Abstract
Background
Deep-brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is an accepted neurosurgical technique for the treatment of medication-resistant Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders. The accurate targeting of the STN is facilitated by precise and reliable identification in pre-stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The aim of the study was to compare and evaluate different promising MRI methods at 7.0 T for the pre-stereotactic visualisation of the STN
Methods
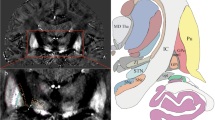
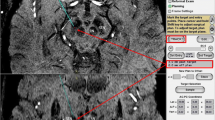
MRI (T2-turbo spin-echo [TSE], T1-gradient echo [GRE], fast low-angle shot [FLASH] two-dimensional [2D] T2* and susceptibility-weighted imaging [SWI]) was performed in nine healthy volunteers. Delineation and image quality for the STN were independently evaluated by two neuroradiologists using a six-point grading system. Inter-rater reliability, contrast-to-noise ratios (CNRs) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) for the STN were calculated. For the anatomical validation, the coronal FLASH 2D T2* images were co-registered with a stereotactic atlas (Schaltenbrand-Wahren).
Results
The STN was clearly and reliably visualised in FLASH 2D T2* imaging (particularly coronal view), with a sharp delineation between the STN, the substantia nigra and the zona incerta. No major artefacts in the STN were observed in any of the sequences. FLASH 2D T2* and SWI images offered significantly higher CNR for the STN compared with T2-TSE. The co-registration of the coronal FLASH 2D T2* images with the stereotactic atlas affirmed the correct localisation of the STN in all cases.
Conclusion
The STN is best and reliably visualised in FLASH 2D T2* imaging (particularly coronal orientation) at 7.0-T MRI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease Study Group (2001) Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 345: 956–963
Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Paek SH, Lee JY, Kim CK, Kim DG (2010) Bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease patients with severe tremor. Neurosurgery 67:626–632, discussion 632
Rehncrona S, Johnels B, Widner H, Tornqvist AL, Hariz M, Sydow O (2003) Long-term efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation for tremor: double-blind assessments. Mov Disord 18:163–170
Tisch S, Rothwell JC, Limousin P, Hariz MI, Corcos DM (2007) The physiological effects of pallidal deep brain stimulation in dystonia. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 15:166–172
Krack P, Hariz MI, Baunez C, Guridi J, Obeso JA (2010) Deep brain stimulation: from neurology to psychiatry? Trends Neurosci 33:474–484
Sakas DE, Panourias IG, Singounas E, Simpson BA (2007) Neurosurgery for psychiatric disorders: from the excision of brain tissue to the chronic electrical stimulation of neural networks. Acta Neurochir Suppl 97:365–374
Kringelbach ML, Jenkinson N, Owen SL, Aziz TZ (2007) Translational principles of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:623–635
Huang C, Mattis P, Tang C, Perrine K, Carbon M, Eidelberg D (2007) Metabolic brain networks associated with cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 34:714–723
Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Lee JY, Paek SH, Kim DG (2012) The benefit of subthalamic deep brain stimulation for pain in Parkinson disease: a 2-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery 70:18–23, discussion 23–14
Mure H, Hirano S, Tang CC, Isaias IU, Antonini A, Ma Y, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2011) Parkinson’s disease tremor-related metabolic network: characterization, progression, and treatment effects. NeuroImage 54:1244–1253
Trost M, Su S, Su P, Yen RF, Tseng HM, Barnes A, Ma Y, Eidelberg D (2006) Network modulation by the subthalamic nucleus in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 31:301–307
Voges J, Volkmann J, Allert N, Lehrke R, Koulousakis A, Freund HJ, Sturm V (2002) Bilateral high-frequency stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson disease: correlation of therapeutic effect with anatomical electrode position. J Neurosurg 96:269–279
Yelnik J (2002) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. Mov Disord 17(Suppl 3):S15–S21
Mallet L, Schupbach M, N’Diaye K, Remy P, Bardinet E, Czernecki V, Welter ML, Pelissolo A, Ruberg M, Agid Y, Yelnik J (2007) Stimulation of subterritories of the subthalamic nucleus reveals its role in the integration of the emotional and motor aspects of behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10661–10666
Abosch A, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, Harel N (2010) An assessment of current brain targets for deep brain stimulation surgery with susceptibility-weighted imaging at 7 tesla. Neurosurgery 67:1745–1756, discussion 1756
Carpenter M (1976) The subthalamic region. In: Carpenter M (ed) Human neuroanatomy. Wiliams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 509–511
Benabid AL, Krack PP, Benazzouz A, Limousin P, Koudsie A, Pollak P (2000) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson’s disease: methodologic aspects and clinical criteria. Neurology 55:S40–S44
Burdick AP, Foote KD, Wu S, Bowers D, Zeilman P, Jacobson CE, Ward HE, Okun MS (2011) Do patient’s get angrier following STN, GPi, and thalamic deep brain stimulation. NeuroImage 54(Suppl 1):S227–S232
Halpern C, Hurtig H, Jaggi J, Grossman M, Won M, Baltuch G (2007) Deep brain stimulation in neurologic disorders. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13:1–16
Halpern CH, Danish SF, Baltuch GH, Jaggi JL (2008) Brain shift during deep brain stimulation surgery for Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86:37–43
Temel Y, Wilbrink P, Duits A, Boon P, Tromp S, Ackermans L, van Kranen-Mastenbroek V, Weber W, Visser-Vandewalle V (2007) Single electrode and multiple electrode guided electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 61:346–355, discussion 355–347
Hariz MI, Bergenheim AT (1990) A comparative study on ventriculographic and computerized tomography-guided determinations of brain targets in functional stereotaxis. J Neurosurg 73:565–571
Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Roberts DW, Darcey TM (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for target localization in functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 45:290–297, discussion 297–298
den Dunnen WF, Staal MJ (2005) Anatomical alterations of the subthalamic nucleus in relation to age: a postmortem study. Mov Disord 20:893–898
Ashkan K, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L, Tisch S, Yousry T, Limousin-Dowsey P, Hariz MI (2007) Variability of the subthalamic nucleus: the case for direct MRI guided targeting. Br J Neurosurg 21:197–200
Hamani C, Richter EO, Andrade-Souza Y, Hutchison W, Saint-Cyr JA, Lozano AM (2005) Correspondence of microelectrode mapping with magnetic resonance imaging for subthalamic nucleus procedures. Surg Neurol 63:249–253, discussion 253
Starr PA, Vitek JL, DeLong M, Bakay RA (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging-based stereotactic localization of the globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus. Neurosurgery 44:303–313, discussion 313–304
Ullman M, Vedam-Mai V, Krock N, Sudhyadhom A, Foote KD, Yachnis AT, Merritt S, Resnick AS, Zeilman P, Okun MS (2011) A pilot study of human brain tissue post-magnetic resonance imaging: information from the National Deep Brain Stimulation Brain Tissue Network (DBS-BTN). NeuroImage 54(Suppl 1):S233–S237
Massey LA, Miranda MA, Zrinzo L, Al-Helli O, Parkes HG, Thornton JS, So PW, White MJ, Mancini L, Strand C, Holton JL, Hariz MI, Lees AJ, Revesz T, Yousry TA (2011) High resolution MR anatomy of the subthalamic nucleus: imaging at 9.4 T with histological validation. Neuroimage 59:2035-2044
Traynor CR, Barker GJ, Crum WR, Williams SC, Richardson MP (2011) Segmentation of the thalamus in MRI based on T1 and T2. NeuroImage 56:939–950
Amirnovin R, Williams ZM, Cosgrove GR, Eskandar EN (2006) Experience with microelectrode guided subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery 58:ONS96–ONS102, discussion ONS196-102
Gross RE, Krack P, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Rezai AR, Benabid AL (2006) Electrophysiological mapping for the implantation of deep brain stimulators for Parkinson’s disease and tremor. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 14):S259–S283
Bejjani BP, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Yelnik J, Damier P, Arnulf I, Bonnet AM, Marsault C, Agid Y, Philippon J, Cornu P (2000) Bilateral subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson’s disease by using three-dimensional stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 92:615–625
Nowinski WL, Chua BC, Volkau I, Puspitasari F, Marchenko Y, Runge VM, Knopp MV (2010) Simulation and assessment of cerebrovascular damage in deep brain stimulation using a stereotactic atlas of vasculature and structure derived from multiple 3- and 7-tesla scans. J Neurosurg 113:1234–1241
Park JH, Chung SJ, Lee CS, Jeon SR (2011) Analysis of hemorrhagic risk factors during deep brain stimulation surgery for movement disorders: comparison of the circumferential paired and multiple electrode insertion methods. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:1573–1578
Terao T, Takahashi H, Yokochi F, Taniguchi M, Okiyama R, Hamada I (2003) Hemorrhagic complication of stereotactic surgery in patients with movement disorders. J Neurosurg 98:1241–1246
Xiaowu H, Xiufeng J, Xiaoping Z, Bin H, Laixing W, Yiqun C, Jinchuan L, Aiguo J, Jianmin L (2010) Risks of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with Parkinson’s disease receiving deep brain stimulation and ablation. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:96–100
Bronte-Stewart H, Louie S, Batya S, Henderson JM (2010) Clinical motor outcome of bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease using image-guided frameless stereotaxy. Neurosurgery 67:1088–1093, discussion 1093
Dormont D, Ricciardi KG, Tande D, Parain K, Menuel C, Galanaud D, Navarro S, Cornu P, Agid Y, Yelnik J (2004) Is the subthalamic nucleus hypointense on T2-weighted images? a correlation study using MR imaging and stereotactic atlas data. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1516–1523
Hariz MI, Krack P, Melvill R, Jorgensen JV, Hamel W, Hirabayashi H, Lenders M, Wesslen N, Tengvar M, Yousry TA (2003) A quick and universal method for stereotactic visualization of the subthalamic nucleus before and after implantation of deep brain stimulation electrodes. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 80:96–101
Kitajima M, Korogi Y, Kakeda S, Moriya J, Ohnari N, Sato T, Hayashida Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Yamashita Y (2008) Human subthalamic nucleus: evaluation with high-resolution MR imaging at 3.0 T. Neuroradiology 50:675–681
Brunenberg EJ, Platel B, Hofman PA, Ter Haar Romeny BM, Visser-Vandewalle V (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for visualization of the subthalamic nucleus. J Neurosurg 115:971–984
Duyn JH, van Gelderen P, Li TQ, de Zwart JA, Koretsky AP, Fukunaga M (2007) High-field MRI of brain cortical substructure based on signal phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11796–11801
Nolte IS, Gerigk L, Al-Zghloul M, Groden C, Kerl HU (2012) Visualization of the internal globus pallidus: sequence and orientation for deep brain stimulation using a standard installation protocol at 3.0 Tesla. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:481-494
O’Gorman RL, Shmueli K, Ashkan K, Samuel M, Lythgoe DJ, Shahidiani A, Wastling SJ, Footman M, Selway RP, Jarosz J (2011) Optimal MRI methods for direct stereotactic targeting of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus. Eur Radiol 21:130–136
Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR (2004) Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med 52:612–618
Cho ZH, Min HK, Oh SH, Han JY, Park CW, Chi JG, Kim YB, Paek SH, Lozano AM, Lee KH (2010) Direct visualization of deep brain stimulation targets in Parkinson disease with the use of 7-tesla magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 113:639–647
Maj JK, Paxinos G, Assheuer JK (2003) Atlas of the human brain. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart
Slavin KV, Thulborn KR, Wess C, Nersesyan H (2006) Direct visualization of the human subthalamic nucleus with 3 T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:80–84
Vertinsky AT, Coenen VA, Lang DJ, Kolind S, Honey CR, Li D, Rauscher A (2009) Localization of the subthalamic nucleus: optimization with susceptibility-weighted phase MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1717–1724
Stark DD, Brandley WG (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging. C.V. Mosby, St. Louis
Haneder S, Attenberger UI, Biffar A, Dietrich O, Fink C, Schoenberg SO, Michaely HJ (2011) Gadofosveset: parameter optimization for steady-state imaging of the thoracic and abdominal vasculature. Investig Radiol 46:678-685
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 33:363–374
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Bushberg JT, Seibert JA, Boone JM, Leidholdt EM (2006) The essential physics of medical imaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Krack P, Benazzouz A, Pollak P, Limousin P, Piallat B, Hoffmann D, Xie J, Benabid AL (1998) Treatment of tremor in Parkinson’s disease by subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Mov Disord 13:907–914
Ostergaard K, Sunde N, Dupont E (2002) Effects of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with severe Parkinson’s disease and motor fluctuations. Mov Disord 17:693–700
Lee KH, Blaha CD, Garris PA, Mohseni P, Horne AE, Bennet KE, Agnesi F, Bledsoe JM, Lester DB, Kimble C, Min HK, Kim YB, Cho ZH (2009) Evolution of deep brain stimulation: human electrometer and smart devices supporting the next generation of therapy. Neuromodulation 12:85–103
McIntyre CC, Savasta M, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Vitek JL (2004) Uncovering the mechanism(s) of action of deep brain stimulation: activation, inhibition, or both. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1239–1248
Cuny E, Guehl D, Burbaud P, Gross C, Dousset V, Rougier A (2002) Lack of agreement between direct magnetic resonance imaging and statistical determination of a subthalamic target: the role of electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 97:591–597
Biswas J, Nelson CB, Runge VM, Wintersperger BJ, Baumann SS, Jackson CB, Patel T (2005) Brain tumor enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) at 1.5 versus 3 tesla. Investig Radiol 40:792–797
Toda H, Sawamoto N, Hanakawa T, Saiki H, Matsumoto S, Okumura R, Ishikawa M, Fukuyama H, Hashimoto N (2009) A novel composite targeting method using high-field magnetic resonance imaging for subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg 111:737–745
Lambert C, Zrinzo L, Nagy Z, Lutti A, Hariz M, Foltynie T, Draganski B, Ashburner J, Frackowiak R (2011) Confirmation of functional zones within the human subthalamic nucleus: patterns of connectivity and sub-parcellation using diffusion weighted imaging. Neuroimage 60:83-94
Kurian MA, McNeill A, Lin JP, Maher ER (2011) Childhood disorders of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Dev Med Child Neurol 53:394–404
McNeill A, Chinnery PF (2011) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Handb Clin Neurol 100:161–172
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3:41–51
Schicha H, Kasperek K, Feinendegen LE, Siller V, Klein HJ (1971) Iron content of the human brain and its correlation to age. Beitr Pathol 142:268–274
Griffiths PD, Dobson BR, Jones GR, Clarke DT (1999) Iron in the basal ganglia in Parkinson’s disease. An in vitro study using extended X-ray absorption fine structure and cryo-electron microscopy. Brain 122(Pt 4):667–673
Zhang W, Sun SG, Jiang YH, Qiao X, Sun X, Wu Y (2009) Determination of brain iron content in patients with Parkinson’s disease using magnetic susceptibility imaging. Neurosci Bull 25:353–360
Gelman N, Gorell JM, Barker PB, Savage RM, Spickler EM, Windham JP, Knight RA (1999) MR imaging of human brain at 3.0 T: preliminary report on transverse relaxation rates and relation to estimated iron content. Radiology 210:759–767
Elolf E, Bockermann V, Gringel T, Knauth M, Dechent P, Helms G (2007) Improved visibility of the subthalamic nucleus on high-resolution stereotactic MR imaging by added susceptibility (T2*) contrast using multiple gradient echoes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1093–1094
Haacke EM, Ayaz M, Khan A, Manova ES, Krishnamurthy B, Gollapalli L, Ciulla C, Kim I, Petersen F, Kirsch W (2007) Establishing a baseline phase behavior in magnetic resonance imaging to determine normal vs. abnormal iron content in the brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:256–264
Ben-Haim S, Asaad WF, Gale JT, Eskandar EN (2009) Risk factors for hemorrhage during microelectrode-guided deep brain stimulation and the introduction of an improved microelectrode design. Neurosurgery 64:754–762, discussion 762–753
Rauscher A, Sedlacik J, Barth M, Haacke EM, Reichenbach JR (2005) Nonnvasive assessment of vascular architecture and function during modulated blood oxygenation using susceptibility weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 54:87–95
Daniluk S, Davies GK, Ellias SA, Novak P, Nazzaro JM (2010) Assessment of the variability in the anatomical position and size of the subthalamic nucleus among patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease using magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:201–210, discussion 210
Balachandran R, Welch EB, Dawant BM, Fitzpatrick JM (2010) Effect of MR distortion on targeting for deep-brain stimulation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:1729–1735
Duchin Y, Abosch A, Yacoub E, Sapiro G, Harel N (2012) Feasibility of using ultra-high field (7 T) MRI for clinical surgical targeting. PLoS One 7:e37328
Shmueli K, de Zwart JA, van Gelderen P, Li TQ, Dodd SJ, Duyn JH (2009) Magnetic susceptibility mapping of brain tissue in vivo using MRI phase data. Magn Reson Med 62:1510–1522
Yacoub E, Shmuel A, Pfeuffer J, Van De Moortele PF, Adriany G, Andersen P, Vaughan JT, Merkle H, Ugurbil K, Hu X (2001) Imaging brain function in humans at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 45:588–594
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hans U. Kerl and Lars Gerigk contributed equally to this article
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kerl, H.U., Gerigk, L., Pechlivanis, I. et al. The subthalamic nucleus at 7.0 Tesla: evaluation of sequence and orientation for deep-brain stimulation. Acta Neurochir 154, 2051–2062 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1476-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1476-0