in surgically managed patients with typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of results following microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 96:527–531
Zakrzewska JM, Lopez BC (2003) Quality of reporting in evaluations of surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: recommendations for future reports. Neurosurgery 53:110–122
Zakrzewska JM, Lopez BC, Kim SE, Varian EA, Coakham HB (2005) Patient satisfaction after surgery for trigeminal neuralgia—development of a questionnaire. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:925–932
Zhang H, Lei D, You C, Mao BY, Wu B, Fang Y (2013) The long-term outcome predictors of pure microvascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 79:756–762
Author contributions
Chloe Dumot
Substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data. Drafting the article and critical revision for all intellectual content. Final approval of the version to be published.
Andrei Brinzeu
Substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data. Drafting the article and critical revision for all intellectual content. Final approval of the version to be published.
Julien Berthillier
Statistical analysis.
Marc Sindou
Principal surgeon—responsible for all surgical procedures. Substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data. Drafting the article and critical revision for all intellectual content. Final approval of the version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organisation or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical standards and patient consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Comments
The Lyon group has provided us with another careful analysis of their surgical experience for microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia. This time they focus on the response of venous decompression in pain relief from trigeminal neuralgia.
In 17.5 % of their patients, venous compression played a significant role. Their results in performing venous decompression was similar to their arterial decompression series. This is an important observation as previous studies in the literature have downplayed the role of venous compression in the pathophysiology of trigeminal neuralgia. Some authors go as far as advocating a partial rhizotomy when encountering venous compression only.
The authors have correctly pointed out the dangers of sacrificing the offending vein which may lead to a cerebellar infarct. In this scenario, when the offending vein cannot be separated from the trigeminal root, a partial rhizolysis may be an alternative safer maneuver.
Another contribution in the manuscript is to point out the poor response rate of patients with arachnoiditis to the surgical procedure. When encountering this pathology, a surgical partial rhizolysis could be a useful addition to the procedure.
The authors are to be congratulated on this important contribution to the surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
Zvi Harry Rappaport
Petah Tiqva, Israel
Portions of this work have been delivered through oral presentations to the Annual Meeting of the French-Speaking Society of Neurosurgery, Paris, France, 2014
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumot, C., Brinzeu, A., Berthiller, J. et al. Trigeminal neuralgia due to venous neurovascular conflicts: outcome after microvascular decompression in a series of 55 consecutive patients. Acta Neurochir 159, 237–249 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2994-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2994-y