Abstract
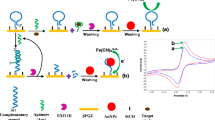
The authors describe a voltammetric method for the determination of arsenite [As(III)] based on an As(III)-specific binding probe DNA (SBP DNA; a single-stranded DNA) and the electrochemical indicator Methylene Blue (MB). The SBP DNA was first hybridized with a capture probe (CP) DNA on the surface of a gold electrode. Then, MB was intercalated into the SBP/CP hybrid on the electrode. On addition of As(III), it specifically binds to the SBP DNA, and this results in a conformational change and the dissociation of the SBP DNA from the electrode into solution. Consequently, the amount of MB remaining on the modified electrode is reduced, and this decreases the peak current of MB (best measured at −0.28 V vs. SCE). The findings are exploited in an assay for As(III) that has a linear response in the 0.1 to 200 ppb concentration range and a detection limit as low as 75 ppt. Conceivably, this method can be extended by designing various specific ssDNA oligonucleotides for other heavy metal ions or for small molecules.

Electrochemical method for trace As(III) detection based on As(III)-induced specific binding probe ssDNA (SBP DNA) conformational change and the electrochemical indicator Methylene blue (MB). CP refers to capture probe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma J, Sengupta MK, Yuan D, Dasgupta PK (2014) Speciation and detection of arsenic in aqueous samples: a review of recent progress in non-atomic spectrometric methods. Anal Chim Acta 831:1–23. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2014.04.029
Sharma VK, Sohn M (2009) Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ Int 35:743–759. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2009.01.005
WHO Arsenic:WHO response http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs372/en/ Accessed June 2016
Huang M, Chen X, Zhao Y, Chan CY, Wang W, Wang X, Wong MH (2014) Arsenic speciation in total contents and bioaccessible fractions in atmospheric particles related to human intakes. Environ Pollut 188:37–44. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.001
Sitko R, Janik P, Zawisza B, Talik E, Margui E, Queralt I (2015) Green approach for Ultratrace determination of divalent metal ions and arsenic species using Total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and Mercapto-modified graphene oxide Nanosheets as a novel adsorbent. Anal Chem 87:3535–3542. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00283
Fendorf S, Michael HA, van Geen A (2010) Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in south and Southeast Asia. Science 328:1123–1127. doi:10.1126/science.1172974
EPA drinking water requirements for states and public water systems: chemical contaminant rules-Background Information on Arsenic. http://water.epa.gov/lawsregs/rulesregs/sdwa/arsenic/regulations.cfm Accessed Nov 2013
Rabieh S, Bagheri M, Planer-Friedrich B (2013) Speciation of arsenite and arsenate by electrothermal AAS following ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Microchim Acta 180:415–421. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0946-2
Hassanpoor S, Khayatian G, Azar ARJ (2015) Ultra-trace determination of arsenic species in environmental waters, food and biological samples using a modified aluminum oxide nanoparticle sorbent and AAS detection after multivariate optimization. Microchim Acta 182:1957–1965. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1532-6
Musil S, Matoušek T, Currier JM, Stýblo M, Dědina J (2014) Speciation analysis of arsenic by selective hydride generation-Cryotrapping-atomic fluorescence spectrometry with flame-in-gas-shield atomizer: achieving extremely low detection limits with inexpensive instrumentation. Anal Chem 86:10422–10428. doi:10.1021/ac502931k
Wu Y, Zhan S, Wang F, He L, Zhi W, Zhou P (2012) Cationic polymers and aptamers mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of arsenic (III) in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 48:4459–4461. doi:10.1039/c2cc30384a
Liang RP, Wang ZX, Zhang L, Qiu JD (2013) Label-free colorimetric detection of Arsenite utilizing G−/T-rich oligonucleotides and unmodified au nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 19:5029–5033. doi:10.1002/chem.201203402
Gong L, Du B, Pan L, Liu Q, Yang K, Wang W, Zhao H, Wu L, He Y (2017) Colorimetric aggregation assay for arsenic(III) using gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:1185–1190. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2122-6
Roy S, Palui G, Banerjee A (2012) The as-prepared gold cluster-based fluorescent sensor for the selective detection of As III ions in aqueous solution. Nano 4:2734–2740. doi:10.1039/c2nr11786j
Zhou Y, Huang X, Liu C, Zhang R, Gu X, Guan G, Jiang C, Zhang L, Du S, Liu B, Han M-Y, Zhang Z (2016) Color-multiplexing-based fluorescent test paper: dosage-sensitive visualization of arsenic(III) with discernable scale as low as 5 ppb. Anal Chem 88:6105–6109. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01248
Wu Y, Zhan S, Xing H, He L, Xu L, Zhou P (2012) Nanoparticles assembled by aptamers and crystal violet for arsenic(iii) detection in aqueous solution based on a resonance Rayleigh scattering spectral assay. Nano 4:6841–6849. doi:10.1039/c2nr31418e
Li J, Chen L, Lou T, Wang Y (2011) Highly sensitive SERS detection of As3+ ions in aqueous media using glutathione functionalized silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:3936–3941. doi:10.1021/am200810x
Song L, Mao K, Zhou X, Hu J (2016) A novel biosensor based on Au@Ag core–shell nanoparticles for SERS detection of arsenic (III). Talanta 146:285–290. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.052
Lan Y, Luo H, Ren X, Wang Y, Liu Y (2012) Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of arsenic(III) using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold-palladium bimetallic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 178:153–161. doi:10.1007/s00604-012-0827-0
Zhou S-F, Han X-J, Fan H-L, Zhang Q-X, Liu Y-Q (2015) Electrochemical detection of As (III) through mesoporous MnFe2O4 nanocrystal clusters by square wave stripping voltammetry. Electrochim Acta 174:1160–1166. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.06.036
Devi P, Bansod B, Kaur M, Bagchi S, Nayak MK (2016) Co-electrodeposited rGO/MnO2 nanohybrid for arsenite detection in water by stripping voltammetry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 237:652–659. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.124
Cui L, Wu J, Ju H (2016) Label-free signal-on aptasensor for sensitive electrochemical detection of arsenite. Biosens Bioelectron 79:861–865. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.01.010
Luong JH, Lam E, Male KB (2014) Recent advances in electrochemical detection of arsenic in drinking and ground waters. Anal Methods 6:6157–6169. doi:10.1039/c4ay00817k
Liu Z-G, Huang X-J (2014) Voltammetric determination of inorganic arsenic. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 60:25–35. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2014.04.014
Gupta R, Gamare JS, Pandey AK, Tyagi D, Kamat JV (2016) Highly sensitive detection of Arsenite based on its affinity toward ruthenium nanoparticles decorated on glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chem 88:2459–2465. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04625
Moghimi N, Mohapatra M, Leung KT (2015) Bimetallic nanoparticles for arsenic detection. Anal Chem 87:5546–5552. doi:10.1021/ac504116d
Cui L, Wu J, Ju H (2015) Electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions with inorganic, organic and bio-materials. Biosens Bioelectron 63:276–286. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.052
Saidur MR, Aziz ARA, Basirun WJ (2017) Recent advances in DNA-based electrochemical biosensors for heavy metal ion detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 90:125–139. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.039
Liu R, Chen Z, Wang Y, Cui Y, Zhu H, Huang P, Li W, Zhao Y, Tao Y, Gao X (2011) Nanoprobes: quantitatively detecting the femtogram level of arsenite ions in live cells. ACS Nano 5:5560–5565. doi:10.1021/nn200994r
Farjami E, Clima L, Gothelf KV, Ferapontova EE (2010) DNA interactions with a methylene blue redox indicator depend on the DNA length and are sequence specific. Analyst 135:1443–1448. doi:10.1039/c0an00049c
Hou T, Li W, Liu X, Li F (2015) Label-free and enzyme-free homogeneous electrochemical biosensing strategy based on hybridization chain reaction: a facile, sensitive, and highly specific MicroRNA assay. Anal Chem 87:11368–11374. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02790
Park N, Hahn JH (2004) Electrochemical sensing of DNA hybridization based on duplex-specific charge compensation. Anal Chem 76:900–906. doi:10.1021/ac026368r
Wang Y, Wang P, Wang Y, He X, Wang K (2015) Single strand DNA functionalized single wall carbon nanotubes as sensitive electrochemical labels for arsenite detection. Talanta 141:122–127. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.03.040
Sakira AK, Somé IT, Ziemons E, Dejaegher B, Mertens D, Hubert P, Kauffmann JM (2015) Determination of arsenic(III) at a nanogold modified solid carbon paste electrode. Electroanalysis 27:309–316. doi:10.1002/elan.201400485
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675078, 21475056), the Program for Major Academic and Technical Leaders of Jiangxi Province (20123BCB22003, 20162BCB22013) and the Landing Project of Science and Technology of Colleges in Jiangxi Province (KJLD13010, KJLD14009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 182 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, S., Zhang, C., Liang, R. et al. Highly sensitive voltammetric determination of arsenite by exploiting arsenite-induced conformational change of ssDNA and the electrochemical indicator Methylene Blue. Microchim Acta 184, 4047–4054 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2432-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2432-8