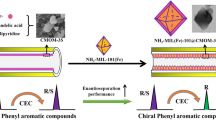
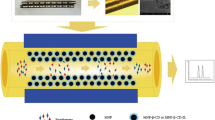
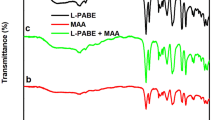
Abstract
A novel chiral molecularly imprinted polymer TiO2 nanoparticle was synthesized in one step for the enantioseparation of phenylalanine in coated capillary electrochromatography. To the author’s knowledge, the chiral molecularly imprinted nanomaterials have still not been reported, to date. Chiral molecularly imprinted TiO2 nanomaterials (L-PHE@MIP(APTES-TEOS)@TiO2) were used as a chiral stationary phase to separate the phenylalanine enantiomers in coated capillary electrochromatography (CEC). The imprinted coating was prepared from L-phenylalanine (L-PHE) as the template, TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) as the support substrate, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) as the functional monomer, and tetraethyl silicate (TEOS) as the cross-linker. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) were used for the characterization of the L-PHE@MIP(APTES-TEOS)@TiO2@capillary. Fourier transform infrared spectra (FT-IR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were employed for the characterization of the L-PHE@MIP(APTES-TEOS)@TiO2. The effects of the applied voltage, pH value, buffer concentration, and acetonitrile content were investigated experimentally to determine the optimum conditions for CEC. The best resolution for phenylalanine enantiomers by CEC reached a value of 3.48. In addition, the specific recognition effect of L-PHE@MIP(APTES-TEOS)@TiO2 on PHE enantiomers was studied by selective experiment. Finally, adsorption kinetic research, adsorption equilibrium isotherm study, and adsorption thermodynamic experiment were carried out to investigate the separation mechanism of PHE enantiomers with the L-PHE@MIP (APTES-TEOS)@TiO2@capillary, and the results were consistent with those of CEC experiments.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Zhou J, Sheth S, Zhou H, Song Q (2020) Highly selective detection of l-Phenylalanine by molecularly imprinted polymers coated Au nanoparticles via surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Talanta 211:120745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120745
Romero AG, Darlington WH, McMillan MW (1997) Synthesis of the selective D2 receptor agonist PNU-95666E from D-phenylalanine using a sequential oxidative cyclization strategy. J Org Chem 62:6582–6587. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo970526a
Tang S, Wu X, Zhao P, Tang K, Chen Y, Fu J, Lei H, Yang Z, Zhang Z (2022) Ratiometric fluorescence capillary sensor-integrated molecular imprinting for simultaneous detection of two biological indicators of Parkinson’s disease. Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03926
Feng L, Wang H, Feng T, Yan B, Yu Q, Zhang J, Guo Z, Yuan Y, Ma C, Liu T (2022) In situ synthesis of uranyl-imprinted nanocage for selective uranium recovery from seawater. Angewandte Chemie 134:e202101015. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202101015
Shah NS, Thotathil V, Zaidi SA, Sheikh H, Mohamed M, Qureshi A, Sadasivuni KK (2022) Picomolar or beyond limit of detection using molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors: a review. Biosensors 12:1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121107
BelBruno JJ (2018) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 119:94–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Liu CY, Lin CC (2004) An insight into molecularly imprinted polymers for capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 25:3997–4007. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200406160
Mu LN, Wei ZH, Liu ZS (2015) Current trends in the development of molecularly imprinted polymers in CEC. Electrophoresis 36:764–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201400389
Katz A, Davis ME (2000) Molecular imprinting of bulk, microporous silica. Nature 403:286–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002032
Zaidi SA, Cheong WJ (2009) Preparation of an open-tubular capillary column with a monolithic layer of S-ketoprofen imprinted and 4-styrenesulfonic acid incorporated polymer and its enhanced chiral separation performance in capillary electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 1216:2947–2952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.015
Akgönüllü S, Yavuz H, Denizli A (2017) Preparation of imprinted cryogel cartridge for chiral separation of l-phenylalanine. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 45:800–807. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1175445
Xie X, Pan X, Han S, Wang S (2015) Development and characterization of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective enrichment of endocrine disrupting chemicals in water and milk samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:1735–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8425-0
Zhang H (2020) Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv Mater 32:1806328. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201806328
Zhai J, Zhao M, Cao X, Li M, Zhao M (2018) Metal-ion-responsive bionanocomposite for selective and reversible enzyme inhibition. J Am Chem Soc 140:16925–16928. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b10848
Zhang J, Qin L, Yang Y, Liu X (2021) Porous carbon nanospheres aerogel based molecularly imprinted polymer for efficient phenol adsorption and removal from wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 274:119029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119029
Cao Y, Huang Z, Luo L, Li J, Li P, Liu X (2021) Rapid and selective extraction of norfloxacin from milk using magnetic molecular imprinting polymers nanoparticles. Food Chem 353:129464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129464
Cui F, Zhou Z, Zhou HS (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers and surface imprinted polymers based electrochemical biosensor for infectious diseases. Sensors 20:996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040996
Zhang W, Li Y, Wang Q, Wang C, Wang P, Mao K (2013) Performance evaluation and application of surface-molecular-imprinted polymer-modified TiO2 nanotubes for the removal of estrogenic chemicals from secondary effluents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1431–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0983-0
Yuan W, Zhu B, Li X-Y, Hansen TW, Ou Y, Fang K, Yang H, Zhang Z, Wagner JB, Gao Y (2020) Visualizing H2O molecules reacting at TiO2 active sites with transmission electron microscopy. Science 367:428–430. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay2474
Ma X, Kan Z, Du Y, Yang J, Feng Z, Zhu X, Chen C (2019) Enantioseparation of amino alcohol drugs by nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis with a maltobionic acid-based ionic liquid as the chiral selector. Analyst 144:7468–7477. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN01162E
Tang S, Wu X, Zhao P, Tang K, Chen Y, Fu J, Zhou S, Yang Z, Zhang Z (2022) A near-infrared fluorescence capillary imprinted sensor for chiral recognition and sensitive detection of l-histidine. Anal Chim Acta 1206:339794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339794
Bao T, Tang P, Mao Z, Chen Z (2016) An immobilized carboxyl containing metal-organic framework-5 stationary phase for open-tubular capillary electrochromatography. Talanta 154:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.089
Wang M, Wen B, Fan B, Zhang H (2020) Study on adsorption mechanism of silicate adsorbents with different morphologies and pore structures towards formaldehyde in water. Colloids Surf: A Physicochem Eng Aspects 599:124887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124887
Wang H, Huang F, Zhao Z-L, Wu R-R, Xu W-X, Wang P, Xiao R-B (2021) High-efficiency removal capacities and quantitative adsorption mechanisms of Cd2+ by thermally modified biochars derived from different feedstocks. Chemosphere 272:129594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129594
Song X, Liu D, Zhang G, Frigon M, Meng X, Li K (2014) Adsorption mechanisms and the effect of oxytetracycline on activated sludge. Biores Technol 151:428–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.055
Bandura L, Franus M, Madej J, Kołodyńska D, Hubicki Z (2020) Zeolites in phenol removal in the presence of Cu (II) ions—comparison of sorption properties after chitosan modification. Materials 13:643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030643
Lin J-M, Nakagama T, Wu X-Z, Uchiyama K, Hobo T (1997) Capillary electrochromatographic separation of amino acid enantiomers with molecularly imprinted polymers as chiral recognition agents. Fresenius J Anal Chem 357:130–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050126
Wang X-N, Liang R-P, Meng X-Y, Qiu J-D (2014) One-step synthesis of mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted magnetic polymer as stationary phase for chip-based open tubular capillary electrochromatography enantioseparation. J Chromatogr A 1362:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.044
Song W-F, Zhao Q-L, Zhou X-J, Zhang L-S, Huang Y-P, Liu Z-S (2019) A star-shaped molecularly imprinted polymer derived from polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes with improved site accessibility and capacity for enantiomeric separation via capillary electrochromatography. Microchim Acta 186:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3151-5
Derazshamshir A, Göktürk I, Yılmaz F, Denizli A (2021) S-citalopram imprinted monolithic columns for capillary electrochromatography enantioseparations. Electrophoresis 42:2672–2682. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.202100222
Funding
This work was supported by the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82073809).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xu, G., Chen, J. et al. One-step synthesis of chiral molecularly imprinted polymer TiO2 nanoparticles for enantioseparation of phenylalanine in coated capillary electrochromatography. Microchim Acta 190, 279 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05854-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05854-4