Summary
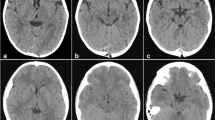
We report the case of an adult with a posttraumatic intradiploic pseudomeningocele which caused an expanded osteolytic skull lesion. Local pain and swelling, the only symptoms of the lesion, regressed after surgery. Intradiploic pseudomeningocele must be distinguished from intradiploic leptomeningeal cyst, which is of traumatic origin or arachnoid cyst and epidermoid cyst, which are of congenital origin. We also discuss the development of intradiploic pseudomeningoceleafter head trauma without skull fracture in adulthood and suggest a possible mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menkü, A., Koç, R., Tucer, B. et al. Is skull fracture necessary for developing an intradiploic pseudomeningocele as a complication of head injury in adulthood?. Acta Neurochir 146, 623–627 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0263-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0263-y