Abstract
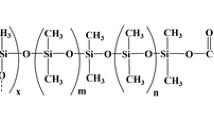
The authors have synthesized a superhydrophobic silica aerogel by using a sol-gel technique. The material is shown to be an efficient sorbent for needle trap microextraction of chlorobenzenes. Hydrophobicity affects the performance of the sorbent as shown by altering the ratio between tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) and methyltrimethoxysilane when synthesizing the sorbent. The observed contact angle (which is >150°) underpins the superhydrophobic properties of the aerogel. The microstructure of the sorbent was investigated by BET adsorption, revealing a surface area above 1000 m2 g−1. The sorbent was applied to needle trap extraction of chlorobenzenes from aqueous samples, and their subsequent determination by GC/MS. The effects of extraction temperature and extraction time, ionic strength, desorption temperature and time were optimized. The method has a detection limit range of 0.4–1.1 ng mL−1, and quantification limits from 2.2 to 7.3 ng L−1. The relative standard deviations (at a level of 10 ngL−1) are between 4 and 8% (for n = 3). The calibration plots for chlorobenzenes are linear in the 2 to 100 ng L-1 concentration range. The method was successfully applied to the analysis of water samples, and relative recoveries were between 88 and 109%.

Schematic presentation of new method for needle-trap microextraction of chlorobenzenes by using a superhydrophobic sol/gel-based silica aerogel as a sorbent.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62:2145–2148. doi:10.1021/ac00218a019
Bagheri H, Ayazi Z, Aghakhani A (2011) A novel needle trap sorbent base on carbon nanotube-sol-gel for microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aquatic media. Anal Chim Acta 683:212–220. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.10.026
Bagheri H, Aghakhani A, Akbari A, Ayazi Z (2011) Electrospun composite of polypyrrole-polyamide as a micro-solid phase extraction sorbent. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:3607–3613. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4993-4
Wang Y, Xie J, Wu Y, Hu X (2014) A magnetic metal-organic framework as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of copper (II), and its determination by electrothermal AAS. Microchim Acta 181:949–956. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1183-z
Rezvani M, Asgharinezhad AA, Ebrahimzadeh H, Shekari N (2014) A polyaniline-magnetite nanocomposite as an anion exchange sorbent for solid-phase extraction of chromium(VI) ions. Microchim Acta 181:1887–1895. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1262-1
Bagheri H, Asgari S, Piri-Moghadam H (2014) On-line micro solid-phase extraction of Clodinafop Propargyl from water, soil and wheat samples using electrospun polyamide nanofibers. Chromatographia 77:723–728. doi:10.1007/s10337-014-2660-6
Bagheri H, Roostaie A (2012) Aniline-silica nanocomposite as a novel solid phase microextraction fiber coating. J Chromatogr A 1238:22–29. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.027
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol-gel science. The physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic Press, New-York
Shao Z, Luo F, Cheng X, Zhang Y (2013) Superhydrophobic sodium silicate based silica aerogel prepared by ambient pressure drying mater. Chem Phys 141:570–575. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.05.064
Xu L, Xiao G, Chen C, Li R, Mai YY, Sun G, Yan D (2015) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic graphene aerogel prepared by facile chemical reduction. J Mater Chem A 3:7498–7504. doi:10.1039/C5TA00383K
Lermontov SA, Straumal EA, Mazilkin AA, Zverkova II, Baranchikov AE, Straumal BB, Ivanov VK (2016) How to tune the alumina aerogels structure by the variation of a supercritical solvent. Evolution of the structure during heat treatment. J Phys Chem C 6:3319–3325. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b10461
Fei T, Chen H, Lin J (2014) Transparent superhydrophobic films possessing high thermal stability and improved moisture resistance from the deposition of MTMS-based aerogels. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 443:255–264. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.11.027
Kistler SS (1932) Coherent expanded aerogels. J Phys Chem 36:52–64. doi:10.1021/j150331a003
Roach P, Shirtcliffe NJ, Newton MI (2008) Progess in superhydrophobic surface development. Soft Matter 4:224–240. doi:10.1039/b712575p
Edmiston PL, West LJ, Chin A, Mellor N, Barth D (2016) Adsorption of Gas Phase Organic Compounds by Swellable Organically Modified Silica 55: 12068–12079. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02403
Prakash SS, Brinker CJ, Hurd AJ, Rao SM (1995) Silica aerogel films prepared at ambient pressure by using surface derivatization to induce reversible drying shrinkage. Nature 374:439–443. doi:10.1038/374439a0
Zhu JJ, Xie JM, Lü XM, Jiang DL (2009) Synthesis and characterization of superhydrophobic silica and silica/titania aerogels by sol-gel method at ambient pressure. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 342:97–101. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.04.016
Sarawade PB, Kim JK, Hilonga A, Kim HT (2010) Production of low-density sodium silicate-based hydrophobic silica aerogel beads by a novel fast gelation process and ambient pressure drying process. Solid State Sci 12:911–918. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.01.032
Saraji M, Mehrafza N (2015) Polysiloxane coated steel fibers for solid-phase microextraction of chlorobenzenes. Microchim Acta 182:841–848. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1395-2
Bagheri H, Roostaie A (2014) Electrospun modified silica-polyamide nanocomposite as a novel fiber coating. J Chromatogr A 1324:11–20. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.11.024
Vidala L, Canalsa A, Kalogerakisb N (2005) Psillakisb E headspace single-drop microextraction for the analysis of chlorobenzenes in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1089:25–30. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.06.058
Alonso M, Cerdan L, Godayol A, Antic E, Sanchez JM (2011) Headspace needle-trap analysis of priority volatile organic compounds from aqueous samples: application to the analysis of natural and waste waters. J Chromatogr A 1218:8131–8139. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.09.042
Acknowledgements
The Research Council (Grant number G940603) and Graduates School of Sharif University of Technology (SUT) are acknowledged for supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 570 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baktash, M.Y., Bagheri, H. A superhydrophobic silica aerogel with high surface area for needle trap microextraction of chlorobenzenes. Microchim Acta 184, 2151–2156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2212-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2212-5