Abstract
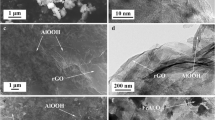
A multilayer Bi-BTC/reduced graphene oxide (Bi-BTC/rGO) (BTC, 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid) film electrode was adopted to construct a highly sensitive Pb2+ electrochemical sensor. The multilayer Bi-BTC/rGO films were prepared via alternate cast of Bi-BTC and graphene oxide (GO) on a glassy carbon electrode, followed by electro-reduction of the GO components. Bi-BTC has porous broom-like structure and its organic ligand has abundant functional groups, which are favorable for Pb2+ adsorption and preconcentration. The introduction of rGO layer improves the conductivity of the MOFs material. Moreover, the multilayer composite structure greatly increased the exposure of active sites and the surface area of reactive contact, finally realizing the highly sensitive detection of Pb2+. Pb2+ was determined by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry and the response current was recorded at − 0.62 V. The [Bi-BTC/rGO]2 electrode provides a wide linear response ranging from 0.062 to 20.72 μg/L and a low limit of detection (LOD) of 0.021 μg/L (S/N = 3) for Pb2+, which is lower than the guideline value proposed by the World Health Organization. The method has been applied to determine Pb2+ in industrial wastewater with recoveries of 99.2–104% and RSDs of 3.4–4.0% (n = 3).

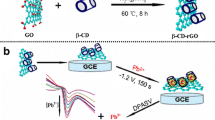
Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract
Schematic representation of an electrochemical sensor for the detection of Pb2+ was designed based on long broom-like structure bismuth(II) metallic organic framework/reduced graphene oxide ([Bi-BTC /rGO]2)







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Needleman HL, Bellinger DC (1991) The health effects of low level exposure to lead. Annu Rev Public Health 12(1):111–140
Loomis D, Grosse Y, Laubysecretan B, Ghissassi FE, Bouvard V, Benbrahimtallaa L, Guha N, Baan RA, Mattock H, Straif K (2013) The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. Lancet Oncol 14(13):1262–1263
Priya T, Dhanalakshmi N, Karthikeyan V, Thinakaran N (2019) Highly selective simultaneous trace determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ using porous graphene/carboxymethyl cellulose/fondaparinux nanocomposite modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 833:543–551
Arai Y, Lanzirotti A, Sutton SR, Davis JA, Sparks DL (2003) Arsenic speciation and reactivity in poultry litter. Environ Sci Technol 37(18):4083–4090
Soylak M, Kizil N (2011) Determination of some heavy metals by flame atomic absorption spectrometry before coprecipitation with neodymium hydroxide. J AOAC Int 94(3):978–984
Yu LY, Zhang Q, Yang BR, Xu Q, Xu Q, Hu XY (2018) Electrochemical sensor construction based on Nafion/calcium lignosulphonate functionalized porous graphene nanocomposite and its application for simultaneous detection of trace Pb2+ and Cd2+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:540–551
Anjos MJD, Lopes RT, Jesus EFOD, Assis JT, Cesareo R, Barradas CAA (2000) Quantitative analysis of metals in soil using X-ray fluorescence. Spectrochim Acta B Atom Spectrosc 55(7):1189–1194
Yang S, Dai X, Stogin BB, Wong TS (2016) Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(2):268–273
Zhi L, Zuo W, Chen F, Wang B (2016) 3D MoS2 composition aerogels as chemosensors and adsorbents for colorimetric detection and high-capacity adsorption of Hg2+. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(6):3398–3408
Xing H, Xu J, Zhu X, Duan X, Yang T (2016) Highly sensitive simultaneous determination of cadmium (ii), lead (ii), copper (ii), and mercury (ii) ions on n-doped graphene modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 760:52–58
Zuo YX, Xu JK, Zhu XF, Duan XM, Lu LM, Yu YF (2019) Graphene-derived nanomaterials as recognition elements for electrochemical determination of heavy metal ions: a review. Microchim Acta 186(3):171–188
Shiu K, Chan O, Pang S (1995) Factors affecting the electroanalytical behavior of polypyrrole-modified electrodes bearing complexing ligands. Anal Chem 67(17):2828–2834
Florence TM (1970) Anodic stripping voltammetry with a glassy carbon electrode mercury-plated in situ. J Electroanal Chem 27(2):273–281
Toghill K, Wildgoose G, Moshar A, Mulcahy C, Compton R (2008) The fabrication and characterization of a bismuth nanoparticle modified boron doped diamond electrode and its application to the simultaneous determination of cadmium(ii) and lead(ii). Electroanalysis 20(16):1731–1737
Ghazali NN, Nor NM, Razak KA, Lockman Z, Hattori T (2020) Hydrothermal synthesis of bismuth nanosheets for modified APTES-functionalized screen-printed carbon electrode in lead and cadmium detection. J Nanopart Res 22(7):1–11
Shi L, Li Y, Rong X, Wang Y, Ding S (2017) Facile fabrication of a novel 3D graphene framework/Bi nanoparticle film for ultrasensitive electrochemical assays of heavy metal ions. Anal Chim Acta 968:21–29
Stassen I, Styles MJ, Van Assche TR, Campagnol N, Fransaer J, Denayer JF, Tan JC, Falcaro P, Vos DED, Ameloot R (2015) Electrochemical film deposition of the zirconium metal-organic framework UIO-66 and application in a miniaturized sorbent trap. Chem Mater 27(5):1801–1807
Li Y, Jiang K, Zhang J, Xia T, Cui Y, Yang Y, Qian G (2018) A turn-on fluorescence probe based on post-modified metal–organic frameworks for highly selective and fast-response hypochlorite detection. Polyhedron 148:76–80
Li C, Xu H, Gao J, Du W, Shangguan L, Zhang X, Lin RB, Wu H, Zhou W, Liu XF, Yao JM, Chen B (2019) Tunable titanium metal–organic frameworks with infinite 1D Ti-O rods for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution. J Mater Chem 7(19):11928–11933
Gich M, Fernandezsanchez C, Cotet LC, Niu P, Roig A (2013) Facile synthesis of porous bismuth–carbon nanocomposites for the sensitive detection of heavy metals. J Mater Chem 1(37):11410–11418
Sahoo PK, Panigrahy B, Sahoo S, Satpati AK, Li D, Bahadur D (2013) In situ synthesis and properties of reduced graphene oxide/Bi nanocomposites: as an electroactive material for analysis of heavy metals. Biosens Bioelectron 43:293–296
Cerovac S, Guzsvány V, Kónya Z, Ashrafi AM, Švancara I, Rončević S, Kukovecz Á, Dalmacija B, Vytřas K (2015) Trace level voltammetric determination of lead and cadmium in sediment pore water by a bismuth-oxychloride particle-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 134:640–649
Tan Z, Wu WQ, Feng CQ, Wu HM, Zhang ZW (2020) Simultaneous determination of heavy metals by an electrochemical method based on a nanocomposite consisting of fluorinated graphene and gold nanocage. Microchim Acta 187(7):414–423
Yang Y, Wang Q, Qiu W, Guo H, Gao F (2016) Covalent immobilization of Cu3(BTC)2 at chitosan–electroreduced graphene oxide hybrid film and its application for simultaneous detection of dihydroxybenzene isomers. J Phys Chem C 120(18):9794–9803
Li XY, Cao L, Wu C, Kang B (2019) Strategy for highly sensitive electrochemical sensing: in situ coupling of a metal-organic framework with ball-mill-exfoliated graphene. Anal Chem 91(9):6043–6050
Rani S, Kapoor S, Sharma B, Kumar S, Malhotra R, Dilbaghi N (2020) Fabrication of Zn-MOF@rGO based sensitive nanosensor for the real time monitoring of hydrazine. J Alloys Compd 816:152509
Wang G, Liu Y, Huang B, Qin X, Zhang X, Dai Y (2015) A novel metal–organic framework based on bismuth and trimesic acid: synthesis, structure and properties. Dalton Trans 44(37):16238–16241
Anson FC (1964) Application of potentiostatic current integration to the study of the adsorption of cobalt(iii)-(ethylenedinitrilo(tetraacetate) on mercury electrodes. Anal Chem 36(4):932–934
Wang ZM, Guo HW, Liu E, Yang GC, Khun NW (2010) Bismuth/polyaniline /glassy carbon electrodes prepared with different protocols for stripping voltammetric determination of trace Cd and Pb in solutions having surfactants. Electroanalysis 22(2):209–215
He Y, Wang ZH, Ma L, Zhou LY, Jiang YJ, Gao J (2020) Synthesis of bismuth nanoparticle-loaded cobalt ferrite for electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. RSC Adv 10(46):27697–27705
Mafa PJ, Idris AO, Mabuba N, Arotiba OA (2016) Electrochemical co-detection of As (III), Hg (II) and Pb (II) on a bismuth modified exfoliated graphite electrode. Talanta 153:99–106
Hwang GH, Han WK, Park JS, Kang SG (2008) Determination of trace metals by anodic stripping voltammetry using a bismuth-modified carbon nanotube electrode. Talanta 76(2):301–308
Sayato Y (1989) WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. Eisei Kagaku 35(5):307–312
Funding
We are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21665010, 51862014, 31741103, and 51302117), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20202ACBL213009, 20192BBEL50029), Jiangxi Outstanding Young Talents Funding Scheme (20162BCB23030), Provincial Projects for Postgraduate Innovation in Jiangxi (NDYC2020-S002), and the Natural Science Foundation of Nanchang City (No. 2018CXTD014) for their financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 537 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, J., Zhong, W., Gao, F. et al. Sensitive electrochemical platform for trace determination of Pb2+ based on multilayer Bi-MOFs/reduced graphene oxide films modified electrode. Microchim Acta 187, 603 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04571-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04571-6