Summary
Background. There is no information regarding the possible role of cerebral substrates in the pathogenesis of neuronal injury in intracerebral haemorrhages (ICHs). Purposes of this prospective study were to clarify whether changes in substrates are the consequence of the initial brain damage in ICH and to elucidate the relationship among the biochemical mechanisms and clinical course of patients with ICH.
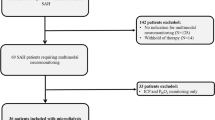
Method. During a period of two years, patients (GCS ≤8) who had ICH secondary to an aneurysm (SAH), stroke (sICH), or trauma (tICH) and underwent ventriculostomy with ICP monitoring and/or underwent cranial surgery were randomly enrolled in this study. Extracellular concentrations of glutamate, aspartate, glycine, GABA, lactate, lactate/pyruvate ratio, and glucose in the CSF were measured by use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The nitric oxide (NO) concentration in the CSF was analyzed by chemiluminescence.
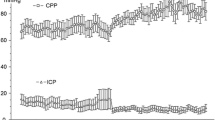
Findings. There were 75 patients (38 women and 37 men) with ICH included in this study. Twenty-one patients had SAH, 28 sICH, and 26 tICH. In tICH patients, there was a 30-fold increase in glutamate and a 10-fold in aspartate over reference values. The levels of glutamate, aspirate, GABA, lactate, glucose, and NO differed significantly among the three groups (p<0.001). There were no significant differences in glycine and L/P ratio among the groups. The initial GCS, the mean CPP and outcome six months after the insult were all significantly correlated with the concentration of substrates (p<0.01), both within groups and among the total sample. The CSF levels of glutamate lactate, NO and glucose correlated significantly with outcome (p<0.005).
Conclusions. This study confirms the correlation between the level of EAAs and the outcome of ICHs, suggesting that neurochemical monitoring of these substances may have a role in caring for patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B Alessandri E Doppenberg R Bullock J Woodward S Choi S Koura HF Young (1999) ArticleTitleGlucose and lactate metabolism after severe human head injury: influence of excitatory neurotransmitters and injury type Acta Neurochir [Suppl] 75 21–24 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXis1akt7c%3D
R Bullock A Zauner JJ Woodward J Myseros SC Choi JD Ward A Marmarou HF Young (1998) ArticleTitleFactors affecting excitatory amino acid release following severe human head injury J Neurosurg 89 507–518 Occurrence Handle9761042 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvjt1WrtA%3D%3D
FC Cheng DY Yang TH Tsai CW Lee SH Chen (2000) ArticleTitleMonitoring of extracellular pyruvate, lactate, and ascorbic acid during cerebral ischemia: a microdialysis study in awake gerbils J Chromatogr [A] 870 389–394 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXpsFKmsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00905-X
EMR Doppenberg JC Watson WC Broaddus KL Holloway HF Young R Bullock (1997) ArticleTitleIntraoperative monitoring of subtrate delivery during aneurysm and hematoma surgery: initial experience in 16 patients J Neurosurg 87 809–816 Occurrence Handle9384388 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FksVSntg%3D%3D
I Fried CL Wilson NT Maidment J Engel SuffixJr E Behnke TA Fields KA MacDonald JW Morrow L Ackerson (1999) ArticleTitleCerebral microdialysis combined with single-neuron and electroencephalographic recording in neurosurgical patients J Neurosurg 91 697–705 Occurrence Handle10507396 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvjsFagsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.1999.91.4.0697
CJ Huang PS Tsai WHT Pan JW Skimming (2005) ArticleTitleMicrodialysis for measurement of hepatic and systemic nitric oxide biosynthesis in rats Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 49 28–34 Occurrence Handle15675978 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXit1yjs70%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1399-6576.2005.00486.x
PJA Hutchinson MT O’Connell PG Al-Rawi LB Maskell R Kett-White AK Gupta HK Richards DB Hutchinson PJ Kirkpatrick JD Pickard (2000) ArticleTitleClinical cerebral microdialysis: a methodological study J Neurosurg 93 37–43 Occurrence Handle10883903 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czjvV2lsA%3D%3D
R Kanthan A Shuaib (1995) ArticleTitleClinical evaluation of extracellular amino acids in severe head trauma by intracerebral in vivo microdialysis J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 59 326–327 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2MvgsVamtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.59.3.326
A Khaldi A Zauner M Reinert JJ Woodward MR Bullock (2001) ArticleTitleMeasurement of nitric oxide and brain tissue oxygen tension in patients after severe subarachnoid haemorrhage Neurosurgery 49 33–40 Occurrence Handle11440457 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzosFynug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200107000-00005
YJ Lai EY Shen WHT Pan (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of ascorbate in microdialysis perfusion medium on the extracellular basal concentration of glutamate in rat’s striatum Neurosci Lett 279 145–148 Occurrence Handle10688050 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosVKqtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00966-0
SA Lipton PA Rosenberg (1994) ArticleTitleExcitatory amino acids as a final pathway for neurological disorders N Engl J Med 330 613–622 Occurrence Handle7905600 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVGhtbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199403033300907
A Mendelwitsch (2001) ArticleTitleMicrodialysis: intraoperative and posttraumatic applications in neurosurgery Methods 23 73–81 Occurrence Handle10.1006/meth.2000.1107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnvFKksA%3D%3D
WH Ng S Moochhala TT Yeo PL Ong PY Ng (2001) ArticleTitleNitric oxide and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Elevated levels in cerebrospinal fluid and their implications Neurosurgery 49 622–627 Occurrence Handle11523672 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvotVSqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200109000-00016
L Persson J Valtysson P Enblad (1996) ArticleTitleNeurochemical monitoring using intracerebral microdialysis in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage J Neurosurg 84 606–616 Occurrence Handle8613852 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK287otVagtg%3D%3D
AI Qureshi Z Ali MF Suri A Shuaib G Baker K Todd LR Guterman LN Hopkins (2003) ArticleTitleExtracellular glutamate and other amino acids in experimental intracerebral haemorrhage: an in vivo microdialysis study Crit Care Med 31 IssueID5 1482–1489 Occurrence Handle12771622 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlvFansbo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.CCM.0000063047.63862.99
Ai Qureshi S Tuhrim JP Broderick HH Batjer H Hondo DF Hanley (2001) ArticleTitleSpontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage N Engl J Med 344 1450–1460 Occurrence Handle11346811 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ntFGgsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM200105103441907
M Reinert A Zauner A Khaldi R Seiler R Bullock (2000) ArticleTitleMicrodialysis nitric oxide levels and brain tissue oxygen tension in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage Acta Neurochir 77 155–157
D Sadamitsu Y Kuroda T Nagamitsu R Tsuruta T Inoue T Udea K Nakashima H Ito T Maekawa (2001) ArticleTitleCerebrospinal fluid and plasma concentrations of nitric oxide metabolites in postoperative patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage Crit Care Med 29 77–79 Occurrence Handle11176164 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjslemtbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-200101000-00018
OW Sakowitz S Wolfrum AS Sarrafzadeh JF Stover JP Dreier A Dendorfer G Benndorf WR Lanksch AW Unterberg (2001) ArticleTitleRelation of cerebral energy metabolism and extacellular nitrite and nitrate concentrations in patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21 1067–1076 Occurrence Handle11524611 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnt1Snu7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004647-200109000-00004
A Sarrafzadeh D Haux O Sakowitz G Benndorf H Herzog I Kuechler A Unterberg (2003) ArticleTitleAcute focal neurological deficits in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: relation of clinical course, CT findings, and metabolite abnormalities monitored with bedside microdialysis Stroke 34 IssueID6 1382–1388 Occurrence Handle12750537 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktVKms74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1161/01.STR.0000074036.97859.02
MK Schulz LP Wang M Tange P Bjerre (2000) ArticleTitleCerebral microdialysis monitoring: determination of normal and ischemic cerebral metabolisms in patients with aneurismal subarachnoid haemorrhage J Neurosurg 93 808–814 Occurrence Handle11059662 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3crgslygsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.2000.93.5.0808
AY Schwartz S Fatima B Joshua (2000) ArticleTitleDecreased nitric oxide availability contributes to acute cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage Neurosurgery 47 208–215 Occurrence Handle10917364 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FnsV2ntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200007000-00042
EY Shen YJ Lai CS Ho YL Lee (1999) ArticleTitleExcitatory and inhibitory amino acid levels in the cerebrospinal fluids of children with neurological disorders Acta Paediatr Sin 40 65–69 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ntFagsw%3D%3D
F Staub R Graf P Gabel M Koechling N Klug WD Heiss (2000) ArticleTitleMultiple interstitial substances measured by microdialysis in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage Neurosurgery 47 1106–1116 Occurrence Handle11063103 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3crgvFOmtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200011000-00016
Y Suzuki K Osuka A Noda T Tanazawa M Takayasu M Shibuya (1997) ArticleTitleNitric oxide metabolites in the cisternal cerebral spinal fluid of patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage Neurosurgery 41 807–812 Occurrence Handle9316041 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svmtFOltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199710000-00008
M Uzan N Tanriover H Bozkus K Gumustas O Guzel C Kuday (2001) ArticleTitleNitric oxide (NO) metabolism in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with severe head injury. Inflammation as a possible cause of elevated no metabolites Surg Neurol 56 350–356 Occurrence Handle11755960 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FlslGqtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0090-3019(01)00633-4
AB Valadka JC Goodman SP Gopinath M Uzura CS Robertson (1998) ArticleTitleComparison of brain tissue oxygen tension to microdialysis-based measures of cerebral ischemia in fatally head-injured humans J Neurotrauma 15 509–519 Occurrence Handle9674554 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czjsleisw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1089/neu.1998.15.509
P Vespa M Prins E Ronn-Engstrom M Caron E Shalmon DA Hovda NA Martin DP Becker (1998) ArticleTitleIncrease in extracellular glutamate caused by reduced cerebral perfusion pressure and seizures after human traumatic brain injury: a microdialysis study J Neurosurg 89 971–982 Occurrence Handle9833824 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXotVaitLg%3D
T Yamamoto S Rossi M Stiefel E Doppenberg A Zauner R Bullock A Marmarou (1999) ArticleTitleCSF and ECF glutamate concentrations in head injured patients Acta Neurochir [Suppl] 75 17–19 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7gtFartQ%3D%3D
A Zauner EMR Doppenberg JJ Woodward SC Choi HF Young R Bullock (1997) ArticleTitleContinuous monitoring of cerebral substrate delivery and clearance: initial experience in 24 patients with severe acute brain injuries Neurosurgery 41 1082–1093 Occurrence Handle9361062 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fis12itA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199711000-00011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, MF., Chiu, WT., Lin, F. et al. Multiparametric analysis of cerebral substrates and nitric oxide delivery in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage: correlation with hemodynamics and outcome. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148, 615–621 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0771-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0771-z