Summary
Background. Blood clot evacuation through an osteoplastic craniotomy, a procedure requiring neurosurgical expertise and modern medical facilities, is the accepted method for treatment of a pure traumatic epidural haematoma following closed head injury. In certain emergency situations and/or in less sophisticated settings, however, use of this procedure may not be feasible. The present study was undertaken to ascertain whether placement of a burr hole and drainage under negative pressure constituted a rapid, effective and safe approach to manage patients with simple epidural haematomas.
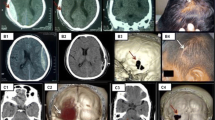
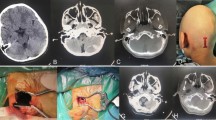
Methods. Thirteen patients suffering from a traumatic epidural haematoma were treated from January, 1999 to October, 2002. Twelve patients presented with skull fracture but no fracture was depressed. Placement of flexible tubes through a burr hole, followed by continuous suction under negative pressure, enabled aspiration of the clot and drainage of the cavity. In 8 cases, the procedure was performed under local anaesthesia with 2% Xylocaine™ and with intravenous sedation with propofol as needed. The operative procedure was accomplished within 30 min, and the drainage tube was left in place for 3–5 days. CT scans were performed daily from days 1 to 5.
Results. In 11 of 13 cases, clots were evacuated successfully and patients regained consciousness within 2 hours. Recoveries occurred without significant sequelae. In the remaining 2 cases, the drainage tube was found to be obstructed by a blood clot such that the haematoma was unaffected. A traditional craniotomy was performed within 8–12 hours, and these 2 patients recovered consciousness within the subsequent 6 hours.
Conclusion. Burr hole evacuation followed by drainage under negative pressure is a safe and effective method for emergency management of a pure traumatic epidural haematoma. To assure safety patients given this procedure should be monitored by daily CT scans. Decompressive craniotomy should be performed if consciousness does not improve within several hours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Baykaner H Alp N Cerviker S Keskil Z Seckin (1988) ArticleTitleObservation of 95 patients with extradural hematoma and review of the literature. Surg Neurol 30 339–341 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD2cvlt1w%3D Occurrence Handle3055383
GK Bejjani DJ Donahue J Rusin JD Broemeling (1996) ArticleTitleRadiologic and clinical criteria for the management of epidural hematomas in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 25 302–308 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fgs1eksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9348150
M Borzone S Gentile C Perria C Rivano M Rosa (1979) ArticleTitleVertex epidural hematomas. Surg Neurol 11 277–284 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSaC1c3hvVY%3D Occurrence Handle441913
AP Bricolo LM Pasut (1984) ArticleTitleExtradural hematoma: toward zero mortality. A prospective study. Neurosurgery 14 8–12 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiuC3MjnvVc%3D Occurrence Handle6694798
TY Chen CW Wong CN Chang TN Liu WC Cheng MD Tsai TK Lin (1993) ArticleTitleThe expectant treatment of “asymptomatic” supratentorial epidural hematomas. Neurosurgery 32 176–179 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC2szisVQ%3D Occurrence Handle8437654
JE Cohen A Montero ZH Israel (1996) ArticleTitlePrognosis and clinical relevance of anisocoria-craniotomy latency for epidural hematoma in comatose patients. J Trauma 41 120–122 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB1M7jt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle8676403
F Cordobes RD Lobato JJ Rivas MJ Munoz D Chillon JM Portillo E Lamas (1981) ArticleTitleObservations on 82 patients with extradural hematoma. Comparison of results before and after the advent of computerized tomography. J Neurosurg 54 179–186 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6D1Mrpt1E%3D Occurrence Handle7452331
R Firsching M Heimann RA Frowein (1997) ArticleTitleEarly dynamics of acute extradural and subdural hematomas. Neurol Res 19 257–260 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA3srntFU%3D Occurrence Handle9192377
J Greenberg WA Cohen PR Cooper (1985) ArticleTitleThe “hyperacute” extraaxial intracranial hematoma: computed tomographic findings and clinical significance. Neurosurgery 17 48–56 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqB28fksVY%3D Occurrence Handle4022287
O Heiskanen (1975) ArticleTitleEpidural hematoma. Surg Neurol 4 23–26 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSmD3szpvVQ%3D Occurrence Handle1166398
R Hooper (1959) ArticleTitleObservations on extradural hemorrhage. Br J Surg 47 71–879 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CC%2BC2Mrmt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle14403008
KG Jamieson JD Yelland (1968) ArticleTitleExtradural hematoma. Report of 167 cases. J Neurosurg 29 13–23 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CCeH3c7gt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle5302643
NR Jones CJ Molloy CN Kloeden JB North DA Simpson (1993) ArticleTitleExtradural hematoma: trends in outcome over 35 years. Br J Neurosurg 7 465–471 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD1M3jsVw%3D Occurrence Handle8267885
EM Kaye PR Cass E Dooling NP Rosman (1985) ArticleTitleChronic epidural hematomas in childhood: increased recognition and non-surgical management. Pediatr Neurol 1 255–259 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0887-8994(85)80013-8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaB2cnnsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle3880412
AM Malek FH Barnett MS Schwartz M Scott (1997) ArticleTitleSpontaneous rapid resolution of an epidural hematoma associated with an overlying skull fracture and subgaleal hematoma in a 17-month-old child. Pediatr Neurosurg 26 160–165 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FnvVynsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9419033
Marshall LF (1985) Neurosurgery 16: 606. Comment on Bullock R, Smith RM, Van Dellen JR (1985) Nonoperative management of extradural hematoma. Neurosurgery 16: 602–606
OF Petersen JO Espersen (1984) ArticleTitleExtradural hematomas: measurement of size by volume summation on CT scanning. Neuroradiology 26 363–367 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00327488 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimD2c%2FnvFQ%3D Occurrence Handle6544377
I Reider-Groswasser E Frishman N Razon (1991) ArticleTitleEpidural haematoma: computerized tomography (CT) parameters in 19 patients. Brain Inj 5 17–21 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B2MrovVw%3D Occurrence Handle2043903
FC Roberson PR Kishore JD Miller MH Lipper DP Becker (1979) ArticleTitleThe value of serial computerized tomography in the management of severe head injury. Surg Neurol 12 161–167 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi%2BD1c7pslU%3D Occurrence Handle515911
JM Seelig LF Marshall SM Toutant BM Toole MR Klauber SA Bowers JA Varnell (1984) ArticleTitleTraumatic acute epidural hematoma: unrecognized high lethality in comatose patients. Neurosurgery 15 617–620 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqD287oslc%3D Occurrence Handle6504278
D Weaver L Pobereskin JA Jane (1981) ArticleTitleSpontaneous resolution of epidural hematomas. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 54 248–251 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6D1MrptlM%3D Occurrence Handle7452340
K Wester (1999) ArticleTitleDecompressive surgery for “pure” epidural hematomas: does neurosurgical expertise improve the outcome? Neurosurgery 44 495–500 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7mslWitA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10069586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Tyan, Y., Lee, Y. et al. Emergency management of epidural haematoma through burr hole evacuation and drainage. A preliminary report. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148, 313–317 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0723-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0723-z