Summary
Background. Several studies have investigated the relation between intraoperative abnormal muscle response (AMR) findings and postoperative results in patients undergoing microvascular decompression (MVD) for hemifacial spasm (HFS). However, there is some debate over the reliability of AMR as an indicator of postoperative outcome. We investigated whether AMR findings obtained during MVD reflect postoperative outcome in patients with HFS.
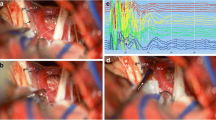
Method. Subjects were 60 HFS patients who underwent AMR monitoring during MVD. AMR recordings were obtained from the mentalis muscle by electrical stimulation of the temporal branch of the facial nerve and from the orbicularis oculi muscles by stimulation of the marginal mandibular branch. Surgical outcome was compared with AMR findings at the completion of MVD. Mean follow-up was 61 months.
Findings. HFS resolved completely in 50 patients in whom AMR disappeared intraoperatively and in 5 patients in whom the AMR amplitude was decreased at the end of MVD. Four patients showed HFS at the final follow-up examination despite cessation or decrease of AMR during surgery. In 1 patient, preoperative AMR waveforms persisted throughout MVD, but the postoperative outcome was excellent.
Conclusions. Our findings suggest that intraoperative cessation or decreased amplitude of AMR at the end of surgery indicates a high likelihood of postoperative relief of HFS. We believe that intraoperative AMR monitoring is useful in MVD surgery for HFS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GK Bejjani LN Sekhar (1997) ArticleTitleRepositioning of the vertebral artery as treatment for neurovascular compression syndromes. Technical note. J Neurosurg 86 728–732 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199709000-00086 Occurrence Handle9120641
A Esteban P Molina-Negro (1986) ArticleTitlePrimary hemifacial spasm: a neurophysiological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49 58–63 Occurrence Handle3958733
M Fukuda S Kameyama Y Honda R Tanaka (1997) ArticleTitleHemifacial spasm resulting from facial nerve compression near the internal acoustic meatus: case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 37 771–774
YA Grigoryan MZ Goncharov VV Lazebny (2000) ArticleTitleHemifacial spasm caused by a contralateral vertebral artery: case report. Surg Neurol 53 493–497 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0090-3019(00)00193-2 Occurrence Handle10874150
SJ Haines F Torres (1991) ArticleTitleIntraoperative monitoring of the facial nerve during decompressive surgery for hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 74 254–257 Occurrence Handle1988595
J Hatem M Sindou C Vial (2001) ArticleTitleIntraoperative monitoring of facial EMG responses during microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. Prognostic value for long-term outcome: a study in a 33-patient series. Br J Neurosurg 15 496–499 Occurrence Handle10.1080/02688690120105101 Occurrence Handle11814001
M Ishikawa T Ohira J Namiki Y Ajimi M Takase S Toya (1996) ArticleTitleAbnormal muscle response (lateral spread) and F-wave in patients with hemifacial spasm. J Neurol Sci 137 109–116 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-510X(95)00308-O Occurrence Handle8782163
M Ishikawa T Ohira J Namiki M Kobayashi M Takase T Kawase S Toya (1997) ArticleTitleElectrophysiological investigation of hemifacial spasm after microvascular decompression: F-waves of the facial muscles, blink reflexes, and abnormal muscle responses. J Neurosurg 86 654–661 Occurrence Handle9120630
T Isu K Kamada S Mabuchi A Kitaoka T Ito M Koiwa H Abe (1996) ArticleTitleIntra-operative monitoring by facial electromyographic responses during microvascular decompressive surgery for hemifacial spasm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138 19–23 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01411718
N Kiya U Bannur A Yamauchi K Yoshida Y Kato T Kanno (2001) ArticleTitleMonitoring of facial evoked EMG for hemifacial spasm: a critical analysis of its prognostic value. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143 365–368 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010170091
MR McLaughlin PJ Jannetta BL Clyde BR Subach CH Comey DK Resnick (1999) ArticleTitleMicrovascular decompression of cranial nerves: lessons learned after 4400 operations. J Neurosurg 90 1–8
AR Møller (1991) ArticleTitleInteraction between the blink reflex and the abnormal muscle response in patients with hemifacial spasm: results of intraoperative recordings. J Neurol Sci 101 114–123 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-510X(91)90025-3 Occurrence Handle2027024
AR Møller PJ Jannetta (1984) ArticleTitleOn the origin of synkinesis in hemifacial spasm: results of intracranial recordings. J Neurosurg 61 569–576 Occurrence Handle6086858
AR Møller PJ Janetta (1985) ArticleTitleHemifacial spasm: results of electrophysiologic recording during microvascular decompression operations. Neurology 35 969–974 Occurrence Handle4010963
AR Møller PJ Jannetta (1985) ArticleTitleMicrovascular decompression in hemifacial spasm: intraoperative electrophysiological observations. Neurosurgery 16 612–618 Occurrence Handle4000433
AR Møller PJ Jannetta (1986) ArticleTitlePhysiological abnormalities in hemifacial spasm studied during microvascular decompression operations. Exp Neurol 93 584–600 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-4886(86)90178-0 Occurrence Handle3743704
AR Møller PJ Jannetta (1987) ArticleTitleMonitoring facial EMG responses during microvascular decompression operations for hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 66 681–685 Occurrence Handle3572493
JJ Mooij MK Mustafa TW van Weerden (2001) ArticleTitleHemifacial spasm: intraoperative electromyographic monitoring as a guide for microvascular decompression. Neurosurgery 49 1365–1371 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200112000-00012 Occurrence Handle11846935
S Nagahiro A Takada Y Matsukado Y Ushio (1991) ArticleTitleMicrovascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. Patterns of vascular compression in unsuccessfully operated patients. J Neurosurg 75 388–392 Occurrence Handle1869939
VK Nielsen (1984) ArticleTitlePathophysiology of hemifacial spasm: I. Ephaptic transmission and ectopic excitation. Neurology 34 418–426 Occurrence Handle6322048
VK Nielsen (1984) ArticleTitlePathophysiology of hemifacial spasm: II. Lateral spread of the supraorbital nerve reflex. Neurology 34 427–431 Occurrence Handle6322049
VK Nielsen (1985) ArticleTitleElectrophysiology of the facial nerve in hemifacial spasm: ectopic/ephaptic excitation. Muscle Nerve 8 545–555 Occurrence Handle10.1002/mus.880080702 Occurrence Handle2995804
H Ryu S Yamamoto K Sugiyama K Uemura T Miyamoto (1998) ArticleTitleHemifacial spasm caused by vascular compression of the distal portion of the facial nerve. Report of seven cases. J Neurosurg 88 605–609 Occurrence Handle9488322
JC Shin UH Chung YC Kim CI Park (1997) ArticleTitleProspective study of microvascular decompression in hemifacial spasm. Neurosurgery 40 730–735 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199704000-00013 Occurrence Handle9092846
S Yamashita T Kawaguchi M Fukuda K Suzuki M Watanabe R Tanaka S Kameyama (2002) ArticleTitleLateral spread response elicited by double stimulation in patients with hemifacial spasm. Muscle Nerve 25 845–849 Occurrence Handle10.1002/mus.10123 Occurrence Handle12115973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, S., Kawaguchi, T., Fukuda, M. et al. Abnormal muscle response monitoring during microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 933–938 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0571-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0571-x