Abstract
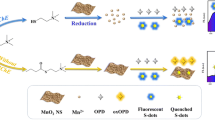
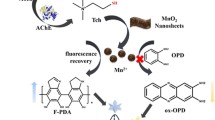
By using graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and o-phenylenediamine (OPD), a ratiometric fluorescence probe was designed for the highly sensitive and selective detection of AChE. GQDs with strong fluorescence were synthesized by the one-step hydrothermal method. The optimal emission wavelength of GQDs was 450 nm at the excitation wavelength of 375 nm. MnO2 nanosheets with a wide absorption band of 300–600 nm were prepared at room temperature. Because of the extensive overlap between the absorption spectrum of MnO2 nanosheets and the excitation and emission spectra of GQDs, the fluorescence of GQDs at 450 nm was efficiently quenched by the inner-filter effect. Meanwhile, due to the peroxidase-like activity of MnO2 nanosheets, OPD was catalytically oxidized to 2,3-diaminophenazine (oxOPD), a yellow fluorescent substance with a new emission peak at 572 nm. When AChE was present, the substrate acetylthiocholine (ATCh) was hydrolyzed to thiocholine (TCh) that is capable of decomposing MnO2 nanosheets. Therefore, the quench of GQDs and the oxidation of OPD by MnO2 nanosheets were suppressed, resulting in the fluorescence recovery of GQDs at 450 nm, while the fluorescence decrease of oxOPD at 572 nm. Utilizing the fluorescence intensity ratio F450/F572 as the signal readout, the ratiometric fluorescence method was established to detect AChE activity. The ratio F450/F572 against the AChE concentration demonstrated two linear relationships in the range 0.1–2.0 and 2.0–4.5 mU mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.09 mU mL−1. The method was applied to the detection of positive human serum samples and the analysis of the inhibitor neostigmine. Due to the advantages of high sensitivity, favorable selectivity, and strong anti-interference, the method possesses an application prospect in clinical diagnosis of AChE and the screening of inhibitors.

Schematic presentation of a ratiometric fluorescence method for the detection of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The fluorescence of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) is quenched and o-phenylenediamine (OPD) is oxidized to generate fluorescent product 2,3-diaminophenazine (oxOPD) by MnO2 nanosheets. When AChE is present, acetylthiocholine iodide (ATCh) is hydrolyzed to thiocholine (TCh) with reducibility for decomposing MnO2 nanosheets. Due to the decomposition of MnO2 nanosheets, the quenching of GQDs and oxidation of OPD are suppressed. The fluorescence of GQDs at 450 nm is enhanced, while the fluorescence of oxOPD at 572 nm is reduced. The fluorescence intensity ratio F450/F572 is used to establish the ratiometric fluorescence method for AChE activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Hei T, Cai Y, Gao Q, Zhang Q (2012) Affinity binding-guided fluorescent nanobiosensor for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors via distance modulation between the fluorophore and metallic nanoparticle. Anal Chem 84:2830–2836. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300436m
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Jin R, Xing Z, Kong D, Yan X, Liu F, Gao Y, Sun P, Liang X, Lu G (2019) Sensitive colorimetric sensor for point-of-care detection of acetylcholinesterase using cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflakes. J Mater Chem B 7:1230–1237. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02987C
Lv J, He B, Wang N, Li M, Lin Y (2018) A gold nanoparticle based colorimetric and fluorescent dual-channel probe for acetylcholinesterase detection and inhibitor screening. RSC Adv 8:32893–32898. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA06165C
Panraksa Y, Siangproh W, Khampieng T, Chailapakul O, Apilux A (2018) Paper-based amperometric sensor for determination of acetylcholinesterase using screen-printed graphene electrode. Talanta 178:1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.096
Zhao H, Ji X, Wang B, Wang N, Li X, Ni R, Ren J (2015) An ultra-sensitive acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide-Au nanoparticles-β-cyclodextrin/Prussian blue-chitosan nanocomposites for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Biosens Bioelectron 65:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.10.007
Qian Z, Chai L, Tang C, Huang Y, Chen J, Feng H (2016) A fluorometric assay for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor screening with carbon quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem 222:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.023
Yang J, Song N, Lv X, Jia Q (2018) UV-light-induced synthesis of PEI-CuNCs based on Cu2+-quenched fluorescence turn-on assay for sensitive detection of biothiols, acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.045
Yang M, Liu M, Wu Z, He Y, Ge Y, Song G, Zhou J (2019) Carbon dots co-doped with nitrogen and chlorine for “off-on” fluorometric determination of the activity of acetylcholinesterase and for quantification of organophosphate pesticides. Microchim Acta 186:585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3715-z
Yang M, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Hu Z, Niu N, Yu C (2018) Controlled synthesis of polydopamine: a new strategy for highly sensitive fluorescence turn-on detection of acetylcholinesterase activity. Microchim Acta 185:132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2678-9
Wu Z, Gao M, Wang T, Wan X, Zheng L, Huang C (2014) A general quantitative pH sensor developed with dicyandiamide N-doped high quantum yield graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 6:3868–3874. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR06353D
Pathan S, Jalal M, Prasad S, Bose S (2019) Aggregation-induced enhanced photoluminescence in magnetic graphene oxide quantum dots as a fluorescence probe for as(III) sensing. J Mater Chem A 7:8510–8520. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA11358K
Zhang C, Lin B, Cao Y, Guo M, Yu Y (2017) Fluorescence determination of omethoate based on a dual strategy for improving sensitivity. J Agric Food Chem 65:3065–3073. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00166
Zhao J, Zhao L, Lan C, Zhao S (2016) Graphene quantum dots as effective probes for label-free fluorescence detection of dopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.105
Liu X, Na W, Liu Q, Su X (2018) A novel label-free fluorescent sensor for highly sensitive detection of bleomycin based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 1028:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.038
Chen C, Zhang G, Ni P, Jiang Y, Lu Y, Lu Z (2019) Fluorometric and colorimetric dual-readout alkaline phosphatase activity assay based on enzymatically induced formation of colored Au@Ag nanoparticles and an inner filter effect. Microchim Acta 186:348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3478-6
Fan H, Zhao Z, Yan G, Zhang X, Yang C, Meng H, Chen Z, Liu H, Tan W (2015) A smart DNAzyme–MnO2 nanosystem for efficient gene silencing. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:4801–4805. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201411417
Ma Z, Wu T, Li P, Liu M, Huang S, Li H, Zhang Y, Yao S (2019) A dual (colorimetric and fluorometric) detection scheme for glutathione and silver (I) based on the oxidase mimicking activity of MnO2 nanosheets. Microchim Acta 186:498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3613-4
Yan X, Kong D, Jin R, Zhao X, Li H, Liu F, Lin Y, Lu G (2019) Fluorometric and colorimetric analysis of carbamate pesticide via enzyme-triggered decomposition of gold nanoclusters-anchored MnO2 nanocomposite. Sensors Actuators B Chem 290:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.045
Peng C, Xing H, Fan X, Xue Y, Li J, Wang E (2019) Glutathione regulated inner filter effect of MnO2 nanosheets on boron nitride quantum dots for sensitive assay. Anal Chem 91:5762–5767. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05961
Zhai W, Wang C, Yu P, Wang Y, Mao L (2014) Single-layer MnO2 nanosheets suppressed fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarin: mechanistic study and application for sensitive sensing of ascorbic acid in vivo. Anal Chem 86:12206–12213. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503215z
Ge J, Cai R, Chen X, Wu Q, Zhang L, Jiang Y, Cui C, Wan S, Tan W (2019) Facile approach to prepare HSA-templated MnO2 nanosheets as oxidase mimic for colorimetric detection of glutathione. Talanta 195:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.11.024
Tan X, Li Z, Du Y, Zheng A, Zeng Y, Zhang X, Liu X, Peng N (2018) A MnO2 nanosheets–o-phenylenediamine oxidative system for the sensitive fluorescence determination of alkaline phosphatase activity. Anal Methods 10:5341–5346. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY02061B
Sun Y, Tan H, Li Y (2018) A colorimetric assay for acetylcholinesterase activity and inhibitor screening based on the thiocholine–induced inhibition of the oxidative power of MnO2 nanosheets on 3,3′,5,5′–tetramethylbenzidine. Microchim Acta 185:446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2974-4
Li H, Yan X, Lu G, Su X (2018) Carbon dot-based bioplatform for dual colorimetric and fluorometric sensing of organophosphate pesticides. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:563–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.170
Yan X, Song Y, Wu X, Zhu C, Su X, Du D, Lin Y (2017) Oxidase-mimicking activity of ultrathin MnO2 nanosheets in colorimetric assay of acetylcholinesterase activity. Nanoscale 9:2317–2323. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR08473G
Zhang Z, Feng J, Huang P, Li S, Wu F (2019) Ratiometric fluorescent detection of phosphate in human serum with functionalized gold nanoclusters based on chelation-enhanced fluorescence. Sensors Actuators B Chem 298:126891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126891
Niu C, Liu Q, Shang Z, Zhao L, Ouyang J (2015) Dual-emission fluorescent sensor based on AIE organic nanoparticles and Au nanoclusters for the detection of mercury and melamine. Nanoscale 7:8457–8465. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR00554J
Ju J, Zhang R, He S, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots-based fluorescent probe for the sensitive turn-on detection of glutathione and its cellular imaging. RSC Adv 4:52583–52589. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA10601F
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge L, Song L, Alemany LB, Zhan X, Gao G, Vithayathil SA, Kaipparettu BA, Marti AA, Hayashi T, Zhu J-J, Ajayan PM (2012) Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett 12:844–849. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl2038979
Lee SH, Kim DY, Lee J, Lee SB, Han H, Kim YY, Mun SC, Im SH, Kim T-H, Park OO (2019) Synthesis of single-crystalline hexagonal graphene quantum dots from solution chemistry. Nano Lett 19:5437–5442. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01940
Wang J, Wang D, Tang A, Kong D (2019) Highly integrated, biostable, and self-powered DNA motor enabling autonomous operation in living bodies. Anal Chem 91:5244–5251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00007
Sun J, Liu F, Yu W, Jiang Q, Hu J, Liu Y, Wang F, Liu X (2019) Highly sensitive glutathione assay and intracellular imaging with functionalized semiconductor quantum dots. Nanoscale 11:5014–5020. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR09801H
Liu Z, Xu K, Sun H, Yin S (2015) One-step synthesis of single-layer MnO2 nanosheets with multi-role sodium dodecyl sulfate for high-performance pseudocapacitors. Small 11:2182–2191. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201402222
Liu Y, Ouyang Q, Li H, Zhang Z, Chen Q (2017) Development of an inner filter effects-based upconversion nanoparticles–curcumin nanosystem for the sensitive sensing of fluoride ion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:18314–18321. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04978
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21575043, 21275056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 10212 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, M., Lin, B., Yu, Y. et al. A ratiometric fluorescence probe based on graphene quantum dots and o-phenylenediamine for highly sensitive detection of acetylcholinesterase activity. Microchim Acta 187, 511 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04522-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04522-1