Abstract
Background
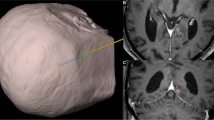
Intraoperative localisation of a stereotactic probe remains challenging. Stereotactic X-ray, the “gold standard”, as well as intraoperative magnetic resonance (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), require a dedicated operating room (OR). Fluoroscopy with crosshairs confirms only grossly the target position. An alternative would be a mobile three-dimensional (3D) fluoroscopy C-arm. To our knowledge, this is the first report on 3D C-arm fluoroscopy to verify stereotactical trajectories. The objective was to assess the feasibility of using a 3D C-arm to verify the intraoperative trajectory and target.
Methods
A total of 12 stereotactic trajectories in 10 patients were analysed, comprising 8 biopsies and 4 electrode trajectories. The fluoroscopic scan was performed after implantation of the deep brain stimulation electrode or after advancing the biopsy needle to the tumour. An image set is acquired during a rotation of the 3D C-arm. The image set is reconstructed and merged to the preoperative CT scan. Calculating the vector error and the deviation assesses target and trajectory accuracy.
Results
The mean trajectory deviation was 0.6 mm (±0.54 mm) and the mean vector error was 1.44 mm (±1.43 mm). There was no influence on the surgical time and the mean irradiation dosage was 401.9 cGycm².
Conclusions
This target and trajectory verification is feasible. Its accuracy seems comparable with MRI and CT. There is no additional time consumption. Irradiation is comparable with stereotactic X-ray.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjartmarz H, Rehncrona S (2007) Comparison of accuracy and precision between frame-based and frameless stereotactic navigation for deep brain stimulation electrode implantation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:235–242
Brown SM, Sadoughi B, Cuellar H, von Jako R, Fried MP (2007) Feasibility of near real-time image-guided sinus surgery using intraoperative fluoroscopic computed axial tomography. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:268–273
Caire F, Gantois C, Torny F, Ranoux D, Maubon A, Moreau JJ (2010) Intraoperative use of the Medtronic O-arm for deep brain stimulation procedures. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 88:109–114
Citak M, Stubig T, Kendoff D, O’Loughlin PF, Hufner T, Krettek C (2010) Navigated minimally invasive thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement with flat panel 3-D imaging. A feasibility study. Technol Health Care 18:101–110
Hassler R, Riechert T, Mundinger F (1969) The precision in anatomical localization of stereotactic Parkinson operations checked with data from autopsies. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 212:97–116
Heiland M, Schmelzle R, Hebecker A, Schulze D (2004) Intraoperative 3D imaging of the facial skeleton using the SIREMOBIL Iso-C3D. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 33:130–132
Holly LT, Foley KT (2003) Three-dimensional fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement. Technical note. J Neurosurg 99:324–329
Hunsche S, Sauner D, Maarouf M, Poggenborg J, Lackner K, Sturm V, Treuer H (2009) Intraoperative X-ray detection and MRI-based quantification of brain shift effects subsequent to implantation of the first electrode in bilateral implantation of deep brain stimulation electrodes. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87:322–329
Huston OO, Watson RE, Bernstein MA, McGee KP, Stead SM, Gorman DA, Lee KH, Huston J (2011) Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging findings during deep brain stimulation surgery. J Neurosurg 115(4):852–857
Ito Y, Sugimoto Y, Tomioka M, Hasegawa Y, Nakago K, Yagata Y (2008) Clinical accuracy of 3D fluoroscopy-assisted cervical pedicle screw insertion. J Neurosurg Spine 9:450–453
Kelman C, Ramakrishnan V, Davies A, Holloway K (2010) Analysis of stereotactic accuracy of the cosman-robert-wells frame and nexframe frameless systems in deep brain stimulation surgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 88:288–295
Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner MJ, Stubig T, Krettek C, Hufner T (2009) Intraoperative 3D imaging: value and consequences in 248 cases. J Trauma 66:232–238
Lee MW, De Salles AA, Frighetto L, Torres R, Behnke E, Bronstein JM (2005) Deep brain stimulation in intraoperative MRI environment—comparison of imaging techniques and electrode fixation methods. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 48:1–6
Maciunas RJ, Galloway RL Jr, Latimer JW (1994) The application accuracy of stereotactic frames. Neurosurgery 35:682–694, discussion 694–685
Patil AA (2010) Stereotactic approach to the trigeminal ganglion using a stereotactic frame and intraoperative computed tomography scans: technical note. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 88:277–280
Pinsker MO, Herzog J, Falk D, Volkmann J, Deuschl G, Mehdorn M (2008) Accuracy and distortion of deep brain stimulation electrodes on postoperative MRI and CT. Zentralbl Neurochir 69:144–147
Schulder M, Spiro D (2011) Intraoperative MRI for stereotactic biopsy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 109:81–87
Shahlaie K, Larson PS, Starr PA (2011) Intraoperative computed tomography for deep brain stimulation surgery: technique and accuracy assessment. Neurosurgery 68:114–124, discussion 124
Starr PA, Christine CW, Theodosopoulos PV, Lindsey N, Byrd D, Mosley A, Marks WJ Jr (2002) Implantation of deep brain stimulators into the subthalamic nucleus: technical approach and magnetic resonance imaging-verified lead locations. J Neurosurg 97:370–387
Starr PA, Martin AJ, Larson PS (2009) Implantation of deep brain stimulator electrodes using interventional MRI. Neurosurg Clin N Am 20:193–203
Starr PA, Martin AJ, Ostrem JL, Talke P, Levesque N, Larson PS (2010) Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulator placement using high-field interventional magnetic resonance imaging and a skull-mounted aiming device: technique and application accuracy. J Neurosurg 112:479–490
Thani NB, Bala A, Swann GB, Lind CR (2011) Accuracy of postoperative computed tomography and magnetic resonance image fusion for assessing deep brain stimulation electrodes. Neurosurgery 69:207–214, discussion 214
Tilgner J, Herr M, Ostertag C, Volk B (2005) Validation of intraoperative diagnoses using smear preparations from stereotactic brain biopsies: intraoperative versus final diagnosis—influence of clinical factors. Neurosurgery 56:257–265, discussion 257–265
Tonn JC, Schichor C, Schnell O, Zausinger S, Uhl E, Morhard D, Reiser M (2011) Intraoperative computed tomography. Acta Neurochir Suppl 109:163–167
Villavicencio AT, Burneikiene S, Bulsara KR, Thramann JJ (2005) Intraoperative three-dimensional fluoroscopy-based computerized tomography guidance for percutaneous kyphoplasty. Neurosurg Focus 18:e3
Wang MY, Kim KA, Liu CY, Kim P, Apuzzo ML (2004) Reliability of three-dimensional fluoroscopy for detecting pedicle screw violations in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Neurosurgery 54:1138–1142, discussion 1142–1133
Weise LM, Schneider GH, Kupsch A, Haumesser J, Hoffmann KT (2010) Postoperative MRI examinations in patients treated by deep brain stimulation using a non-standard protocol. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:2021–2027
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weise, L., Eibach, S., Seifert, V. et al. Intraoperative 3D fluoroscopy in stereotactic surgery. Acta Neurochir 154, 815–821 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1288-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1288-2