Abstract
Background
Because of a degenerative component, degenerative rotatory scoliosis seems different from congenital and idiopathic subtypes of the disease. This study aims to examine the orientation of facet joints, as a known cause of degeneration, in patients with degenerative rotatory scoliosis.
Methods
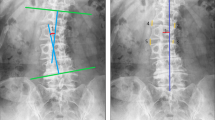
Lumbar magnetic resonance (MR) images and plain radiographs of 52 symptomatic patients (mean age, 50.17 years) with degenerative rotatory lumbar scoliosis (mean curve, 19.22 degrees) and 50 healthy individuals were reviewed. Facet joint angles in rotated segments and the minimum neural foramen width at all lumbar levels were measured by three observers and the average was recorded.
Results
The maximum vertebral rotation was most frequent at L4-L5 (75 %), and the majority was of type I (84.6 %) according to the Nash-Moe classification. At all lumbar spinal levels the mean facet joint angles were significantly higher on the side of rotation (L2-L3, 57.92 degrees; L3-L4, 45.00 degrees; L4-L5, 43.88 degrees) compared to those on the contralateral side (L2-L3, 20.42 degrees; L3-L4, 15.48 degrees; L4-L5, 13.12 degrees) and in controls (L2-L3, 30.21 degrees; L3-L4, 40.81 degrees; L4-L5, 45.20 degrees) (p < 0.001 for all comparisons). The mean facet joint angle increased significantly from L4-L5 to L2-L3 in cases and reversely in controls. The mean minimum neural foramen width was 1.29 ± 0.85 mm on the side of rotation, 5.50 ± 1.09 mm on the contralateral side, and 6.78 ± 1.75 mm in controls (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Substantial asymmetries and abnormal orientations in facet joints were documented in patients with degenerative rotatory lumbar scoliosis. Such asymmetries may adversely affect neural foramen width.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi M (2005) The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J 14:925–948
Ailon T, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Lenke LG, Brodke D, Harrop JS, Fehlings M, Ames CP (2015) Degenerative spinal deformity. Neurosurgery 77:S75–S91
Ameri E, Fouladi DF, Ghandhari H, Vahid Tari H, Safari MB (2015) The effect of concomitant rib deformity in congenital scoliosis on spinal curve correction after segmental pedicle screw instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000275
Bao H, Zhu F, Liu Z, Bentley M, Mao S, Zhu Z, Ding Y, Qiu Y (2014) Vertebral rotatory subluxation in degenerative scoliosis: facet joint tropism is related. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 39:B45–B51
Benoist M (2003) Natural history of the aging spine. Eur Spine J 12:S86–S89
Benzel EC (2001) Biomechanics of spine stabilization. Thieme/AANS, Illinois
Berlemann U, Jeszenszky DJ, Buhler DW, Harms J (1998) Facet joint remodeling in degenerative spondylolisthesis: an investigation of joint orientation and tropism. Eur Spine J 7:376–380
Birknes JK, White AP, Albert TJ, Shaffrey CI, Harrop JS (2008) Adult degenerative scoliosis: a review. Neurosurgery 63:94–103
Blankenbaker DG, Haughton VM, Rogers BP, Meyerand ME, Fine JP (2006) Axial rotation of the lumbar spinal motion segments correlated with concordant pain on discography: a preliminary study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:795–799
Cho SH, Shim JK, Park HM, Yoon DM, Kim WO, Yoon KB (2007) Relationship between lumbar lordosis and asymmetry of facet joints. Korean J Anesthesiol 53:630
Cobb JR (1948) Outline for the study of scoliosis: surgeons. Instr Course Lect 5:261–275
Cyron BM, Hutton WC (1980) Articular tropism and stability of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 5:168–172
Czaprowski D (2014) Generalised joint hypermobility in caucasian girls with idiopathic scoliosis: relation with age, curve size, and curve pattern. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:370134
D’Arpa P, Beardmore C, Liu LF (1990) Involvement of nucleic acid synthesis in cell killing mechanisms of topoisomerase poisons. Cancer Res 50:6919–6924
Daffner SD, Vaccaro AR (2003) Adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 32:77–82
Daghighi MH, Pouriesa M, Maleki M, Fouladi DF, Pezeshki MZ, Khameneh RM, Bazzazi AM (2014) Migration patterns of herniated disk fragments, a study on 1020 patients with extruded lumbar disk herniation. Spine J 14:1970–1977
Dai LY (2001) Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop 25:40–42
Davies A, Saifuddin A (2009) Imaging of painful scoliosis. Skeletal Radiol 38:207–223
de Vries AA, Mullender MG, Pluymakers WJ, Castelein RM, van Royen BJ (2010) Spinal decompensation in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J 19:1540–1544
DePalma MJ (2011) iSpine: evidence-based interventional spine care. Demos Medical, New York
Don AS, Robertson PA (2008) Facet joint orientation in spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 21:112–115
Fardon DF, Milette PC (2001) Nomenclature and classification of lumbar disc pathology. Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, American Society of Spine Radiology, and American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:E93–E113
Feiz HH, Afrasiabi A, Parvizi R, Safarpour A, Fouladi RF (2012) Scoliosis after thoracotomy/sternotomy in children with congenital heart disease. Indian J Orthop 46:77–80
Fujiwara A, An HS, Lim TH, Haughton VM (2001) Morphologic changes in the lumbar intervertebral foramen due to flexion-extension, lateral bending, and axial rotation: an in vitro anatomic and biomechanical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:876–882
Gallucci M, Puglielli E, Splendiani A, Pistoia F, Spacca G (2005) Degenerative disorders of the spine. Eur Radiol 15:591–598
Ghandhari H, Fouladi DF, Safari MB, Ameri E (2015) Correlation between pelvic tilt and the sacro-femoral-pubic angle in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, patients with congenital scoliosis, and healthy individuals. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-3952-8
Ghandhari H, Tari HV, Ameri E, Safari MB, Fouladi DF (2015) Vertebral, rib, and intraspinal anomalies in congenital scoliosis: a study on 202 Caucasians. Eur Spine J 24:1510-1521
Ghandhari H, Tari HV, Ameri E, Safari MB, Fouladi DF (2015) Vertebral, rib, and intraspinal anomalies in congenital scoliosis: a study on 202 Caucasians. Eur Spine J 24:1510–1521
Gremeaux V, Casillas JM, Fabbro-Peray P, Pelissier J, Herisson C, Perennou D (2008) Analysis of low back pain in adults with scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:402–405
Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, Pope MH (1993) Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:80–91
Haaga JR, Boll D, Dogra VS, Forsting M, Gilkeson RC, Ha KH, Sundaram M (2008) CT and MRI of the Whole Body. Mosby, Maryland Heights
Kobayashi T, Atsuta Y, Takemitsu M, Matsuno T, Takeda N (2006) A prospective study of de novo scoliosis in a community based cohort. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:178–182
Kong MH, He W, Tsai YD, Chen NF, Keorochana G, Do DH, Wang JC (2009) Relationship of facet tropism with degeneration and stability of functional spinal unit. Yonsei Med J 50:624–629
Kouwenhoven JW, Castelein RM (2008) The pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:2898–2908
Lee DY, Ahn Y, Lee SH (2006) The influence of facet tropism on herniation of the lumbar disc in adolescents and adults. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 88:520–523
Masharawi YM, Alperovitch-Najenson D, Steinberg N, Dar G, Peleg S, Rothschild B, Salame K, Hershkovitz I (2007) Lumbar facet orientation in spondylolysis: a skeletal study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32:E176–E180
Masharawi YM, Peleg S, Albert HB, Dar G, Steingberg N, Medlej B, Abbas J, Salame K, Mirovski Y, Peled N, Hershkovitz I (2008) Facet asymmetry in normal vertebral growth: characterization and etiologic theory of scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:898–902
Masharawi Y, Rothschild B, Salame K, Dar G, Peleg S, Hershkovitz I (2005) Facet tropism and interfacet shape in the thoracolumbar vertebrae: characterization and biomechanical interpretation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:E281–E292
Miyazaki M, Hong SW, Yoon SH, Zou J, Tow B, Alanay A, Abitbol JJ, Wang JC (2008) Kinematic analysis of the relationship between the grade of disc degeneration and motion unit of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:187–193
Nash CL Jr, Moe JH (1969) A study of vertebral rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:223–229
Nowicki BH, Haughton VM, Schmidt TA, Lim TH, An HS, Riley LH 3rd, Yu L, Hong JW (1996) Occult lumbar lateral spinal stenosis in neural foramina subjected to physiologic loading. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1605–1614
Park JB, Chang H, Kim KW, Park SJ (2001) Facet tropism: a comparison between far lateral and posterolateral lumbar disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:677–679
Ploumis A, Liu H, Mehbod AA, Transfeldt EE, Winter RB (2009) A correlation of radiographic and functional measurements in adult degenerative scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:1581–1584
Ploumis A, Transfeldt EE, Gilbert TJ Jr, Mehbod AA, Dykes DC, Perra JE (2006) Degenerative lumbar scoliosis: radiographic correlation of lateral rotatory olisthesis with neural canal dimensions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:2353–2358
Ploumis A, Transfledt EE, Denis F (2007) Degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis. Spine J 7:428–436
Poureisa M, Daghighi MH, Yousefi J, Hagigi A (2014) Correlation of axial vertebral rotation with nerve root involvement: the first clinical study in literature. J Med Sci 14:235–240
Roberts SB, Tsirikos AI (2015) Thoracolumbar kyphoscoliosis with unilateral subluxation of the spine and postoperative lumbar spondylolisthesis in Hunter syndrome. J Neurosurg Spine 20:1–5
Sapkas G, Papagelopoulos PJ, Kateros K, Koundis GL, Boscainos PJ, Koukou UI, Katonis P (2003) Prediction of Cobb angle in idiopathic adolescent scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res (411):32–39
Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, El Fegoun AB, Hwang K, Pagala M, Farcy JP (2005) Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:1082–1085
Serhan HA, Varnavas G, Dooris AP, Patwadhan A, Tzermiadianos M (2007) Biomechanics of the posterior lumbar articulating elements. Neurosurg Focus 22: E1
Sharma L, Kapoor D, Issa S (2006) Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:147–156
Shea KG, Ford T, Bloebaum RD, D’Astous J, King H (2004) A comparison of the microarchitectural bone adaptations of the concave and convex thoracic spinal facets in idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A:1000–1006
Toyone T, Ozawa T, Kamikawa K, Watanabe A, Matsuki K, Yamashita T, Wada Y (2009) Facet joint orientation difference between cephalad and caudad portions: a possible cause of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:2259–2262
Toyone T, Tanaka T, Kato D, Kaneyama R, Otsuka M (2005) Anatomic changes in lateral spondylolisthesis associated with adult lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:E671–E675
Trammell TR, Schroeder RD, Reed DB (1988) Rotatory olisthesis in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 13:1378–1382
Wang J, Yang X (2009) Age-related changes in the orientation of lumbar facet joints. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:E596–E598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poureisa, M., Behzadmehr, R., Daghighi, M.H. et al. Orientation of the facet joints in degenerative rotatory lumbar scoliosis: an MR study on 52 patients. Acta Neurochir 158, 473–479 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2690-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2690-3