Abstract
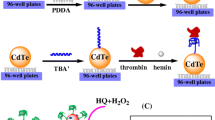
A method is presented for sensitive determination of thrombin activity. It is based on (a) the interaction between fibrinogen after activation with thrombin, and (b) an enzymatic amplification step consisting of in-situ growth of CdS quantum dots (QDs). Fibrinogen is immobilized on the surface of the wells of a microplate and then incubated with a mixture of biotinylated fibrinogen and thrombin. Thrombin activates immobilized fibrinogen and free biotinylated fibrinogen. This leads to the formation of insoluble biotinylated fibrin that remains bound on the surface of the wells. Afterwards, the samples are incubated with avidin-labeled alkaline phosphatase (ALP) which binds to biotinylated fibrin. ALP hydrolyzes the substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) under formation of phosphate ions which stabilize CdS QDs that are grown in-situ from cadmium(II) and sulfide. The generation of fibrin is correlated with the activity of thrombin. Increased thrombin concentration results in increased fluorescence that can be measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 300/510 nm. The introduction of such an amplification step (the enzyme-triggered growth of QDs) allows for the quantification of thrombin in the picomolar concentration range, with a linear response up to 2.5 pM and a detection limit of 0.05 pM. The method was applied to the determination of thrombin activity in human plasma and of the thrombin inhibitor argatroban.

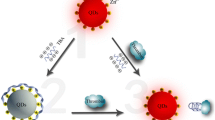
Schematic representation of a fluorometric method for determination of thrombin activity in the picomolar concentration range based on the interaction between fibrinogen after activation with thrombin, and an enzymatic amplification step consisting of in-situ growth of CdS quantum dots (CdS QD).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker RC, Spencer FA (1998) Thrombin: structure, biochemistry, measurement, and status in clinical medicine. J Thromb Thrombolysis 5:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008843925851
Strukova SM (2001) Thrombin as a regulator of inflammation and reparative processes in tissues. Biochemistry 66:8–18. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002869310180
Weaver F, Ham SW, Lew WK (2010) Thrombin use in surgery: an evidence-based review of its clinical use. J Blood Med 1:135–142. https://doi.org/10.2147/JBM.S6622
Bichler J, Heit JA, Owen WG (1996) Detection of thrombin in human blood by ex-vivo hirudin. Thromb Res 84:289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(96)00189-2
Wolberg AS (2007) Thrombin generation and fibrin clot structure. Blood Rev 21:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2006.11.001
Chang J-Y (1985) Thrombin specificity. Eur J Biochem 151:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09091.x
Yang Z, Mochalkin I, Doolittle RF (2000) A model of fibrin formation based on crystal structures of fibrinogen and fibrin fragments complexed with synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:14156–14161. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.26.14156
Pavlov V, Xiao Y, Shlyahovsky B, Willner I (2004) Aptamer-functionalized au nanoparticles for the amplified optical detection of thrombin. J Am Chem Soc 126:11768–11769. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja046970u
Chen YX, Huang KJ, He LL, Wang YH (2018) Tetrahedral DNA probe coupling with hybridization chain reaction for competitive thrombin aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron 100:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.09.022
Li J, Jiao Y, Liu Q, Chen Z (2018) Colorimetric detection of thrombin based on intensity of gold nanoparticle oligomers with dark-field microscope. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:6738–6745. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00521
Wen D, He M, Ma K, Cui Y, Kong J, Yang H, Liu Q (2018) Highly sensitive fluorometric determination of thrombin by on-chip signal amplification initiated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Microchim Acta 185:380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2903-6
Mackie IJ, Kitchen S, Machin SJ, Lowe GDO (2003) Guidelines on fibrinogen assays. Br J Haematol 121:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04256.x
Oberfrank S, Drechsel H, Sinn S, Northoff H, Gehring FK (2016) Utilisation of quartz crystal microbalance sensors with dissipation (QCM-D) for a clauss fibrinogen assay in comparison with common coagulation reference methods. Sensors 16:282. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030282
Hou S, Zhang A, Su M (2016) Nanomaterials for biosensing applications. Nanomaterials 6:58. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6040058
Li YJ, Chiu WJ, Unnikrishnan B, Huang CC (2014) Monitoring thrombin generation and screening anticoagulants through pulse laser-induced fragmentation of biofunctional nanogold on cellulose membranes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:15253–15261. https://doi.org/10.1021/am503615c
Niu Y, Wang P, Zhao Y, Fan A (2013) Turn-on colorimetric sensor for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin using fibrinogen-gold nanoparticle conjugate. Analyst 138:1475–1482. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an36269d
Chen C-K, Huang C-C, Chang H-T (2010) Label-free colorimetric detection of picomolar thrombin in blood plasma using a gold nanoparticle-based assay. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1922–1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.01.005
Lin J-H, Huang K-H, Zhan S-W, Yu C-J, Tseng W-L, Hsieh M-M (2019) Inhibition of catalytic activity of fibrinogen-stabilized gold nanoparticles via thrombin-induced inclusion of nanoparticle into fibrin: application for thrombin sensing with more than 104-fold selectivity. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 210:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.013
Chen YY, Tseng CW, Chang HY, Hung YL, Huang CC (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays for coagulation-related proteins and their inhibition reactions. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3160–3166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.12.019
Gao X, Liu X, Lin Z, Liu S, Su X (2012) CuInS2 quantum dots as a near-infrared fluorescent probe for detecting thrombin in human serum. Analyst 137:5620–5624. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35888c
Saa L, Pavlov V (2012) Enzymatic growth of quantum dots: applications to probe glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase and sense glucose. Small 8:3449–3455. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201201364
Garai-Ibabe G, Möller M, Pavlov V (2012) Ultrasensitive assay for detection of serum paraoxonase by modulating the growth of fluorescent semiconductor nanoparticles. Anal Chem 84:8033–8037. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3018857
Malashikhina N, Garai-Ibabe G, Pavlov V (2013) Unconventional application of conventional enzymatic substrate: first fluorogenic immunoassay based on enzymatic formation of quantum dots. Anal Chem 85:6866–6870. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4011342
Yin J, Zhang A, Dong C, Ren J (2015) An aptamer-based single particle method for sensitive detection of thrombin using fluorescent quantum dots as labeling probes. Talanta 144:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.034
Zhang X, Hu R, Shao N (2013) Label-free sensing of thrombin based on quantum dots and thrombin binding aptamer. Talanta 107:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.01.003
Chen Z, Tan L, Hu L, Zhang Y, Wang S, Lv F (2016) Real colorimetric thrombin Aptasensor by masking surfaces of catalytically active gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08975
Cheng T, Li X, Huang P, Wang H, Wang M, Yang W (2019) Colorimetric and electrochemical (dual) thrombin assay based on the use of a platinum nanoparticle modified metal-organic framework (type Fe-MIL-88) acting as a peroxidase mimic. Microchim Acta 186:94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3209-4
Shuai H-L, Wu X, Huang K-J (2017) Molybdenum disulfide sphere-based electrochemical aptasensors for protein detection. J Mater Chem B 5:5362–5372. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB01276D
Xiong Y, Liang M, Cheng Y, Zou J, Li Y (2019) An “off–on” phosphorescent aptasensor for the detection of thrombin based on PRET. Analyst 144:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN01571F
Lox CD, Strohm GH, Corrigan JJ Jr (1978) Radioimmunoassay of human prothrombin—the quantitation of plasma factor II antigen. Am J Hematol 4:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.2830040308
Koldas M, Uras F (2001) Avidin-biotin ELISA for measurement of prothrombin in human plasma. Thromb Res 102:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(01)00257-2
Hursting MJ, Alford KL, Becker JP, Brooks RL, Joffrion JL, Knappenberger GD, Kogan PW, Kogan TP, Mckinney AA, Schwarz RP (1997) Novastan® (brand of Argatroban): a small-molecule, direct thrombin inhibitor. Semin Thromb Hemost 23:503–516. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-996128
Morita T, Iwanaga S. (1981) Prothrombin activator from Echis carinatus venom. Methods Enzymol 80:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(81)80026-2
Virel A, Saa L, Pavlov V (2012) Quantification of prothrombin in human plasma amplified by autocatalytic reaction. Anal Chem 84:2380–2387. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac203138y
Hemker HC, Giesen P, Al Dieri R, Regnault V, De Smedt E, Wagenvoord R, Lecompte T, Béguin S (2003) Calibrated automated thrombin generation measurement in clotting plasma. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 33:4–15. https://doi.org/10.1159/000071636
Hemker HC, Giesen P, Aldieri R, Regnault V, De SE, Wagenvoord R, Lecompte T, Béguin S (2002) The calibrated automated Thrombogram (CAT): a universal routine test for hyper- and hypocoagulability. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 32:249–253
Danzer K, Currie LA (1998) Guidelines for calibration in analytical chemistry. Part I. fundamentals and single component calibration (IUPAC recommendations 1998). Pure Appl Chem 70:993–1014. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199870040993
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities/AEI/FEDER, UE (RETOS I + D – Grant No.BIO2017-88030-R and the Maria de Maeztu Units of Excellence Programme – Grant No. MDM-2017-0720).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies did not involve neither human participants nor animals. Lyophilized human plasma and other blood derived materials were obtained from Sigma Inc.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Size distribution of the CdS QDs, comparison between colorimetric and fluorogenic methods and effect of argatroban on the detection system. (DOCX 465 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saa, L., Díez-Buitrago, B., Briz, N. et al. CdS quantum dots generated in-situ for fluorometric determination of thrombin activity. Microchim Acta 186, 657 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3765-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3765-2