Abstract
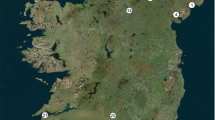
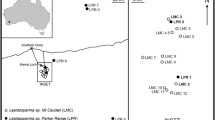
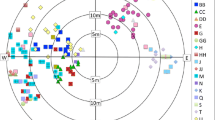
Sub-arctic willow scrub is an endangered habitat in Britain, and typically occurs on steep crags inaccessible to grazing animals. These willows can reproduce both sexually and asexually, although the relative importance of each is unknown. Knowledge of reproductive mode is important for the design of grazing management and restoration programmes. Accordingly, clonality was assessed in the largest stand of sub-arctic willow scrub in the UK, focusing on Salix lanata and S. lapponum. Little evidence of clonal growth was detected; most individuals possessed distinct multi-locus genotypes. Thus despite the capacity for vegetative reproduction, and seedlings being rarely observed, sexual reproduction is the predominant means of perpetuation and dispersal at this site. We also examined clonal growth in a common willow species (Salix herbacea) that occupies a different habitat type (exposed mountain tops and ridges). Multiple individuals shared identical genotypes up to 7 m apart, suggesting an important role for clonal growth in local patch formation in this species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beerling DJ (1998). Biological flora of the British Isles No. 202 Salix herbacea L. J Ecol 86: 872–895
Bengtsson BO (2003). Genetic variation in organisms with sexual and asexual reproduction. J Evol Biol 16: 189–199
Bradshaw T (2002) Personal communication, Biological Science, department of Biology, Plant laboratory, Box 355325, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195
Cheffings CM, Farrell L (eds) Dines TD, Jones RA, Leach SJ, Mckean DR, Pearman DA, Preston CD, Rumsey FJ, Taylor I (2005) The vascular plant Red Data list for Great Britain. Species Status. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough 7: 1–116
Douhovnikoff V and Dodd RS (2003). Intra-clonal variation and a similarity threshold for identification of clones: application to Salix exigua using AFLP molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 106: 1307–1315
Douhovnikoff V, Mcbride JR and Dodd RS (2005). Salix exigua clonal growth and population dynamics in relation to disturbance regime variation. Ecology 86: 446–452
Elven R and Karlsson T (2000). Salicaceae. In: Jonsell, B (eds) Flora Nordica 1. Lycopodiaceae – Polygonaceae, pp 118–195. Bergius Foundation, Stockholm
Eriksson O (1989). Seedling dynamics and life histories in clonal plants. Oikos 55: 231–238
Forrest A, Hollingsworth ML, Hollingsworth PM, Sydes C and Bateman RM (2004). Population genetic structure in European populations of Spiranthes romanzoffiana set in the context of other published studies on the Orchidaceae. Heredity 92: 218–227
Forrest AD (2006) Hybridisation in sub-arctic willows. PhD Thesis, University of Edinburgh and Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh
French GC, Corner RWM, Roberts FJ and Hollingsworth PM (2005). Clonal diversity in two recently discovered English populations of Carex vaginata Tausch (Cyperaceae). Watsonia 25: 389–395
Goudet J (2002) FSTAT, a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices (version 2.9.3.2). http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.htm
Lian C, Oishi R, Miyashita N, Nara K, Nakaya H, Wu B, Zhou Z and Hogetsu T (2003). Genetic structure and reproduction dynamics of Salix reinii during primary succession on Mount Fuji, as revealed by nuclear and chloroplast microsatellite analysis. Molec Ecol 12: 609–618
Mardon DK (1991). Conservation of montane willow scrub in Scotland. Trans Bot Soc Edinburgh 45: 427–436
Mardon DK (2003). Conserving montane willow scrub on Ben Lawers NNR. Bot J Scotland 55: 189–203
Marriot RW (1999). Salix lanata L. (Salicaceae). In: Wigginton, MJ (eds) British Red Data Books 1: Vascular plants, pp 323–324. JNCC, Peterborough
Mcleod CR, Yeo M, Brown AE, Burn AJ, Hopkins JJ, Way SF (2005) The habitats directive: selection of Special Areas of Conservation in the UK. 2nd edn. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough. www.jncc.gov/SACselection
McVean DN and Ratcliffe DA (1962). Plant communities of the Scottish Highlands. HMSO, London
Meirmans PG and Van-Tienderen PH (2004). GENOTYPE and GENODIVE: two programs for the analysis of genetic diversity of asexual organisms. Molec Ecol Notes 4: 792–794
Parks SDE (2001) Trypanotolerance in West African cattle and the population genetic effects of selection. PhD thesis, University of Dublin
Preston CD, Pearman DA and Dines TD (2002). New Atlas of the British & Irish Flora. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Shaw RF (2006) Plant-herbivore interactions in montane willow communities. PhD Thesis, University of Aberdeen
Stace CA (1997). New Flora of the British Isles, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Stamati K, Blackie S, Brown JWS and Russell J (2003). A set of polymorphic SSR loci for sub-arctic willow (S. lanata, S. lapponum, and S. herbacea). Molec Ecol Notes 3: 280–282
Stenberg P, Lundmark M and Saura A (2003). MLGsim: a program for detecting clones using a simulation approach. Molec Ecol Notes 3: 329–331
UK Biodiversity Group (1998) Woolly Willow (Salix lanata). Tranche 2 Action Plans, Volume 1: Vertebrates and vascular plants, English Nature, Peterborough, p 221
Widén B, Cronberg N and Widén M (1994). Genotypic diversity, molecular markers and the spatial distribution of genets in clonal plants: a literature survey. Folia Geobot Phytotax 29: 245–263
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stamati, K., Hollingsworth, P. & Russell, J. Patterns of clonal diversity in three species of sub-arctic willow (Salix lanata, Salix lapponum and Salix herbacea). Plant Syst. Evol. 269, 75–88 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0578-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0578-2