Abstract.
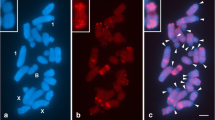
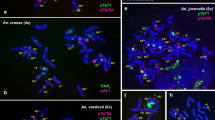
The present study analyzed the distribution pattern of the Ae. speltoides–derived repetitive clone pGc1R-1 in the Triticum/Aegilops complex. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis showed that clone pGc1R-1 is a S-genome-specific repetitive sequence that hybridized to the S-genome of three species in the section Sitopsis, Aegilops speltoides (S), Ae. longissima (Sl), and Ae. sharonensis (Ssh), but not to Ae. bicornis (Sb) and Ae. searsii (Ss), nor to any other diploid Aegilops species. This clone also hybridized to the very closely related G-genome of T. timopheevii subsp. armeniacum and T. timopheevii ssp. timopheevii, but not to the B-genome of T. turgidum and T. aestivum. Hybridization also was observed in the polyploid Aegilops species, Ae. kotschyi (UkSk), Ae. peregrina (UpSp), and Ae. vavilovii (XvaDvaSva). Large inter- and intraspecific variations were observed. Our results confirm that the S genome is related more to the Sl and Ssh genomes than to the Sb and Ss genomes; there is a greater affinity between the G and S genomes than between the B and S genomes. Mechanisms to account for the variation in the FISH pattern with different genomes include sequence amplification and deletion. Variation in the distribution of this genome-specific DNA sequence, pGc1R-1, on chromosomes can be used to reveal evolutionary relationships in the Triticum and Aegilops complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received April 10, 2002; accepted July 12, 2002 Published online: November 28, 2002
Address of the authors: Peng Zhang, Bernd Friebe (e-mail: friebe@ksu.edu), Bikram S. Gill, Wheat Genetics Resource Center, Department of Plant Pathology, 4024 Throckmorton, Plant Sciences Center, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS 66506-5502, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Friebe, B. & Gill, B. Variation in the distribution of a genome-specific DNA sequence on chromosomes reveals evolutionary relationships in the Triticum and Aegilops complex. Plant Syst. Evol. 235, 169–179 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-002-0224-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-002-0224-y