Abstract
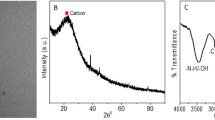
The capacitively coupled plasma (CCP) discharge of an ionic liquid solution of citric acid produces carbon dots (CDs) with excitation-independent fluorescent dual-emissions peaking at 410 nm and 480 nm. The intensity of the purple photoluminescence at 410 nm increases with (a) the flow rate of O2 plasma gas supply from 2.0 to 30 standard cubic centimeters per minute (sccm), (b) the 2-h exposure of the CDs to 254 nm light, and (c) the 8-h immersion of the CDs in a solution of NaBH4. The UV exposure and the hydride immersion reduce the fluorescence intensity peaking at 480 nm, which is highest at 5.0 and 10 sccm. The two emissive states were revealed by UV–vis absorption, XPS spectra, and time-resolved fluorescence. Control of the O2 flow rate can simply tune the ratiometric fluorescence of the CCP-CDs. The CDs obtained from 5 and 30 sccm O2 supplies present a high-intensity ratio (I480 nm/I410 nm ≈ 3.35) and a low one (≈ 0.48), respectively. The 480 nm fluorescence of the former CDs is quenched by mercury(II) ions in the 0.2 to 50 μM concentration range. The 410 nm fluorescence of the latter CDs is enhanced by norfloxacin in the 25 nM to 1.0 μM concentration range. The detection limits are 75 nM for Hg(II) and 7.3 nM for norfloxacin.

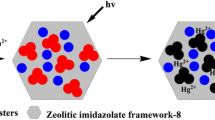
Schematic presentation of the effect of the oxygen flow rate in capacitively coupled radio frequency (RF) plasma on the formed CDs. The emission can be quenched by Hg2+ or enhanced by norfloxacin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De B, Karak N (2017) Recent progress in carbon dot–metal based nanohybrids for photochemical and electrochemical applications. J Mater Chem A 5:1826–1859
Peng Z, Han X, Li S, Al-Youbi AO, Bashammakh AS, El-Shahawi MS, Leblanc RM (2017) Carbon dots: biomacromolecule interaction, bioimaging and nanomedicine. Coord Chem Rev 343:256–277
Ke C-B, Lu T-L, Chen J-L (2018) Capacitively coupled plasma discharge of ionic liquid solutions to synthesize carbon dots as fluorescent sensors. Nanomaterials 8:372–383
Zhu A, Qu Q, Shao X, Kong B, Tian Y (2012) Carbon-dot-based dual-emission nanohybrid produces a ratiometric fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of cellular copper ions. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:7185–7189
Liu X, Zhang N, Bing T, Shangguan D (2014) Carbon dots based dual-emission silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric nanosensor for Cu2+. Anal Chem 86:2289–2296
Lu L, Feng C, Xu J, Wang F, Yu H, Xu Z, Zhang W (2017) Hydrophobic-carbon-dot-based dual-emission micelle for ratiometric fluorescence biosensing and imaging of Cu2+ in liver cells. Biosens Bioelectron 92:101–108
Wang C, Lin H, Xu Z, Huang Y, Humphrey MG, Zhang C (2016) Tunable carbon-dot-based dual-emission fluorescent nanohybrids for ratiometric optical thermometry in living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6621–6628
Dong Y, Cai J, Fang Q, You X, Chi Y (2016) Dual-emission of lanthanide metal−organic frameworks encapsulating carbon-based dots for ratiometric detection of water in organic solvents. Anal Chem 88:1748–1752
Wu J-X, Yan B (2017) A dual-emission probe to detect moisture and water in organic solvents based on green-Tb3+ post-coordinated metal–organic frameworks with red carbon dots. Dalton Trans 46:7098–7105
Shangguan J, He D, He X, Wang K, Xu F, Liu J, Tang J, Yang X, Huang J (2016) Label-free carbon-dots-based ratiometric fluorescence pH nanoprobes for intracellular pH sensing. Anal Chem 88:7837–7843
Zhao J, Huang M, Zhang L, Zou M, Chen D, Huang Y, Zhao S (2017) Unique approach to develop carbon dot-based nanohybrid near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent sensor for the detection of mercury ions. Anal Chem 89:8044–8049
He Y, He J, Wang L, Yu Z, Zhang H, Liu Y, Lei B (2017) Synthesis of double carbon dots co-doped mesoporous Al2O3 for ratiometric fluorescent determination of oxygen. Sensors Actuators B Chem 251:918–926
Yan F, Bai Z, Liu F, Zu F, Zhang R, Xu J, Chen L (2018) Ratiometric fluorescence probes based on carbon dots. Curr Org Chem 22:57–66
Barati A, Shamsipur M, Abdollahi H (2016) Carbon dots with strong excitation-dependent fluorescence changes towards pH. Application as nanosensors for a broad range of pH. Anal Chim Acta 931:25–33
Chandra A, Singh N (2017) Biocompatible fluorescent carbon dots for ratiometric intracellular pH sensing. ChemistrySelect 2:5723–5728
Wang R, Wang X, Sun Y (2017) Aminophenol-based carbon dots with dual wavelength fluorescence emission for determination of heparin. Microchim Acta 184:187–193
Zhu S, Song Y, Zhao X, Shao J, Zhang J, Yang B (2015) The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): current state and future perspective. Nano Res 8:355–381
Wang W, Wang B, Embrechts H, Damm C, Cadranel A, Strauss V, Distaso M, Hinterberger V, Guldi DM, Peukert W (2017) Shedding light on the effective fluorophore structure of high fluorescence quantum yield carbon nanodots. RSC Adv 7:24771–24780
Song Y, Zhu S, Zhang S, Fu Y, Wang L, Zhao X, Yang B (2015) Investigation from chemical structure to photoluminescent mechanism: a type of carbon dots from the pyrolysis of citric acid and an amine. J Mater Chem C 3:5976–5984
Nie H, Li M, Li Q, Liang S, Tan Y, Sheng L, Shi W, Zhang SX-A (2014) Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem Mater 26:3104–3112
Ding H, Ji Y, Wei J-S, Gao Q-Y, Zhou Z-X, Xiong H-M (2017) Facile synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots from pulp-free lemon juice for bioimaging. J Mater Chem B 5:5272–5277
Song Y, Zhu S, Xiang S, Zhao X, Zhang J, Zhang H, Fu Y, Yang B (2014) Investigation into the fluorescence quenching behaviors and applications of carbon dots. Nanoscale 6:4676–4682
Xiong Y, Schneider J, Reckmeier CJ, Huang H, Kasák P, Rogach AL (2017) Carbonization conditions influence the emission characteristics and the stability against photobleaching of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Nanoscale 9:11730–11738
Zheng H, Wang Q, Long Y, Zhang H, Huang X, Zhu R (2011) Enhancing the luminescence of carbon dots with a reduction pathway. Chem Commun 47:10650–10652
Zhu S, Zhang J, Tang S, Qiao C, Wang L, Wang H, Liu X, Li B, Li Y, Yu W, Wang X, Sun H, Yang B (2012) Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: from fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv Funct Mater 22:4732–4740
Zhu S, Shao J, Song Y, Zhao X, Du J, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang K, Zhang J, Yang B (2015) Investigating the surface state of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 7:7927–7933
Yang M, Li H, Liu J, Kong W, Zhao S, Li C, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2014) Convenient and sensitive detection of norfloxacin with fluorescent carbon dots. J Mater Chem B 2:7964–7970
Hua J, Jiao Y, Wang M, Yang Y (2018) Determination of norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin by carbon dots fluorescence enhancement using magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent. Microchim Acta 185:137–145
Acknowledgments
Support for this work by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant No. MOST–106–2113–M–039–006 and the China Medical University under Grant No. CMU106–S–17 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6.41 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, CB., Lu, TL. & Chen, JL. Excitation-independent dual emissions of carbon dots synthesized by plasma irradiation of ionic liquids: Ratiometric fluorometric determination of norfloxacin and mercury(II). Microchim Acta 186, 376 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3505-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3505-7