Abstract.
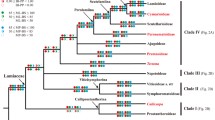
A phylogenetic analysis of the ‘core’ Laureae (Litsea complex) was conducted using the chloroplast gene matK and nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS sequences to investigate generic relationships and boundaries within the complex. Despite low genetic divergence for matK, rooting of the tree with Sassafras resulted in Iteadaphne as the basal member of the complex and five resolved clades: a Neolitsea clade and then Laurus, Parasassafras, Litsea and Lindera clades in a large polytomy with unresolved Lindera sections plus Umbellularia. A combined analysis of the data (identical to the ITS results) provided a more resolved phylogeny of the Laureae, with four major lineages: the Laurus, Litsea, Lindera and Actinodaphne II clades. These clades also appear to reflect the importance of inflorescence structure and ontogeny within the Laureae, as well as data from cuticular micromorphology, but there was no support for traditional generic characters such as 2- versus 4- celled anthers. As a result, genera such as Actinodaphne, Litsea, Neolitsea and Lindera were polyphyletic in all analyses. Parasassafras was related to Sinosassafras by the matK data, but distant from it in the ITS and combined analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Christophel, D., Conran, J. et al. Phylogenetic relationships within the ‘core’ Laureae (Litsea complex, Lauraceae) inferred from sequences of the chloroplast gene matK and nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS regions. Plant Syst. Evol. 246, 19–34 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-003-0113-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-003-0113-z