Summary
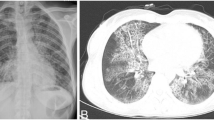
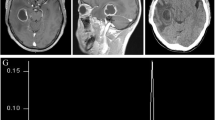
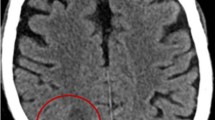
Nocardia brain abscess is a rare central nervous system (CNS) infection that carries a high mortality rate reaching 34% which is considered the highest amongst brain abscesses caused by microorganisms. All available literature is in the form of retrospective studies and small case series. In this case report the authors present a patient whose course of disease was stormy and required multiple neurosurgical procedures. The clinical outcome, long-term follow up and a review of the literature is discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baikie AG, MacDonald CB, Mundy GR (1970) Systemic nocardiosis treated with trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. Lancet 2:261 (letter)
Barnicoat MJ, Wierzbicki AS, Norman PM (1989) Cerebral nocardiosis in immuno-suppressed patients: five cases. Q J Med 72:689–691
Beaman BL, Beaman L (1994) Nocardia species host–parasite relationship. Clin Microbiol Rev 7:213–264
Beaman BL, Burnside J, Edwards B, Causey W (1976) Nocardial infections in the United States 1972–1974. J Infectious Dis 134:286–290
Curry WA (1980) Human nocardiosis. A clinical review with selected case reports. Arch Intern Med 140:818–827
Elwatidy S (2005) Bi-frontal decompressive craniotomy in a 6-month-old infant with post-traumatic refractory intracranial hypertension. Pediatr Neurosurg 41:151–154
Elwatidy S (2006) Bi-frontal decompressive craniotomy for malignant brain oedema. Neurosciences 11(4):241–247
Fleetwood IG, Embil JM, Ross IB (2000) Nocardia asteroides brain abscess in immuno-competent hosts: report of 3 cases and review of surgical recommendations. Surg Neurol 53(6):605–610
Lee GY, Daniel RT, Brophy BP, Reilly PL (2002) Surgical treatment of nocardial brain abscess. Neurosurgery 51(3):668–672
Mamelak AN, Obana WG, Flaherty JF, Rosenblum ML (1994) Nocardial brain abscess: treatment strategies and factors influencing outcome. Neurosurgery 35(4):622–628
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
This is a single case report of a patient with a cerebral Nocardia abscess complicated by ventriculitis. The infection was treated by antibiotics and aspiration of the abscess. Aggressive treatment of brain swelling and subsequent hydrocephalus lead to recovery. The report illustrates some of the hazards of this serious infection, occurring most often in immunocompromised patients, and the steps to successful treatment.
There is a good review of views about the place or timing of aspiration versus excision of abscesses.
The authors state that the patient in this report recovered with "moderate disability "according to the GOS. The details given of his state at 12 months surely place him in the "severe disability" category.
Peter Reilly
University of Adelaide
This is a detailed article on Nocardia brain abscess which covers the subject almost fully. However the primordial question that may be asked is, “Had the surgeon operated on the patient primarily and removed the abscess, without rupturing it, rather than aspirating it, would that have averted all the complications that ensued?” In fact the patient was later subjected to a more serious surgery while he was in a much more critical situation. The authors should be commended on their accurate discussion.
Professor Fuad S Haddad
American University of Beirut
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakaria, A., Elwatidy, S. & Elgamal, E. Nocardia brain abscess: severe CNS infection that needs aggressive management; case report. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150, 1097–1101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-008-0026-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-008-0026-2