Abstract
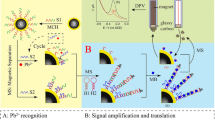
A photoelectrochemical (PEC) aptasensing platform is devised for sensitive detection of an organophosphorus pesticide based on dissolution of core-shell MnO2 nanoflower@CdS (MnO2 NF@CdS) by thiocholine (TCh). TCH is produced from the butyrylcholinesterase-acetylthiocholine system, accompanied by target-triggered rolling circle amplification (RCA). The core-shell MnO2 NF@CdS with excellent PEC performance was synthesized and employed as a photo-sensing platform. The target was detected on a functionalized magnetic probe with the corresponding aptamer. Upon malathion introduction, the aptamer was detached from the magnetic beads, while capture DNA (cDNA, with primer fragment) remained on the beads. The primer fragment in cDNA can trigger the RCA reaction to form a long single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Furthermore, a large number of butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) were assembled on the long ssDNA strands through the hybridization with the S2-Au-BChE probe. Thereafter, TCh generated from hydrolysis of ATCh by BChE can reduce MnO2 NF (core) to Mn2+ and release the CdS nanoparticles (shell) from the platform electrode, significantly enhancing the PEC signal. Under optimal conditions, the proposed aptasensor exhibited high sensitivity for malathion with a low detection limit of 0.68 pg mL−1. Meanwhile, it also presents outstanding specificity, reproducibility, and stability. Importantly, the sensing platform provides a new concept for detection of pesticide.

Herein, this work devised a photoelectrochemical (PEC) aptasensing platform for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticide based on dissolution of core-shell MnO2 nanoflower@CdS (MnO2 NF@CdS) by the as-produced thiocholine (TCh) from the butyrylcholinesterase-acetylthiocholine system, accompanying with the target-triggered rolling circle amplification (RCA).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan X, Song Y, Zhu C, Li H, Du D, Su X, Lin Y (2018) MnO2 nanosheet-carbon dots sensing platform for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chem 90:2618–2624
Lv B, Wei M, Liu Y, Liu X, Wei W, Liu S (2016) Ultrasensitive photometric and visual determination of organophosphorus pesticides based on the inhibition of enzyme-triggered formation of core-shell gold-silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:2941–2948
Gai P, Zhang S, Yu W, Li H, Li F (2018) Light-driven self-powered biosensor for ultrasensitive organophosphate pesticide detection via integration of the conjugated polymer-sensitized CdS and enzyme inhibition strategy. J Mater Chem B 6:6842–6847
Zhao Y, Yang M, Fu Q, Ouyang H, Wen W, Song Y, Zhu C, Lin Y, Du D (2018) A nanozyme- and ambient light-based smartphone platform for simultaneous detection of dual biomarkers from exposure to organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chem 90:7391–7398
Cacho JI, Campillo N, Viñas P, Hernández-Córdoba M (2018) In situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides. J Chromatogr A 1559:95–101
Su R, Li D, Wang X, Yang H, Shi X, Liu S (2016) Determination of organophosphorus pesticides in ginseng by carbon nanotube envelope-based solvent extraction combined with ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 1022:141–152
Cequier E, Sakhi AK, Haug LS, Thomsen C (2016) Development of an ion-pair liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry method for determination of organophosphate pesticide metabolites in large-scale biomonitoring studies. J Chromatogr A 1454:32–41
Zhang L, Shen Y, Fan G, Xiong M, Yu X, Zhao W (2019) Preparation of an AgI/CuBi2O4 heterojunction on a fluorine-doped tin oxide electrode for cathodic photoelectrochemical assays: application to the detection of L-cysteine. Microchim Acta 186:284–291
Li X, Kong W, Qin X, Qu F, Lu L (2020) Self-powered cathodic photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on in situ-synthesized CuO-Cu2O nanowire array for detecting prostate-specific antigen. Microchim Acta 187:325–333
Shu J, Tang D (2020) Recent advances in photoelectrochemical sensing: from engineered photoactive materials to sensing devices and detection modes. Anal Chem 92:363–377
Tang J, Xiong P, Li J, Cheng Y, Tian X, Chen Y, Sun Y, Tang D (2019) Target-induced elimination of photosensitizer and formation insulation layer enabling ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical detection of ochratoxin A. Sens Actuators B Chem 297:126707
Deng H, Huang L, Chai Y, Yuan R, Yuan Y (2019) Ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical detection of multiple metal ions based on wavelength-resolved dual-signal output triggered by click reaction. Anal Chem 91:2861–2868
Tang J, Xiong P, Cheng Y, Chen Y, Peng S, Zhu Z (2019) Enzymatic oxydate-triggered AgNPs etching: a novel signal-on photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform based on Ag@AgCl nanocubes loaded RGO plasmonic heterostructure. Biosens Bioelectron 130:125–131
Ge L, Hong Q, Li H, Liu C, Li F (2019) Direct-laser-writing of metal sulfide-graphene nanocomposite photoelectrode toward sensitive photoelectrochemical sensing. Adv Funct Mater 29:1904000
Luo J, Liang D, Li X, Deng L, Wang Z, Yang M (2020) Aptamer-based photoelectrochemical assay for the determination of MCF-7. Microchim Acta 187:257–263
Jia J, Wu J, Dong J, Fan L, Huang M, Lin J, Lan Z (2018) Cadmium sulfide as an efficient electron transport material for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Chem Commun 54:3170–3173
Zhang X, Zhang R, Yang A, Wang Q, Kong R, Qu F (2017) Aptamer based photoelectrochemical determination of tetracycline using a spindle-like ZnO-CdS@Au nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 184:4367–4374
Vaquero F, Navarro RM, Fierro JLG (2017) Influence of the solvent on the structure, morphology and performance for H2 evolution of CdS photocatalysts prepared by solvothermal method. Appl Catal B 203:753–767
Zhang J, Li W, Li Y, Zhong L, Xu C (2017) Self-optimizing bifunctional CdS/Cu2S with coexistence of light-reduced Cu0 for highly efficient photocatalytic H2 generation under visible-light irradiation. Appl Catal B 217:30–36
Yang H, Lu M, Chen D, Chen R, Li HW (2019) Efficient and rapid removal of Pb2+ from water by magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2 core-shell nanoflower attached to carbon microtube: adsorption behavior and process study. J Colloid Interface Sci 563:218–228
Ma Q, Wang H, Zhang H, Cheng X, Xie M, Cheng Q (2017) Fabrication of MnO2/TiO2 nano-tube arrays photoelectrode and its enhanced visible light photoelectrocatalytic performance and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 189:193–203
Mo Z, Xu H, Chen Z, She X, Song Y, Lian J, Zhu X, Yan P, Lei Y, Yuan S, Li H (2019) Construction of MnO2/monolayer g-C3N4 with Mn vacancies for Z-scheme overall water splitting. Appl Catal B 241:452–460
Rahmat M, Rehman A, Rahmat S, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M, Khan WS, Bajwa SZ, Rahmat R, Nazir A (2019) Highly efficient removal of crystal violet dye from water by MnO2 based nanofibrous mesh/photocatalytic process. J Mater Res Technol 8:5149–5159
Lin Y, Zhou Q, Tang D, Niessner R, Knopp D (2017) Signal-on photoelectrochemical immunoassay for aflatoxin B1 based on enzymatic product-etching MnO2 nanosheets for dissociation of carbon dots. Anal Chem 89:5637–5645
Zhang X, Zhao C, Shu Y, Wang J (2019) Gold nanoclusters/iron oxyhydroxide platform for ultrasensitive detection of butyrylcholinesterase. Anal Chem 91:15866–15872
Zhang K, Lv S, Lin Z, Li M, Tang D (2018) Bio-bar-code-based photoelectrochemical immunoassay for sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen using rolling circle amplification and enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation. Biosens Bioelectron 101:159–166
Li M, Xu X, Cai Q, Luo X, Zhou Z, Xu G, Xie Y (2019) Graphene oxide-based fluorometric determination of microRNA-141 using rolling circle amplification and exonuclease III-aided recycling amplification. Microchim Acta 186:531–537
Hu J, Zhang C (2010) Sensitive detection of nucleic acids with rolling circle amplification and surface-enhanced raman scattering spectroscopy. Anal Chem 82:8991–8997
Cheng X, Yu X, Chen L, Zhang H, Wu Y, Fu F (2017) Visual detection of ultra-trace levels of uranyl ions using magnetic bead-based DNAzyme recognition in combination with rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 184:4259–4267
Aveiro LR, da Silva AGM, Antonin VS, Candido EG, Parreira LS, Geonmonond RS, de Freitas IC, Lanza MRV, Camargo PHC, Santos MC (2018) Carbon-supported MnO2 nanoflowers: introducing oxygen vacancies for optimized volcano-type electrocatalytic activities towards H2O2 generation. Electrochim Acta 268:101–110
Ibrahim I, Lim HN, Abou-Zied OK, Huang NM, Estrela P, Pandikumar A (2016) Cadmium sulfide nanoparticles decorated with au quantum dots as ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical sensor for selective detection of copper (II) ions. J Phys Chem C 120:22202–22214
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21864013; 21802133), the Open Project Program of Key Laboratory of Functional Small Organic Molecule, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi Normal University (No. KLFS-KF-201917), and China outstanding Youth Funds of Jiangxi Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 768 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Li, J., Xiong, P. et al. Rolling circle amplification promoted magneto-controlled photoelectrochemical biosensor for organophosphorus pesticides based on dissolution of core-shell MnO2 nanoflower@CdS mediated by butyrylcholinesterase. Microchim Acta 187, 450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04434-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04434-0