Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA), as a typical endocrine disruptor, poses a serious threat to human health. Therefore, it is urgent to establish a rapid, sensitive, and simple method for the determination of BPA. In this paper, based on the aptamer-mediated single-atom Fe carbon dot catalyst (SAFe) catalyzing the HAuCl4-ethylene glycol (EG) nanoreaction, a new SERS/RRS di-mode detection method for BPA was established. The results show that SAFe exhibits a strong catalytic effect on the HAuCl4-EG nanoreaction, which could generate purple gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) signals and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effects. After the addition of BPA aptamer (Apt), it could encapsulate SAFe through intermolecular interaction, thus inhibiting its catalytic action, resulting in the reduction of AuNPs generated and the decrease of RRS and SERS signals of the system. With the addition of BPA, Apt was specifically combined with BPA, and SAFe was re-released to restore the catalytic ability; the generated AuNPs increased. As a result of this RRS and SERS signals of the system recovered, and their increment was linear with the concentration of BPA. Thus, the quantification of 0.1–4.0 nM (RRS) and 0.1–12.0 nM (SERS) BPA was realized, and the detection limits were 0.08 nM and 0.03 nM, respectively. At the same time, we used molecular spectroscopy and electron microscopy to study the SAFe-HAuCl4-ethylene glycol indicator reaction, and proposed a reasonable SAFe catalytic reaction mechanism.
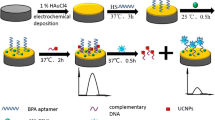
Graphical abstract

Based on Apt-mediated SAFe catalysis gold nanoreaction amplification, a SERS/RRS di-mode analytical platform was established for targets such as BPA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostovar B, Cai Y, Ahmadivand A et al (2020) Increased intraband transitions in smaller gold nanorods enhance light emission. ACS Nano 14:15757–15765
Hack D, Deckers K, Chauhan P et al (2016) Asymmetric synthesis of spiropyrazolones by sequential organo- and silver catalysis. Angew Chem 128:1829–1832
Cai Y, Bhattacharjee U, Zhang R et al (2019) Single-particle emission spectroscopy resolves d-hole relaxation in copper nanocubes. ACS Energy Lett 4:2458–2465
Renard D, Tian S, Ahmadivand A et al (2019) Polydopamine stabilized aluminum nanocrystals: aqueous stability and benzo[a]pyrene detection. ACS Nano 13(3):3117-3124. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b08445
Okumura S, Komine T, Shigeki E, Semba K, Nakao Y (2018) Site-selective linear alkylation of anilides by cooperative nickel/aluminum catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:929–932
Nie L, Mei D, Xiong H, Peng B, Ren Z, Hernandez XIP, DeLaRiva A, Wang M, Engelhard MH, Kovarik L, Datye AK, Wang Y (2017) Activation of surface lattice oxygen in single-atom Pt/CeO2 for low-temperature CO oxidation. Science 358:1419–1423
Huang W, Wang G, Li W, Li T (2020) Porous ligand creates new reaction route: bifunctional single-atom palladium catalyst for selective distannylation of terminal alkynes. Chem 6:1–14
Chen Z, Vorobyeva E, Mitchell S, Fako E, Ortuño MA, López N, Collins SM, Midgley PA, Richard S, Vilé G, Pérez-Ramírez J (2018) A heterogeneous single-atom palladium catalyst surpassing homogeneous systems for Suzuki coupling. Nature Nanotech 13:702–707
Hou T, Peng H, Xin Y, Wang S, Zhu W, Chen L, Yao Y, Zhang W, Liang S, Wang L (2020) Fe single-atom catalyst for visible-light-driven photofixation of nitrogen sensitized by triphenylphosphine and sodium iodide. ACS Catal 10:5502–5510
Qu Y, Wang L, Li Z, Li P, Zhang Q, Lin Y, Zhou F, Wang H, Yang Z, Hu Y, Zhu M, Zhao X, Han X, Wang C, Xu Q, Gu L, Luo J, Zheng L, Wu Y (2019) Ambient synthesis of single-atom catalysts from bulk metal via trapping of atoms by surface dangling bonds. Adv Mater 31:1904496–1904513
Xue Y, Huang B, Yi Y, Guo Y, Zuo Z, Li Y, Jia Z, Liu H, Li Y (2018) Anchoring zero valence single atoms of nickel and iron on graphdiyne for hydrogen evolution. Nat Commun 9:1460–1470
Pan Y, Chen Y, Wu K, Chen Z, Liu S, Cao X, Cheong WC, Meng T, Luo J, Zheng L, Liu C, Wang D, Peng Q, Li J, Chen C (2019) Regulating the coordination structure of single-atom Fe-NxCy catalytic sites for benzene oxidation. Nat Commun 10:4290–4301
Jiao L, Xu W, Yan H, Wu Y, Liu C, du D, Lin Y, Zhu C (2019) Fe–N–C single-atom nanozymes for the intracellular hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal Chem 91:11994–11999
Cheng N, Li J, Liu D et al (2019) Single-atom nanozyme based on nanoengineered Fe–N–C catalyst with superior peroxidase-like activity for ultrasensitive bioassays. Small 15:1901485–1901492
Chen Q, Li S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Tang Y, Chai H, Huang Y (2020) Size-controllable Fe-N/C single-atom nanozyme with exceptional oxidase-like activity for sensitive detection of alkaline phosphatase. Sensors Actuators B Chem 305:127511–127531
Biniuri Y, Luo G, Fadeev M et al (2019) Redox-switchable binding properties of the ATP–aptamer. J Am Chem Soc 141:15567–15576
Zhang T, Tian T, Zhou R, Li S, Ma W, Zhang Y, Liu N, Shi S, Li Q, Xie X, Ge Y, Liu M, Zhang Q, Lin S, Cai X, Lin Y (2020) Design, fabrication and applications of tetrahedral DNA nanostructure-based multifunctional complexes in drug delivery and biomedical treatment. Nat Protoc 15:2728–2757
Liao Q, Wei B, Luo L (2017) Aptamer based fluorometric determination of kanamycin using double-stranded DNA and carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 184:627–632
Wang W, Wang Y, Pan H, Cheddah S, Yan C (2019) Aptamer-based fluorometric determination for mucin 1 using gold nanoparticles and carbon dots. Microchim Acta 186:544–552
Raouafi A, Sánchez A, Raouafi N, Villalonga R (2019) Electrochemical aptamer-based bioplatform for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Sensors Actuators B Chem 297:126762–126768
Li D, Yao D, Li C, Luo Y, Liang A, Wen G, Jiang Z (2020) Nanosol SERS quantitative analytical method: a review. Trends Anal Chem 127:115885–115899
Das R, Parveen S, Bora A, Giri PK (2020) Origin of high photoluminescence yield and high SERS sensitivity of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Carbon 160:273–286
Li C, Fan P, Liang A, Liu Q, Jiang Z (2018) Aptamer based determination of Pb(II) by SERS and by exploiting the reduction of HAuCl4 by H2O2 as catalyzed by graphene oxide nanoribbons. Microchim Acta 185:177–183
Oliveira MJS, Rubira RJG, Furini LN, Batagin-Neto A, Constantino CJL (2020) Detection of thiabendazole fungicide/parasiticide by SERS: quantitative analysis and adsorption mechanism. Appl Surf Sci 517:145786–145805
Lê QT, Ly NH, Lim SH, Son SJ (2021) Nanostructured Raman substrates for the sensitive detection of submicrometer-sized plastic pollutants in water. J Hazard Mater 402:123499–123506
Liu Y, Huang C (2013) Real-time dark-field scattering microscopic monitoring of the in situ growth of single Ag@Hg nanoalloys. ACS Nano 7:11026–11034
Liang A, Liu Q, Wen G, Jiang Z (2012) The surface-plasmon-resonance effect of nanogold/silver and its analytical applications. Trends Anal Chem 37:32–47
Cai H, Pi J, Lin X et al (2015) Gold nanoprobes-based resonance Rayleigh scattering assay platform: sensitive cytosensing of breast cancer cells and facile monitoring of folate receptor expression. Biosens Bioelectron 74:165–169
Ren W, Zhang Y, Chen H et al (2016) Ultrasensitive label-free resonance Rayleigh scattering aptasensor for Hg2+ using Hg2+-triggered exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and growth of G-wires for signal amplification. Anal Chem 88:1385–1390
Wang H, Zhang Z, Chen C, Liang A, Jiang Z (2021) Fullerene carbon dot catalytic amplification-aptamer assay platform for ultratrace As+3 utilizing SERS/RRS/Abs trifunctional Au nanoprobes. J Hazard Mater 403:123633–123643
Li C, Yao D, Jiang X et al (2020) Strong nanocatalysis of silver-doped carbon nitride and its application to aptamer SERS and RRS coupled dual-mode detection of ultra-trace K+. J Mater Chem C 6:972–979
Qi Y, He J, Xiu F et al (2019) A convenient chemiluminescence detection for bisphenol A in E-waste dismantling site based on surface charge change of cationic gold nanoparticles. Microchem J 147:789–796
Lee S, Kim M, Lee S, Lee E (2019) Simple and rapid detection of bisphenol A using a gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric aptasensor. Food Chem 287:205–213
Yun W, Wu H, Chen L, Yang L (2018) Dual enzyme-free amplification strategy for ultra-sensitive fluorescent detection of bisphenol A in water. Anal Chim Acta 1020:104–109
Li Q, Li H, Du G, Xu Z (2010) Electrochemical detection of bisphenol A mediated by [Ru(bpy)3]2+ on an ITO electrode. J Hazard Mater 180:703–709
Wang Z, Yan R, Liao S, Miao Y, Zhang B, Wang F, Yang H (2018) In situ reduced silver nanoparticles embedded molecularly imprinted reusable sensor for selective and sensitive SERS detection of bisphenol A. Appl Surf Sci 457:323–331
Lin P, Hsieh C, Hsieh S (2017) Rapid and sensitive SERS detection of bisphenol A using self-assembled graphitic substrates. Sci Rep 7:16698–16704
Ren X, Qi J, Li X (2018) Silver microspheres coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer as a SERS substrate for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 185:242–248
Yang L, Chen Y, Shen Y, Yang M, Li X, Han X, Jiang X, Zhao B (2018) SERS strategy based on the modified Au nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of bisphenol A residues in milk. Talanta 179:37–42
Liu S, Li N, Han L et al (2018) Size-dependent modulation of fluorescence and light scattering: a new strategy for development of ratiometric sensing. Mater Horiz 5:454–460
Lindquist NC, de Albuquerque CDL, Paci I, Brolo AG (2019) High-speed imaging of surface-enhanced Raman scattering fluctuations from individual nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 14:981–987
Socrates G (2004) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies: tables and chart. Wiley, New York, pp 1–362
Sun X, Li Y (2004) Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:597–601
Yang H, Zha J, Zhang P, Qin Y, Chen T, Ye F (2017) Fabrication of CeVO4 as nanozyme for facile colorimetric discrimination of hydroquinone from resorcinol and catechol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:469–478
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21667006, 21767004) and Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (YCSW2020096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 3125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Li, C., Wang, H. et al. Single-atom Fe catalytic amplification-gold nanosol SERS/RRS aptamer as platform for the quantification of trace pollutants. Microchim Acta 188, 175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04828-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04828-8