Abstract
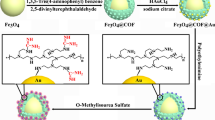
A Ti4+ functionalized β-cyclodextrin covalent organic framework nanoparticle (named as β-CD-COF@Ti4+) was synthesized using a one-pot method successfully realizing the enrichment of phosphorylated peptides and exosomes based on the immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography strategy. The functionalized β-CD-COF@Ti4+ exhibited superior performance on the enrichment of phosphopeptides, including high selectivity (1:1000), low detection limit (0.5 fmol), and loading capacity for phosphopeptides (100 mg·g−1). After treatment with β-CD-COF@Ti4+, 9 phosphopeptides from defatted milk, 29 phosphopeptides related to 23 phosphoproteins from normal group serum, and 24 phosphopeptides related to 22 phosphoproteins from the serum of uremia patients were captured. Through the analysis of Gene Ontology, the captured phosphoprotein is closely related to kidney disease, including lipoprotein metabolism, very-low-density lipoprotein particle, high-density lipoprotein particle, and lipid binding activity process. Furthermore, western blot verification showed that this nanoparticle could successfully capture exosomes from human serum. This study demonstrates great prospects for the enrichment of phosphopeptides and exosomes from actual bio-samples.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data is within the figures and supporting information.
References
Zhu J, Liu ZX, Wang L, Jin QS, Zhao YP, Du AT, Ding N, Wang Y, Jiang H, Zhu L (2022) Exosome mimetics-loaded hydrogel accelerates wound repair by transferring functional mitochondrial proteins. Front Bioeng Biotech 10:866505. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.866505
Wang BC, Xie ZH, Ding CF, Deng CH, Yan YH (2023) Recent advances in metal oxide affinity chromatography materials for phosphoproteomics. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 158:116881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116881
Zhang N, Sun NR, Deng CH (2021) Rapid isolation and proteome analysis of urinary exosome based on double interactions of Fe3O4@TiO2-DNA aptamer. Talanta 221:121571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121571
Saraswat M, Joenvaara S, Musante L, Peltoniemi H, Holthofer H, Renkonen R (2015) N-linked (N-) glycoproteomics of urinary exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 14:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.040345
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, LeBleu VS, Mittendorf EA, Weitz J, Rahbari N, Reissfelder C, Pilarsky C, Fraga MF, Worms DP, Kalluri R (2015) Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 523:177–U82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14581
Donoso-Quezada J, Ayala-Mar S, Gonzaez-Valdez J (2021) The role of lipids in exosome biology and intercellular communication: function, analytics and applications. Traffic 22:204–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12803
Kimiz-Gebologlu I, Oncel SS (2022) Exosomes: large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release 347:533–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.027
Iraci N, Leonardi T, Gessler F, Vega B, Pluchino S (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: physiological role and signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. Int J Mol Sci 17:171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020171
Wang BC, Liu B, Yan YH, Tang KQ, Ding CF (2019) Binary magnetic metal-organic frameworks composites: a promising affinity probe for highly selective and rapid enrichment of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186:832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3916-5
Xu ZX, Wu YL, Hu XF, Deng CH, Sun NR (2022) Inherently hydrophilic mesoporous channel coupled with metal oxide for fishing endogenous salivary glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Chin Chem Lett 33:4695–4699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.12.069
Zhang N, Sun NR, Deng CH (2020) A hydrophilic magnetic MOF for the consecutive enrichment of exosomes and exosomal phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 56:13999–14002. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cc06147f
Ogami K, Suzuki HI (2021) Nuclear RNA exosome and pervasive transcription: dual sculptors of genome function. Int J Mol Sci 22:13401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413401
Zhang N, Hu XF, Chen HL, Deng CH, Sun NR (2021) Specific enrichment and glycosylation discrepancy profiling of cellular exosomes using a dual-affinity probe. Chem Commun 57:6249–6252. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc01530c
Sun NR, Yu HL, Wu H, Shen XZ, Deng CH (2021) Advanced nanomaterials as sample technique for bio-analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 135:116168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116168
Du JL, Tian HH, Fu MY, Yan YH, Wang C, Ding CF (2022) Post-modified porous hollow nanospheres incorporating multiple strategies for comprehensive phosphoproteomics analysis of serum of Alzheimer’s disease. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 341:112066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.112066
Hu XF, Li YL, Miao AZ, Deng CH (2020) Dual metal cations coated magnetic mesoporous silica probe for highly selective capture of endogenous phosphopeptides in biological samples. Microchim Acta 187:7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04323-6
Jia SC, Tang RZ, Zhang S, Gao Z, Gong BL, Ma SJ, Ou JJ (2022) Design and fabrication of reusable core-shell composite microspheres based on nanodiamond for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 189:124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05234-4
Fang XW, Liu XG, Sun NAR, Deng CH (2021) Enhanced specificity of bimetallic ions via mesoporous confinement for phosphopeptides in human saliva. Talanta 233:122587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122587
Wang B, Wang BC, Feng QS, Fang X, Dai XH, Yan YH, Ding CF (2022) Magnetic guanidyl–functionalized covalent organic framework composite: a platform for specific capture and isolation of phosphopeptides and exosomes. Microchim Acta 189:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05394-3
Wu YL, Sun NR, Deng CH (2020) Construction of magnetic covalent organic frameworks with inherent hydrophilicity for efficiently enriching endogenous glycopeptides in human saliva. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:9814–9823. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22601
Wang XH, Wu JQ, Liu X, Qiu X, Cao LQ, Ji YB (2022) Enhanced chiral recognition abilities of cyclodextrin covalent organic frameworks via chiral/achiral functional modification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:25928–25936. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c05572
Lu SY, Wang SL, Wu PA, Wang DQ, Yi JC, Li L, Ding P, Pan HZ (2021) A composite prepared from covalent organic framework and gold nanoparticles for the electrochemical determination of enrofloxacin. Adv Powder Technol 32:2106–2115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.04.025
Wang XH, Yu JL, Yang HD, Shen J, Liu HL, Zhou JH (2021) A new Ti-based IMAC nanohybrid with high hydrophilicity and enhanced absorption capacity for the selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Chromatogr B 1179:122851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122851
Wei HX, Chen JY, Wang SL, Fu FH, Zhu X, Wu CY, Liu ZJ, Zhong GX, Lin JH (2019) A nanodrug consisting of doxorubicin and exosome derived from mesenchymal stem cells for osteosarcoma treatment in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine 14:8603–8610. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S218988
Wang ZZ, Wei BB, Chen Z, Zhu HW, Shen GP, Feng JH (2018) H-1 nuclear magnetic resonance-based investigation of uremia by metabolomic analysis. Chin J Anal Chem 46:1415–1423. https://doi.org/10.11895/j.issn.0253.3820.181286
Telci A, Salmayenli N, Aydin AE, Yamaner S, Sivas A, Eldegez U (1992) Serum lipids and apolipoprotein concentrations and plasma fibronectin concentrations in renal transplant patients. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 30:847–850. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm.1992.30.12.847
Bergesio F, Monzani G, Ciuti R, Pinzani P, Fiaschi N, Priami F, Cirami C, Ciccarelli C, Salvadori M (1998) Total antioxidant capacity (TAC): is it an effective method to evaluate the oxidative stress in uraemia? J Biolumin Chemilumin 13:315–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1271(1998090)13:5<315::AID-BIO491>3.0.CO;2-6
Amadottir M, Dallongeville J, Fruchart JC, NilssonEhle P (1996) Very-low-density lipoprotein of uremic patients is a poor substrate for bovine lipoprotein lipase in vitro. Metab Clin Exp 45:686–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-0495(96)90132-8
Kaesler N, Schreibing F, Speer T, de la Puente-Secades S, Rapp N, Drechsler C, Kabgani N, Kuppe C, Boor P, Jankowski V, Schurgers L, Kramann R, Floege J (2022) Altered vitamin K biodistribution and metabolism in experimental and human chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 101:338–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.10.029
Mirjam S, Markus T, van der Markus G (2015) High-density lipoprotein: structural and functional changes under uremic conditions and the therapeutic consequences. Handb Exp Pharmacol 224:424–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09665-0_13
Moestrup SK, Nielsen LB (2005) The role of the kidney in lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 16:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mol.0000169350.45944.d4
Wu YL, Zhang N, Wu H, Sun NR, Deng CH (2021) Magnetic porous carbon-dependent platform for the determination of N-glycans from urine exosomes. Microchim Acta 188:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04728-x
Liu ZQ, Zhang XG, Yu QG, He JJ (2014) Exosome-associated hepatitis C virus in cell cultures and patient plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 455:218–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.146
Kim JY, Rhim WK, Yoo YI, Kim D, Ko KW, Heo Y, Park CG, Han DK (2021) Defined MSC exosome with high yield and purity to improve regenerative activity. J Tissue Eng 14:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.040345
Lv YN, Chen J, Hu JF, Qian YS, Kong Y, Fu LS (2021) Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA-mediated exosome release via regulation of the rho-associated kinase 1/myosin light chains/actin pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:598592. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.598592
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY22B050008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 4746 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhang, X., Wang, B. et al. Ti4+ functionalized β-cyclodextrin covalent organic framework as a new immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform for selective capture of phosphorylated peptides and exosomes. Microchim Acta 190, 399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05952-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05952-3