Abstract
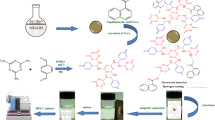
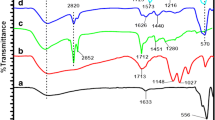
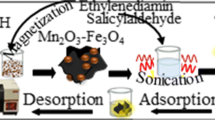
Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe)/PEI are used for the first time as an adsorbent material for the extraction of pesticide residues (epoxiconazole, flusilazole, tebuconazole, and triadimefon) from food matrices. The adsorbent proposed (Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe)/PEI) was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) techniques to evaluate the properties of the sorbent. Then, the Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe)/PEI was employed for the quantification of the four triazole fungicides in fruits and vegetables (apple, orange, tomato, cabbage, and cucumber) using HPLC-UV for separation and detection. During the extraction process, the main parameters such as amount of adsorbent, extraction time, pH value, ionic strength, eluting solvent, and eluting volume were optimized. Under the optimum conditions, good linearity of this method was observed for all analytes, with correlation coefficients (R2) ≥ 0.9908. The limits of detection (LODs) ranged from 0.021–3.04 μg kg−1. The extraction recoveries of the four triazole fungicides varied from 73.9 to 109.4% with relative standard deviations (RSD) in the range 0.5 to 6.2%. Compared with other MOFs, the modification of Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) with PEI shows high efficient adsorption due to the combined benefits of MIL-100 (Fe) and PEI. The material is easily synthesized, has good stability, and is of low cost.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bidari A, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Hosseini MRM, Assadi Y (2011) Sample preparation method for the analysis of some organophosphorus pesticides residues in tomato by ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Food Chem 126:1840–1844. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2010.11.142
Li N, Jiang H-L, Wang X, Wang X, Xu G, Zhang B, Wang L, Zhao RS, Lin JM (2018) Recent advances in graphene-based magnetic composites for magnetic solid-phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 102:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.01.009
Yu M, Wang L, Hu L, Li Y, Luo D, Mei S (2019) Recent applications of magnetic composites as extraction adsorbents for determination of environmental pollutants. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 119:115611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.07.022
Wang D-D, Zhao Y, Ou yang M-N et al (2019) Magnetic polydopamine modified with deep eutectic solvent for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1601:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHROMA.2019.05.011
Xiong Y-B, Lu Z-H, Wang D-D, Yang MNO, Guo HM, Yang ZH (2020) Application of polydopamine functionalized magnetic graphene in triazole fungicides residue analysis. J Chromatogr A 1614:460725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460725
Senosy IA, Lu Z-H, Abdelrahman TM, Yang MNO, Guo HM, Yang ZH, Li JH (2020) The post-modification of magnetic metal–organic frameworks with β-cyclodextrin for the efficient removal of fungicides from environmental water. Environ Sci Nano 7:2087–2101. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EN01372E
Yi X, Liu C, Liu X, Wang P, Zhou Z, Liu D (2019) Magnetic partially carbonized cellulose nanocrystal-based magnetic solid phase extraction for the analysis of triazine and triazole pesticides in water. Microchim Acta 186:825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3911-x
Liu L, Yang M, He M, Liu T, Chen F, Li Y, Feng X, Zhang Y, Zhang F (2020) Magnetic solid phase extraction sorbents using methyl-parathion and quinalphos dual-template imprinted polymers coupled with GC-MS for class-selective extraction of twelve organophosphorus pesticides Microchim Acta 187: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04465-7
Jiao L, Seow JYR, Skinner WS, Wang ZU, Jiang HL (2019) Metal–organic frameworks: structures and functional applications. Mater Today 27:43–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2018.10.038
Hashemi B, Zohrabi P, Raza N, Kim K-H (2017) Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents for the extraction and determination of pollutants from environmental, biological, and food media. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 97:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2017.08.015
Maya F, Palomino Cabello C, Frizzarin RM, Estela JM, Turnes Palomino G, Cerdà V (2017) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 90:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2017.03.004
Li X, Ma W, Li H, Bai Y, Liu H (2019) Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents in sample preparation for small organic analytes. Coord Chem Rev 397:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCR.2019.06.014
Wang C, Liu X, Keser Demir N, Chen JP, Li K (2016) Applications of water stable metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 45:5107–5134. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00362A
Yang Q, Zhao Q, Ren SS, Lu Q, Guo X, Chen Z (2016) Fabrication of core-shell Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) magnetic microspheres for the removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J Solid State Chem 244:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2016.09.010
Aslam S, Zeng J, Subhan F, Li M, Lyu F, Li Y, Yan Z (2017) In situ one-step synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) core-shells for adsorption of methylene blue from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 505:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.090
Pang L, Yang P, Yang H, Ge L, Xiao J, Zhou Y (2018) Application of Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) core-shell magnetic microspheres for evaluating the sorption of organophosphate esters to dissolved organic matter (DOM). Sci Total Environ 626:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.089
Wen M, Li G, Liu H, Chen J, An T, Yamashita H (2019) Metal-organic framework-based nanomaterials for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of gaseous pollutants: recent progress and challenges. Environ Sci Nano 6:1006–1025. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01167b
Meng Q, Liu J, Jiang Y, Teng Q (2019) Branched Polyethyleneimine-functionalized polystyrene resin: preparation and adsorption of Cu2+. J Chem Eng Data 64:2618–2626. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00090
Li N, Chen J, Shi YP (2017) Magnetic polyethyleneimine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a novel magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of polar acidic herbicides in rice. Anal Chim Acta 949:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.11.016
Xian S, Wu Y, Wu J, Wang X, Xiao J (2015) Enhanced dynamic CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/CH4 selectivity on polyethylenimine-impregnated UiO-66. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:11151–11158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03517
Zhang Y, Guan J, Wang X, Yu J, Ding B (2017) Balsam-pear-skin-like porous polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes grafted with polyethyleneimine for postcombustion CO2 capture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:41087–41098. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14635
Buerge IJ, Poiger T, Müller MD, Buser HR (2006) Influence of pH on the stereoselective degradation of the fungicides epoxiconazole and cyproconazole in soils. Environ Sci Technol 40:5443–5450. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060817d
Lv X, Pan L, Wang J, Lu L, Yan W, Zhu Y, Xu Y, Guo M, Zhuang S (2017) Effects of triazole fungicides on androgenic disruption and CYP3A4 enzyme activity. Environ Pollut 222:504–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.051
Yu L, Chen M, Liu Y, Gui W, Zhu G (2013) Thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae following exposure to hexaconazole and tebuconazole. Aquat Toxicol 138–139:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.04.001
Lin CH, Chou PH, Chen PJ (2014) Two azole fungicides (carcinogenic triadimefon and non-carcinogenic myclobutanil) exhibit different hepatic cytochrome P450 activities in medaka fish. J Hazard Mater 277:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.083
Zhu S, Fang S, Huo M, Yu Y, Chen Y, Yang X, Geng Z, Wang Y, Bian D, Huo H (2015) A novel conversion of the groundwater treatment sludge to magnetic particles for the adsorption of methylene blue. J Hazard Mater 292:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2015.03.028
Zhang S, Yang Q, Wang W, Wang C, Wang Z (2016) Covalent bonding of metal-organic framework-5/graphene oxide hybrid composite to stainless steel fiber for solid-phase microextraction of triazole fungicides from fruit and vegetable samples. J Agric Food Chem 64:2792–2801. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05831
Zhang CF, Qiu LG, Ke F, Zhu YJ, Yuan YP, Xu GS, Jiang X (2013) A novel magnetic recyclable photocatalyst based on a core-shell metal-organic framework Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J Mater Chem A 1:14329–14334. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13030d
Tian H, Peng J, Du Q et al (2018) One-pot sustainable synthesis of magnetic MIL-100(Fe) with novel Fe3O4 morphology and its application in heterogeneous degradation. Dalt Trans 47:3417–3424. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7dt04819j
Liu G, Li L, Gao Y, Gao M, Huang X, Lv J, Xu D (2019) A beta-cyclodextrin-functionalized magnetic metal organic framework for efficient extraction and determination of prochloraz and triazole fungicides in vegetables samples. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109546
Han X, Chen J, Li Z, Quan K, Qiu H (2020) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides based on magnetic porous carbon prepared by combustion combined with solvothermal method. Anal Chim Acta 1129:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.06.077
Caon NB, dos Cardoso CS, Faita FL et al (2020) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of triclosan from water using n-octadecyl modified silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104003
Fan YH, Zhang SW, Bin QS et al (2017) Facile preparation of hexadecyl-functionalized magnetic core-shell microsphere for the extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental waters. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:3337–3346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0278-x
Liu C, Liao Y, Huang X (2017) Extraction of triazole fungicides in environmental waters utilizing poly (ionic liquid)-functionalized magnetic adsorbent. J Chromatogr A 1524:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.09.066
Yang J, Fan C, Kong D, Tang G, Zhang W, Dong H, Liang Y, Wang D, Cao Y (2018) Synthesis and application of imidazolium-based ionic liquids as extraction solvent for pretreatment of triazole fungicides in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:1647–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0820-x
Liu G, Li L, Huang X, Zheng S, Xu D, Xu X, Zhang Y, Lin H (2018) Determination of triazole pesticides in aqueous solution based on magnetic graphene oxide functionalized MOF-199 as solid phase extraction sorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 270:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.05.023
Huang X, Liu Y, Liu G, Li L, Xu X, Zheng S, Xu D, Gao H (2018) Preparation of a magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube@polydopamine/zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 composite for magnetic solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides from environmental water samples. RSC Adv 8:25351–25360. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05064c
Farajzadeh MA, Khoshmaram L, Mogaddam MRA (2012) Combination of solid-phase extraction-hollow fiber for ultra-preconcentration of some triazole pesticides followed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. J Sep Sci 35:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100374
Miao Q, Wang J, Nie J, Wu H, Liu Y, Li Z, Qian M (2016) Magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction based on a novel adsorbent for the detection of triazole pesticide residues in honey by HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Methods 8:5296–5303. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00376A
Li D, He M, Chen B, Hu B (2019) Magnetic porous organic polymers for magnetic solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides in vegetables prior to their determination by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. J Chromatogr A 1601:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.04.062
Funding
The present study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China [2019YFD1002103], National Key R&D Program of China [2017YFD020030803], and National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 21507032].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 273 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senosy, I.A., Zhang, XZ., Lu, ZH. et al. Magnetic metal-organic framework MIL-100 (Fe)/polyethyleneimine composite as an adsorbent for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of fungicides and their determination using HPLC-UV. Microchim Acta 188, 33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04648-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04648-2