Abstract
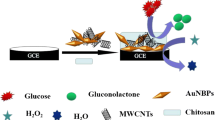
Three-dimensional nanoporous copper (NPC) was fabricated by dealloying ribbons of an Al-Cu alloy. NPC possesses a clean metal surface and high electrical conductivity. Subsequently, a non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor was obtained by modifying a glassy carbon electrode with nanocomposites containing nanoporous copper and carbon black (NPC-CB) in a nafion matrix. The sensor, if operated at a working voltage of 0.6 V (vs. SCE) in 50 mM NaOH solution, has a linear analytical range that extends from 6.0 μM to 3.4 mM of glucose, and a 2.6 μM detection limit (at an S/N ratio of 3). It also shows good selectivity over ascorbic acid, uric acid, dopamine and carbohydrates (fructose, saccharose, and maltose). The sensor also has a rapid amperometric response to hydrogen peroxide which can be quantified with a 1.2 μM detection limit.

Nanoporous copper (NPC) was fabricated by dealloying ribbons of an Al-Cu alloy. NPC exhibits three-dimensional nanoporous structure. A nanocomposite made from NPC and carbon black in a nafion matrix shows good sensing performance toward glucose and H2O2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heller A, Feldman B (2008) Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem Rev 108:2482–2505
Chen XM, Wu GH, Cai ZX, Oyama M, Chen X (2014) Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 181:689–705
Zhao L, Wu GH, Cai ZX, Zhao TT, Yao QH, Chen X (2015) Ultrasensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensing at near-neutral pH values via anodic stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon electrode modified with Pt3Pd nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 182:2055–2060
Mei H, Wu WQ, Yu BB, Li YB, Wu HM, Wang SG, Xia QH (2015) Non-enzymatic sensing of glucose at neutral pH values using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon supported Co@ Pt core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:2055–2060
Rui Q, Komori K, Tian Y, Liu HQ, Luo YP, Sakai Y (2010) Electrochemical biosensor for the detection of H2O2 from living cancer cells based on ZnO nanosheets. Anal Chim Acta 670:57–62
Zhai DY et al. (2013) Highly sensitive glucose sensor based on Pt nanoparticle/polyaniline hydrogel heterostructures. ACS Nano 4:3540–3546
Wang GF, He XP, Wang LL, Gu AX, Huang Y, Fang B, Geng BY, Zhang XJ (2013) Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 180:161–186
Wang J (2008) Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem Rev 108:814–825
Guo C, Huo H, Han X, Xu C, Li H (2014) Ni/CdS bifunctional Ti@TiO2 core-shell nanowire electrode for high-performance nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Anal Chem 86:876–883
Chen XM, Tian XT, Zhao LM, Huang ZY (2014) Nonenzymatic sensing of glucose at neutral pH values using a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene nanosheets and Pt-Pd bimetallic nanocubes. Microchim Acta 181:783–789
Wang J, Zhang WD (2011) Fabrication of CuO nanoplatelets for highly sensitive enzyme-free determination of glucose. Electrochim Acta 56:7510–7516
Zhuang ZJ, Su XD, Yuan HY, Sun Q, Xiao D, Choi MMF (2008) An improved sensitivity non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on a CuO nanowire modified Cu electrode. Analyst 133:126–132
Reitz E, Jia W, Gentile M, Wang Y, Lei Y (2008) CuO nanospheres based nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanalysis 20:2482–2486
Sahay R, Sundaramurthy J, Kumar PS, Thavasi V, Mhaisalkar SG, Ramakrishna S (2012) Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanofibers, and investigation for its suitability as blocking layer in ZnO NPs based dye sensitized solar cell and as photocatalyst in organic dye degradation. J Solid State Chem 186:261–267
Zhang YC, Su L, Dan M (2012) Ultrasensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose detection using copper nanowires. Biosens Bioelectron 31:426–432
Liu GY, Zheng BZ, Jiang YS, Cai YQ (2012) Improvement of sensitive CuO NFs-ITO nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on in situ electrospun fiber. Talanta 101:24–31
Xu CX, Wang LQ, Wang RY, Wang K, Zhang Y, Tian F, Ding Y (2009) Nanotubular mesoporous bimetallic nanostructures with enhanced electrocatalytic performance. Adv Mater 21:2165–2169
Yu F, Ahl S, Caminade AM, Majoral JP, Knoll W, Erlebacher J (2006) Simultaneous excitation of propagating and localized surface plasmon resonance in nanoporous gold membranes. Anal Chem 78:7346–7350
Huang JF, Sun IW (2005) Fabrication and surface functionalization of nanoporous gold by electrochemical alloying/dealloying of Au-Zn in an ionic liquid, and the self-assembly of L-Cysteine monolayers. Adv Funct Mater 15:989–994
Smith AJ, Tran T, Wainwright MS (1999) Kinetics and mechanism of the preparation of Raney® copper. J Appl Electrochem 29:1085–1094
Liu W, Zhang S, Li N, Zheng J, Xing Y (2012) Fabrication and dealloying behavior of monolithic nanoporous copper ribbons with bimodal channel size distributions. J Mater Sci Technol 8:693–699
Li M, Zhou YZ, Geng HR (2012) Fabrication of nanoporous copper ribbons by dealloying of Al-Cu alloys. J Porous Mater 19:791–796
Xu CX, Wang JP, Zhou JH (2013) Nanoporous PtNi alloy as an electrochemical sensor for ethanol and H2O2. Sensors Actuators B 182:408–415
Xu CX, Sun FL, Gao H, Wang JP (2013) Nanoporous platinum-cobalt alloy for electrochemical sensing for ethanol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. Anal Chim Acta 780:20–27
Wang JP, Gao H, Sun FL, Xu CX (2014) Nanoporous PtAu alloy as an electrochemical sensor for glucose and hydrogen peroxide. Sensors Actuators B 191:612–618
Bai YF, Xu TB, Luong JHT, Cui HF (2014) Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase-boron doped diamond interface: A new solution for a classical problem. Anal Chem 86:4910–4918
Zhou J, Liao C, Zhang L, Wang Q, Tian Y (2014) Molecular hydrogel-stabilized enzyme with facilitated electron transfer for determination of H2O2 Released from live cells. Anal Chem 86:4395–4401
Male KB, Hrapovic S, Liu YL, Wang DS, Luong JHT (2004) Electrochemical detection of carbohydrates using copper nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Anal Chim Acta 516:35–41
Huang T, Lin K, Tung S, Cheng T, Chang I, Hsieh Y, Lee C, Chiu H (2009) Glucose sensing by electrochemically grown copper nanobelt electrode. J Electroanal Chem 636:123–127
Kang XH, Mai ZB, Zou XY, Cai PX, Mo JY (2007) A sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor in alkaline media with a copper nanocluster/multiwall carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Biochem 363:43–150
Liu MM, Liu R, Chen W (2013) Graphene wrapped Cu2O nanocubes: Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for the detection of glucose and hydrogen peroxide with enhanced stability. Biosens Bioelectron 45:206–212
Guo SJ, Wen D, Dong SJ, Wang E (2009) Gold nanowire assembling architecture for H2O2 electrochemical sensor. Talanta 77:1510–1517
Zhang KY, Zhang N, Cai H, Wang C (2012) A novel non-enzyme hydrogen peroxide sensor based on an electrode modified with carbon nanotube-wired CuO nanoflowers. Microchim Acta 176:137–142
Gu AX, Wang GF, Zhang XJ, Fang B (2010) Synthesis of CuO nanoflower and its application as a H2O2 sensor. Bull Mater Sci 33:17–20
Vogel AI (1989) Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis. Longman United Kingdom
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20905010), Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (BK20131191 and BK20140416), Qing Lan Project (SZ2014005) and Suzhou Science and Technology Project (SYN201302, SYN201515). The work is also supported by Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (B2011205079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests
Electronic supplementary materials
ESM 1
(DOC 142 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, L., Zhang, P., Chen, J. et al. Non-enzymatic sensing of glucose and hydrogen peroxide using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of nanoporous copper, carbon black and nafion. Microchim Acta 183, 1359–1365 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1764-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1764-0