Abstract
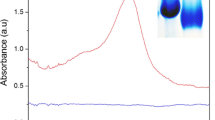
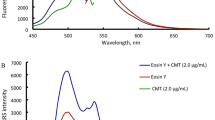
A fluorometric method for the determination of histamine has been developed based on aggregation-induced emission (AIE) effect of D-penicillamine capped copper nanoparticles (DPA-CuNPs). The fluorescent DPA-CuNPs were synthesized by a one-pot method using D-penicillamine as both reducing agent and stabilizing ligand. The size, morphology and physical chemical properties of DPA-CuNPs were examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), fluorescence spectroscopy, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and absorption spectroscopy. The DPA-CuNPs exhibit AIE effect and show intense red fluorescence (650 nm). In the presence of histamine, DPA-CuNPs are dispersed into small homogeneous particles, causing fluorescence quenching. Based on this reaction, a histamine sensor is constructed. The fluorescence of the CuNPs solution has a good linear relationship with histamine concentration in the range 0.05 μM to 5 μM and the determination limit (3σ/slope) is 30 nM. The estimated method was successfully applied to the determination of histamine in fish, pork and red wine.

Schematic representation of copper nanoparticles for histamine analysis. In the presence of histamine, the strong red fluorescence of copper nanoparticles is obvious decreased through interaction of copper nanoparticles and histamine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang X, Zhu M, Li J (2012) Biomedical effects and Nanosafety of engineered Nanomaterials: recent Progress. Chin J Chem 30(9):1931–1194. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201200662
Tang J, Xiong P, Cheng Y, Chen Y, Peng S, Zhu ZQ (2019) Enzymatic oxydate-triggered AgNPs etching: a novel signal-on photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform based on Ag@AgCl nanocubes loaded RGO plasmonic heterostructure. Biosens Bioelectron 130:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.014
Zhang C, Tang J, Huang L, Li Y, Tang D (2017) In-situ amplified voltammetric immunoassay for ochratoxin a by coupling a platinum nanocatalyst based enhancement to a redox cycling process promoted by an enzyme mimic. Microchim Acta 184:2445–2453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2223-2
Bouwmeester H, Brandhoff P, Marvin HJP, Weigel S, Peters RJB (2014) State of the safety assessment and current use of nanomaterials in food and food production. Trends Food Sci Technol 40(2):200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.08.009
Jr ONO, Iost RM, Jr JRS et al (2014) Nanomaterials for diagnosis: challenges and applications in smart devices based on molecular recognition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(17):14745–14766. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5015056
Lu YZ, Wei WT, Chen W (2012) Copper nanoclusters: synthesis, characterization and properties. Chin Sci Bull 57(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4896-y
Roto R, Yusran Y, Kuncaka A (2016) Magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles modified with Thiol Group for Chloroauric ion adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 377:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.099
Guodong F, Mingming G, Qi L et al (2016) One-pot synthesis and application of novel amino-functionalized silica nanoparticles using guanidine as amino group. New journal of chemistry 40 (10):10.1039.C1036NJ02094A. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ02094A
Han Y, Hwang G, Park S, Gomez-Flores A, Jo E, Eom IC, Tong M, Kim HJ, Kim H (2017) Stability of carboxyl-functionalized carbon black nanoparticles: the role of solution chemistry and humic acid. Environmental Science: Nano 4(4):800–810. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EN00530F
Yang X, Feng Y, Zhu S, Luo Y, Zhuo Y, Dou Y (2014) One-step synthesis and applications of fluorescent cu nanoclusters stabilized by l -cysteine in aqueous solution. Anal Chim Acta 847:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.07.019
Luo Y, Miao H, Yang X (2015) Glutathione-stabilized cu nanoclusters as fluorescent probes for sensing pH and vitamin B1. Talanta 144:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.07.001
Zhang H, Lin Z, Su X (2015) Label-free detection of exonuclease III by using dsDNA–templated copper nanoparticles as fluorescent probe. Talanta 131:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.07.065
Lin SM, Geng S, Li N, Li NB, Luo HQ (2016) D-penicillamine-templated copper nanoparticles via ascorbic acid reduction as a mercury ion sensor. Talanta 151:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.01.028
Doeun D, Davaatseren M, Chung MS (2017) Biogenic amines in foods. Food Sci Biotechnol 26(3):1463–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0239-3
Guo YY, Yang YP, Qian P et al (2015) Biogenic amines in wine: a review. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 50(7):1523–1532. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12833
Alvarez MA, Moreno-Arribas MV (2014) The problem of biogenic amines in fermented foods andthe use of potential biogenic amine-degrading microorganisms as a solution. Trends Food Sci Technol 39(2):146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.07.007
Albulushi I, Poole S, Deeth HC et al (2009) Biogenic amines in fish: roles in intoxication, spoilage, and nitrosamine formation-a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 49(4):369–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390802067514
Neumeier BL, Heck JG, Feldmann C (2019) Fluorescence-based histamine sensing with inorganic-organic hybrid nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 7(12):3543–3552. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC05658G
Ailing H, Lin X, Sijia H et al (2018) Highly bright self-assembled copper Nanoclusters: a novel Photoluminescent probes for sensitive detection of histamine. Anal Chem 90(15):9060–9067. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01384
Feng X, Ashley J, Zhou T, Halder A, Sun Y (2018) A facile molecularly imprinted polymer-based Fluorometric assay for detection of histamine. RSC Adv 8(5):2365–2372. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra11507e
Huang C, Wang S, Zhao W, Zong C, Liang A, Zhang Q, Liu X (2017) Visual and photometric determination of histamine using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(7):2249–2254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2253-9
El-Nour KMA, Salam ETA, Soliman HM et al (2017) Gold nanoparticles as a direct and rapid sensor for sensitive analytical detection of biogenic amines. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2014-z
Kumar N, Goyal RN (2018) Silver nanoparticles decorated graphene nanoribbon modified pyrolytic graphite sensor for determination of Histamine Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical S0925400518308402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.136, Silver nanoparticles decorated graphene nanoribbon modified pyrolytic graphite sensor for determination of histamine, 268, 383, 391
Dong XX, Yang JY, Luo L et al (2017) Portable amperometric immunosensor for histamine detection using Prussian blue-chitosan-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite films. Biosensors and bioelectronics 98 (15 Dec):305-309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.014
Basozabal I, Guerreiro A, Gomez-Caballero A, Aranzazu Goicolea M, Barrio RJ (2014) Direct potentiometric quantification of histamine using solid-phase imprinted nanoparticles as recognition elements. Biosens Bioelectron 58:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.054
Horemans F, Alenus J, Bongaers E, Weustenraed A, Thoelen R, Duchateau J, Lutsen L, Vanderzande D, Wagner P, Cleij TJ (2010) MIP-based sensor platforms for the detection of histamine in the nano-and micromolar range in aqueous media. Sensors Actuators B Chem 148(2):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.05.003
Jia X, Li J, Wang E (2013) Cu nanoclusters with aggregation induced emission enhancement. Small 9 (22):3873-3879. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300896
He S, Yao J, Jiang P, Shi D, Zhang H, Xie S, Pang S, Gao H (2001) Formation of silver nanoparticles and self-assembled two-dimensional ordered Superlattice. Langmuir 17(5):1571–1575. https://doi.org/10.1021/la001239w
Shon YS, Cutler E (2004) Aqueous synthesis of alkanethiolate-protected Ag nanoparticles using Bunte salts. Langmuir 20(16):6626–6630. https://doi.org/10.1021/la049417z
Andrej aa, Irena R, Drago K et al (2018) Determination of biogenic amines in cheese by ion chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry detection. J AOAC Int 101 (5):1542–1547. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.16-0006
Schievano E, Guardini K, Mammi S (2009) Fast determination of histamine in cheese by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). J Agric Food Chem 57(7):2647–2652. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803364k
Romero-González R, Alarcón-Flores MI, Vidal JLM, Frenich AG (2012) Simultaneous determination of four biogenic and three volatile amines in anchovy by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 60(21):5324–5329. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf300853p
Todoroki K, Ishii Y, Miyauchi C, Kitagawa S, Min JZ, Inoue K, Yamanaka T, Suzuki K, Yoshikawa Y, Ohashi N, Toyo’oka T (2014) Simple and sensitive analysis of histamine and Tyramine in Japanese soy sauces and their intermediates using the stable isotope dilution HILIC–MS/MS method. J Agric Food Chem 62(26):6206–6211. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf500767p
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21605019), the Research Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists in Fujian Provincial Department of Education (Development of ochratoxin A colorimetric assay based on rolling circle amplification and nanoscale enzyme) and Special Fund for Scientific and Technological Innovation at Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University of China (CXZX2018065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 371 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, Q., Wang, ZW. et al. D-penicillamine modified copper nanoparticles for fluorometric determination of histamine based on aggregation-induced emission. Microchim Acta 187, 329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04271-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04271-1