Summary
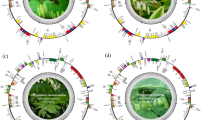
The progesterone 5β-reductase (5β-POR), a key enzyme in the cardenolide biosynthesis, was sequenced for 21 species of Digitalis and Isoplexis to infer phylogenetic and biogeographic relationships. This new secondary metabolism molecular marker was compared to the previously applied nuclear ITS and plastid trnL-F sequences. The results from separate analyses show high congruence within the genus Digitalis and support the conclusion that all species of Isoplexis have a common origin and are embedded in Digitalis. The genus Isoplexis therefore should be reduced to sectional rank within the genus Digitalis. The sequence analyses give further evidence that additional sequence data increase support for relationships. It demonstrates that poorly supported relationships in smaller data sets may lead to erroneous conclusions about the evolution of the investigated taxa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albach DC, Soltis PS, Soltis DE and Olmstead RG (2001). Phylogenetic analysis of asterids based on sequences of four genes. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 88: 163–210
Albach DC, Meudt HM and Oxelman B (2005). Piercing together the “new” Plantaginaceae. Amer J Bot 92: 297–315
APG (2003). An update of the Angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG II. Bot J Linn Soc 141: 399–436
Bocquet G and Zerbst KJ (1974). Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Gattung Digitalis L. II. Candollea 29: 251–266
Böhle U-R, Hilger HH and Martin WF (1996). Island colonization and evolution of the insular woody habit in Echium L. (Boraginaceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 11749–121745
Bräuchler C, Meimberg H and Heubl G (2004). Molecular phylogeny of the genera Digitalis L. and Isoplexis (Lindley) Loudon (Veronicaceae) based on ITS- and trnL-F sequences. Pl Syst Evol 248: 111–128
Carvalho JA and Culham A (1997). Phylogenetic and biogeographic relationships of the genera Isoplexis (Lindl.) Benth. and Digitalis L. (Scrophulariaceae—tribe Digitaleae): nuclear DNA evidence. Amer J Bot 84(6 Suppl): 180
Carvalho JA, Culham A (1998) Conservation status and preliminary results on the phylogenetics of Isoplexis (Lindl.) Benth. (Scrophulariaceae). Bol Mus Mun Funchal (Suppl 5): 109–127
Fairfield KN, Mort ME and Santos-Guerra A (2004). Phylogenetics and evolution of the Macaronesian members of the genus Aichryson (Crassulaceae) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast sequence data. Pl Syst Evol 24: 71–83
Felsenstein J (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791
Finsterbusch A, Lindemann P, Grimm R, Eckerskorn C and Luckner M (1999). Δ5-3ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Digitalis lanata Ehrh.—a multifunctional enzyme in steroid metabolism? Planta 209: 479–486
Framm JJ, Peterson A, Thoeringer C, Pangert Hornung AE, Feussner I, Luckner M and Lindemann P (2000). Cloning and functional expression in Escherichia coli of a cDNA encoding cardenolide 16′-O-glucohydrolase from Digitalis lanata Ehrh. Pl Cell Physiol 41: 1293–1298
Gärtner DE, Keilholz W and Seitz HU (1994). Eur J Biochem 225: 1125–1132
Gavidia I, del Castillo Agudo L and Perez-Bermudez P (1996). Selection and long-term cultures of high-yielding Digitalis obscura plants: RAPD markers for analysis of genetic stability. Pl Sci 121: 197–205
Gavidia I, Perez-Bermudez P and Seitz HU (2002a). Cloning and expression of two novel aldo-keto reductases from Digitalis purpurea leaves. Eur J Biochem 269: 2842–2850
Gavidia I, Seitz HU, Perez-Bermudez P and Vogler B (2002b). LC-NMR applied to the characterisation of cardiac glycosides from three micropropagated Isoplexis species. Phytochemistry 13: 266–271
Gavidia I, Tarrioi R, Rodriguez-Trelles F, Perez-Bermudes P and Seitz HU (2007). Phytochemistry 68: 853–864
Herl V, Fischer G, Mueller-Uri F and Kreis W (2006a). Molecular cloning and heterologous expression of progesterone 5β-reductase from Digitalis lanata Ehrh. Phytochemistry 67(3): 225–231
Herl V, Fischer G, Boetsch R, Mueller-Uri F and Kreis W (2006b). Molecular cloning and expression of progesterone 5β-reductase (5β-POR) from Isoplexis canariensis Planta Med 72: 1163–1165
Herl V, Frankenstein J, Meitinger N, Mueller-Uri F and Kreis W (2007). Δ5-3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) from Digitalis lanata Ehrh. Heterologous expression and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Planta Med 73: 704–710
Hinz P-A (1990). Étude biosystématique de l’agrégat Digitalis purpurea L. (Scrophulariaceae) en Méditerranée occidentale. XII. Synthese. Candollea 44: 181–199
Ivanina LI (1955). Rod Digitalis L. (Naperstyianka) i ego prakticheskoe primenenie. Acta Inst Bot Acad Sci URSS Moskau Ser 1 11: 198–302
Kandzia R, Grimm R, Eckerskorn C, Lindemann P and Luckner M (1998). Purification and characterization of lanatoside 15′-O-acetylesterase from Digitalis lanata Ehrh. Planta 204: 383–389
Kim SC, Crawford DJ, Francisco-Ortega J and Santos-Guerra A (1996). A common origin for woody Sonchus and five related genera in the Macaronesian islands: Molecular evidence for extensive radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 93: 7743–7748
Kreis W, Hensel A and Stuhlemmer U (1998). Cardenolide biosynthesis in foxglove. Planta Med 64: 491–499
Lindemann P, Finsterbusch A, Pangert A, Luckner M (2000) Partial cloning of a Δ5-3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Digitalis lanata. In: Okamoto M, Ishimura Y, Nawata H (eds) Molecular Steroidogenesis, Proceedings Yamada Conference LII. Universal Academy Press, Frontiers Science Series 29, vol XXIV. Tokyo, Japan, pp 333–334
Linné von C (1753) Species plantarum, Stockholm
Luckner M, Wichtl M (2000) Luckner M, Wichtl M (eds) Digitalis, WVGmbH Stuttgart
Metzner M, Ruecknagel K-P, Knudsen J, Kuellertz G, Mueller-Uri F and Diettrich B (2000). Isolation and characterization of two acyl-CoA-binding proteins from proembryogenic masses of Digitalis lanata Ehrh. Planta 210: 683–685
Moore MJ, Francisco-Ortega J, Santos-Guerra A and Jansen RK (2002). Chloroplast DNA evidence for the roles of island colonization and extinction in Tolpis (Asteraceae: Lactuceae). Amer J Bot 89: 518–526
Müller-Uri F and Reva VA (2000). Ehrh Pharm Pharm Lett 10: 5–7
Nebauer SG, del Castillo-Agudo L and Segura J (2000). An assessment of genetic relationships within the genus Digitalis based on PCR-generated RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 100: 1209–1216
Olmstead RG and Reeves PA (1995). Evidence for the polyphyly of the Scrophulariaceae based on chloroplast rbcL and ndhF sequences. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 82: 176–193
Olmstead RG, de Pamphilis CW, Wolfe AD, Young ND, Elisons WJ and Reeves PD (2001). Disintegration of the Scrophulariaceae. Amer J Bot 88: 348–361
Oxelman B, Kornhall P, Olmsted RG and Bremer B (2005). Further disintegration of Scrophulariaceae. Taxon 54(2): 411–425
de Perez Paz J and Roca A (1982). Estudio palinologico preliminar del genero macronesico Isoplexis Lindl. (Scrophulariaceae) y la seccion Frutescentes Benth. De Digitalis L. Bot Macarones 10: 93–107
Pichersky E and Gang DR (2000). Genetics and biochemistry of secondary metabolites in plants: an evolutionary perspective. Pl. Sci 5(10): 439–445
Sales E, Nebauer SG, Mus M and Segura J (2001). Population genetic study in the Balearic endemic plant species Digitalis minor (Scrophulariaceae) using RAPD markers. Amer J Bot 88: 1750–1759
Schaller F (1998) In vitro-Kultivierung von Isoplexis canariensis (L.) Lindl. ex G. Don und Untersuchungen zum Cardenolidgehalt. Dissertation, FAU Erlangen
Scholze C, Peterson A, Diettrich B and Luckner M (1999). Cyclophilin isoforms from Digitalis lanata. Sequences and expression during embryogenesis and stress. Pl Physiol 155: 212–219
Seitz HU and Gärtner DE (1994). Enzymes in cardenolide-accumulating shoot cultures of Digitalis purpurea L. Pl Cell Tiss Org 38: 337–344
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Sinauer Associates, Sutherland. Massachusetts
Templeton AR (1983). Phylogenetic inference from restriction site endonuclease cleavage site maps with particular reference to the humans and apes. Evolution 37: 221–233
Werner K (1965) Taxonomie und Phylogenie der Gattungen Isoplexis (LINDL.) BENTH. und Digitalis L. Feddes Repert indel. Benth. spec nov 70: 109–135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herl, V., Albach, D.C., Müller-Uri, F. et al. Using progesterone 5β-reductase, a gene encoding a key enzyme in the cardenolide biosynthesis, to infer the phylogeny of the genus Digitalis . Plant Syst Evol 271, 65–78 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0616-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0616-0