Summary
Background. The aim of this study was to assess if transforaminal steroid injections applied to cohort of patients waiting for cervical disc surgery, reduce the pain of cervical radiculopathy and hence reduce the need for surgical intervention.
Cervical radiculopathy due to cervical disc herniation or spondylosis is a common indication for cervical disc surgery. Surgery is however not always successful, and is not done without risk of complications.
Transforaminal injection of steroids has gained popularity due to the rationale that inflammation of the spinal nerve roots causes radicular pain, and therefore steroids placed locally should relieve symptoms.
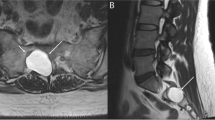
Methods. During a 12-month period, 21 secondary referral patients with unilateral cervical radiculopathy entered the study. Cervical disc herniation or spondylosis affecting the corresponding nerve root was demonstrated by appropriate investigation (MRI or myelography).
The patients then received 2 transforaminal steroid injections, at 2 weeks interval, while waiting for operative treatment.
The pain intensity (VAS), Odom’s criteria and operative indications were registered at 6 weeks and 4 months.
Findings. After receiving injection treatment 5 of the 21 patients decided to cancel the operation due to clinical improvement. A statistically significant reduction (0.02) in radicular pain score was simultaneously measured. This corresponds well with the reduction in operative requirements since radicular pain is the main indication for operative treatment. The responders experienced a long-lasting effect.
Those responding positively however improved neck pain to the same extent as radicular pain, and patients with cervical spondylosis responded as positively as those with disc herniation.
Interpetation. This prospective cohort study indicates a reduction in the need for operative treatment due to injection treatment. The clinical effect is measurable, and a statistically significant improvement of the radicular pain is registered.
Routine transforaminal injection treatment prior to surgery seems rewarding, but the complication risk must be taken into consideration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Baker P Dreyfuss S Mercer N Bogduk (2003) ArticleTitleCervical transforaminal injection of corticosteroids into a radicular artery: a possible mechanism for spinal cord injury. Pain 103 211–215 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00343-3 Occurrence Handle12749976
N Bogduk (1995) ArticleTitleSpine update. Epidural steroids. Spine 20 845–848 Occurrence Handle7701401
P Brouwers E Kottnik M Simon R Prevo (2001) ArticleTitleA cervical anterior spinal artery syndrome after diagnostic blockade of the right C6-nerve root. Pain 91 397–399 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00437-1 Occurrence Handle11275398
K Bush S Hiller (1996) ArticleTitleOutcome of cervical radiculopathy treated with periradicular/epidural corticosteroid injections: a prospective study with independent clinical review. Eur Spine J 5 319–325 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00304347 Occurrence Handle8915637
B Byrod K Olmarker S Konno K Larsen K Takahashi B Rydevik (1995) ArticleTitleA rapid transport route between the epidural space and the nerve roots. Spine 20 IssueID2 138–143 Occurrence Handle7716617
Castagnera P Maurette V Pointillart et al. (1994) ArticleTitleLong term results of cervical epidural steroid injection with and without morphine in chronic cervical radicular pain. Pain 58 239–243 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3959(94)90204-6 Occurrence Handle7816491
Shishido et al. (2002) ArticleTitleDexamethasone decreases blood flow in normal nerves and dorsal root ganglia. Spine 27 518–586 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-200203150-00005
SD Hodges RL Castleberg T Miller et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCervical epidural steroid injection with intrinsic spinal cord damage. Two case reports. Spine 23 2137–2142 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199810010-00020 Occurrence Handle9794061
A Johansson J Hao B Sjobund (1990) ArticleTitleLocal corticosteroids application blocks transmission in normal nocioceptive C fibres. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 34 335–338 Occurrence Handle2167604
HM Lee JN Weinstein ST Meller et al. (1998) ArticleTitleThe role of steroids and their effects on phospholipase A2: an animal modell of radiculopathy. Spine 23 1191–1196 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199806010-00001 Occurrence Handle9636970
L Manchikanti (1999) ArticleTitleCervical epidural steroid injection with intrinsic spinal cord damage. Spine 24 1170–1172 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199906010-00023 Occurrence Handle10361672
LL Marshall ER Trethewie CC Curtain (1973) ArticleTitleChemical irritation of nerve root in disc prolapse. Lancet 2 321–322
RF McCarron MW Wimpee PG Hudkins GS Laros (1987) ArticleTitleThe inflammatory effect of nucleus pulposus: a possible element in the pathogenesis of low back pain. Spine 12 760–764 Occurrence Handle2961088
Morvan G, Mompoint D, Bard M, Levi-Valensis G (1988) Direct intra-foraminal injection of corticosteroids in the treatment of cervico-brachial pain. In: Bard M, Laredo JD (eds) Interventional radiology in bone and joint. Springer, New York, pp 253–257
K Olmarker G Byrod M Cornefjord C Nordborg B Rydevik (1994) ArticleTitleEffects of methyl-prednisolone on nucleus pulposus-induced nerve root injury. Spine 19 1803–1808 Occurrence Handle7973978
K Olmarker RR Myers (1998) ArticleTitlePathogenesis of sciatic pain: role of herniated nucleus pulposus and deformation of spinal nerve root and dorsal root ganglion. Pain 78 99–105 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3959(98)00119-5 Occurrence Handle9839819
K Olmarker B Rydevik C Nordborg (1993) ArticleTitleAutologous nucleus pulposus induced neurophysiological and histological changes in porcine cauda equina nerve roots. Spine 18 1425–1432 Occurrence Handle8235812
K Radhakrishnan WJ Litchy WM O’Fallon LT Kurland (1994) ArticleTitleEpidemiology of cervical radiculopathy: a population-based study from Rochester, Minnesota, 1976 through 1990. Brain 2 325–335
B Rydevik M Brown G Lundborg (1984) ArticleTitlePathoanatomy and patophysiology of nerve root compression. Spine 9 7–15 Occurrence Handle6372124
JS Saal (1990) ArticleTitleThe role of inflammation in lumbar pain. Spine 16 1821–1827
P Sampath M Bendebba JD Davis T Drucker (1999) ArticleTitleOutcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy: prospective, multisenter study with independent clinical review. Spine 24 591–597 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199903150-00021 Occurrence Handle10101827
CW Slipman JS Lipetz HB Jackson DP Rogers EJ Vresilovic (2000) ArticleTitleTherapeutic selective nerve root block in the nonsurgical treatment of atraumatic cervical spondylotic radicular pain: a retrospective analysis with independent clinical review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 81 741–746 Occurrence Handle10857517
H Takahashi T Suguro Y Okazima M Motegi Y Okada T Kakiuchi (1996) ArticleTitleInflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine. Spine 21 218–224 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199601150-00011 Occurrence Handle8720407
J-N Vallee A Feydy R Carlier C Mutschler D Mompoint C Vallee (2001) ArticleTitleChronic cervical radiculopathy: lateral approach periradicular corticosteroid injection. Radiology 218 886–892 Occurrence Handle11230671
S Yabuki Y Kawaguchi C Nordborg S Kikuchi B Rydevik K Olmarker (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of lidocaine on nucleus pulposus induced nerve root injury. A neurophysiological and histologic study of the pig cauda equine. Spine 23 2383–2390 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-199811150-00004 Occurrence Handle9836351
S Yabuki S Kikuchi K Olmarker RR Myers (1998) ArticleTitleAcute effects of nucleus pulposus on blood flow and endoneurinal fluid pressure in rat dorsal root ganglia. Spine 23 2517–2523 Occurrence Handle9854750
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolstad, F., Leivseth, G. & Nygaard, O. Transforaminal steroid injections in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy. A prospective outcome study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 1065–1070 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0542-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0542-2