Summary
Background. Glioblastoma multiforme (WHO Grade IV, GBM) is the most malignant brain tumour with a mean survival time of less than one year. Betulinic acid, ceramide and TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand) represent novel therapeutic agents for potential use in GBM.
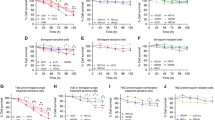
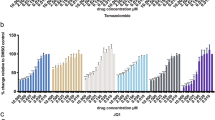
Method. Primary GBM cells of 21 patients with macroscopically complete tumour resection were tested in vitro for cell death induction by betulinic acid, ceramide, TRAIL and established therapeutics (BCNU, cisplatin, doxorubicin, vincristin and γ-irradiation).
Findings. At peak plasma concentrations (PPC), Betulinic acid, ceramide and TRAIL induced cell death in primary GBM cells at higher rates than established cytotoxic drugs. Specific cell death ≥75% was observed in 43% (9/21), 38% (8/21), and 19% (4/21) for betulinic acid, ceramide, and TRAIL respectively, while this was only found in 5% (1/21) of γ-irradiated and cisplatin-treated cells, and in none of the GBM cultures, where BCNU or vincristin were applied in PPC.
Conclusion. Due to a markedly improved cell death of GBM cells as compared with established therapeutics, Betulinic acid, ceramide and TRAIL might represent potent substances for future treatment of GBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeremias, I., Steiner, H., Benner, A. et al. Cell death induction by betulinic acid, ceramide and TRAIL in primary glioblastoma multiforme cells. Acta Neurochir 146, 721–729 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0286-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0286-4