Abstract
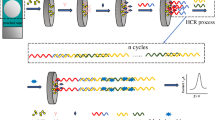
An amperometric aptasensor is reported for the electrochemical determination of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). It is based on a combination of EpCAM-driven toehold-mediated DNA recycling amplification, the specific recognition of EpCAM aptamer, and its binding to EpCAM. Hairpin probe 1 (Hp1) with a toehold region was modified with a 5′-thiol group (5’-SH) and self-assembled onto the surface of a gold electrode. Upon addition of EpCAM, the probe A (a 15-mer) is liberated from the aptamer/probe A complex and then hybridizes with the toehold domain of Hp1. This results in the exposure of another toehold for further hybridizing with hairpin probe 2 (Hp2) to displace probe A in the presence of Hp2 that was labeled with the electrochemical probe Methylene Blue (MB). Subsequently, liberated probe A is hybridized again with another Hp1 to start the next round of DNA recycling amplification by reusing probe A. This leads to the formation of plenty of MB-labeled DNA strands on the electrode surface and generates an amplified current. This 1:N probe-response amplification results in ultrasensitive and specific detection of EpCAM, with a 20 pg·mL−1 detection limit. The electrode is highly stable and regenerable. It was successfully applied to the determination of EpCAM in spiked human serum, urine and saliva, and thus provides a promising tool for early clinical diagnosis.

Schematic illustration of the electrochemical detection for EpCAM. The method is based on aptamer-based recognition and EpCAM-driven toehold-mediated DNA recycling amplification. Hp1: Hairpin probe 1; Hp2: Hairpin probe 2; MB: Methylene blue; MCH: 6-Mercapto-1-hexanol; EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang B, Zhou H, Luo Y, Tang R, Zheng S (2014) Biological interfacial engineering for metastatic cancer diagnosis and intervention. Curr Med Chem 21(22):2510–2521
Chinen AB, Guan CM, Ferrer JR, Barnaby SN, Merkel TJ, Mirkin CA (2015) Nanoparticle probes for the detection of cancer biomarkers, cells, and tissues by fluorescence. Chem Rev 115(19):10530–10574
Huhn S, Weinhold N, Nickel J, Pritsch M, Hielscher T, Hummel M, Bertsch U, Huegle-Doerr B, Vogel M, Angermund R, Hanuel M, Salwender HJ, Weisel K, Dürig J, Görner M, Kirchner H, Peter N, Graeven U, Lordick F, Hoffmann M, Reimer P, Blau IW, Jauch A, Dembowsky K, Möhler T, Wuchter P, Goldschmidt H (2017) Circulating tumor cells as a biomarker for response to therapy in multiple myeloma patients treated within the GMMG-MM5 trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 52(8):1194–1198
Shi J, Lyu J, Tian F, Yang M (2017) A fluorescence turn-on biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets for epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) detection. Biosens Bioelectron 93:182–188
Alhanafy A, Shafei ME, Safan M, Elnour EA, Habib M, Rageh T, Salah El-Din A (2017) Circulating cell free DNA as a biomarker in the serum of colorectal cancer patients. Annal Oncol 28(suppl_7):vii31–vii32
Golubnitschaja O, Flammer J (2007) What are the biomarkers for glaucoma? Sur Ophthalmol 52(Suppl 2):S155–S161
Sadeghi S, Hojati Z, Tabatabaeian H (2017) Cooverexpression of EpCAM and c-myc genes in malignant breast tumours. J Genet 96(1):109–118
Zhang D, Liu X, Gao J, Sun Y, Liu T, Yan Q, Yang X (2017) The role of epithelial cell adhesion molecule N-glycosylation on apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol 39(3):1–8
Roca E, Lacroix R, Judicone C, Laroumagne S, Robert S, Cointe S, Muller A, Kaspi E, Roll P, Brisson AR, Tantucci C, Astoul P, Dignat-George F (2016) Detection of EpCAM-positive microparticles in pleural fluid: a new approach to mini-invasively identify patients with malignant pleural effusions. Oncotarget 7(3):3357–3366
Munz M, Baeuerle PA, Gires O (2009) The emerging role of EpCAM in cancer and stem cell signaling. Cancer Res 69(14):5627–5629
Bravo K, Ortega FG, Messina GA, Sanz MI, Fernandez-Baldo MA, Raba J (2017) Integrated bio-affinity nano-platform into a microfluidic immunosensor based on monoclonal bispecific trifunctional antibodies for the electrochemical determination of epithelial cancer biomarker. Clin Chim Acta 464:64–71
Song Y, Zhu Z, An Y, Zhang W, Zhang H, Liu D, Yu C, Duan W, Yang CJ (2013) Selection of DNA aptamers against epithelial cell adhesion molecule for cancer cell imaging and circulating tumor cell capture. Anal Chem 85(8):4141–4149
Wallwiener CW, Wallwiener M, Kurth RR, Rohm C, Neubauer H, Banys MJ, Staebler A, Schönfisch B, Meuer SC, Giese T, Fehm TN (2011) Molecular detection of breast cancer metastasis in sentinel lymph nodes by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR): identifying, evaluating and establishing multi-marker panels. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130(3):833–844
Phattarataratip E, Masorn M, Jarupoonphol W, Supatthanayut S, Saeoweiang P (2016) Differential expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule in salivary gland neoplasms. Ann Diagn Pathol 24:62–67
Das P, Krull UJ (2017) Detection of a cancer biomarker protein on modified cellulose paper by fluorescence using aptamer-linked quantum dots. Analyst 142(17):3132–3135
Ortega FG, Fernández-Baldo MA, Serrano MJ, Messina GA, Lorente JA, Raba J (2015) Epithelial cancer biomarker EpCAM determination in peripheral blood samples using a microfluidic immunosensor based in silver nanoparticles as platform. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 221:248–256
Fernández-Baldo MA, Ortega FG, Pereira SV, Bertolino FA, Serrano MJ, Lorente JA, Raba J, Messina GA (2016) Nanostructured platform integrated into a microfluidic immunosensor coupled to laser-induced fluorescence for the epithelial cancer biomarker determination. Microchem J 2128:18–25
Jung YK, Woo MA, Soh HT, Park HG (2014) Aptamer-based cell imaging reagents capable of fluorescence switching. Chem Commun 50(82):12329–12332
Xu Y, Zhou W, Zhou M, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) Toehold strand displacement-driven assembly of G-quadruplex DNA for enzyme-free and non-label sensitive fluorescent detection of thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 64:306–310
Yang D, Ning L, Gao T, Ye Z, Li G (2015) Enzyme-free dual amplification strategy for protein assay by coupling toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement reaction with hybridization chain reaction. Electrochem Commun 58:33–36
Zhang H, Wang Q, Yang X, Wang K, Li Q, Li Z, Gao L, Nie W, Zheng Y (2017) An isothermal electrochemical biosensor for the sensitive detection of microRNA based on a catalytic hairpin assembly and supersandwich amplification. Analyst 142(2):389–396
Zhang ZZ, Zhang CY (2012) Highly sensitive detection of protein with aptamer-based target-triggering two-stage amplification. Anal Chem 84(3):1623–1629
Bi S, Cui Y, Dong Y, Zhang N (2014) Target-induced self-assembly of DNA nanomachine on magnetic particle for multi-amplified biosensing of nucleic acid, protein, and cancer cell. Biosens Bioelectron 53(4):207–213
Han C, Li R, Li H, Liu S, Xu C, Wang J, Wang Y, Huang J (2017) Ultrasensitive voltammetric determination of kanamycin using a target-triggered cascade enzymatic recycling couple along with DNAzyme amplification. Microchim Acta 184(8):2941–2948
Wang S, Yang F, Jin D, Dai Q, Tu J, Liu Y, Ning Y, Zhang GJ (2017) Toehold mediated one-step conformation-switchable "signal-on" electrochemical DNA sensing enhanced with homogeneous enzymatic amplification. Anal Chem 89(10):5349–5356
Khodakov DA, Khodakova AS, Linacre A, Ellis AV (2013) Toehold-mediated nonenzymatic DNA strand displacement as a platform for DNA genotyping. J Am Chem Soc 135(15):5612–5619
Wang L, Fang L, Liu S (2015) Responsive hairpin DNA aptamer switch to program the strand displacement reaction for the enhanced electrochemical assay of ATP. Analyst 140(17):5877–5880
Meng Y, Hun X, Zhang Y, Luo X (2016) Toehold-aided DNA recycling amplification using hemin and G-quadruplex reporter DNA on magnetic beads as tags for chemiluminescent determination of riboflavin. Microchim Acta 183(11):2965–2971
Yin D, Tao Y, Tang L, Li W, Zhang Z, Li J, Xie G (2017) Cascade toehold-mediated strand displacement along with non-enzymatic target recycling amplification for the electrochemical determination of the HIV-1 related gene. Microchim Acta 184(10):3721–3728
Chen L, Sha L, Qiu Y, Wang G, Jiang H, Zhang X (2015) An amplified electrochemical aptasensor based on hybridization chain reactions and catalysis of silver nanoclusters. Nano 7(7):3300–3308
Cao Y, Zhu S, Yu J, Zhu X, Yin Y, Li G (2012) Protein detection based on small molecule-linked DNA. Anal Chem 84(10):4314–4320
Chen HG, Ren W, Jia J, Feng J, Gao ZF, Li NB, Luo HQ (2016) Fluorometric detection of mutant DNA oligonucleotide based on toehold strand displacement-driving target recycling strategy and exonuclease III-assisted suppression. Biosens Bioelectron 77:40–45
Liu Y, Tuleouva N, Ramanculov E, Revzin A (2010) Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for interferon gamma detection. Anal Chem 82(19):8131–8136
Acknowledgements
These works were supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Nos.D20172101), the Foundationfor Innovative Research Team of Hubei University of Medicine (2014CXG04), the Science and Technology Key Program of Shiyan (Nos. 16Y70, 17 K74 and 17Y49), the School Foundation for Hubei University of Medicine (No.FDFR201614) and the Key Discipline Project of Hubei University of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 478 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Hu, W., Shang, B. et al. Ultrasensitive amperometric aptasensor for the epithelial cell adhesion molecule by using target-driven toehold-mediated DNA recycling amplification. Microchim Acta 185, 202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2739-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2739-0