Abstract
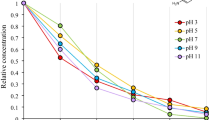
We have investigated the possibility of sampling ammonium ion using the diffusive-gradients-in-thin-films technique (DGT) by introducing a novel binding agent that is based on micro-sized zeolite. The performance of zeolite-DGT was characterized by measurement of the following parameters: (1) the diffusion coefficient of ammonium ion in hydrogel; (2) the adsorption rate of ammonium ion by the zeolite binding gel; (3) the elution efficiency, and (4) the effects of pH, ionic strength and interfering ions on DGT. The method was validated by studying the uptake of ammonium ion from in freshwaters by zeolite gels which was found to be fast enough to meet the requirements of DGT. The concentrations determined via DGT agreed well with the concentrations determined in bulk solutions. Sampling of ammonium ion using zeolite-DGT was consistent over the pH 3 to 8 range and the 0.001 to 10 mM ionic strength range. The method also performs predictably in natural waters containing various metal ions. The technique is considered to be a viable passive tool for sampling ammonium from aqueous solutions.

Schematic representation of the principle of DGT and the determination of mass accumulated on the binding gel.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paerl H (2007) Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu lake. Science 317:1166
Yang M, Yu J-W, Li Z-H (2008) Taihu lake not to blame for Wuxi, s woes. Science 319:158
Ancuta A, Kaušpėdienė D, Gefenienė A, Snukiškis J, Vasilevičiūtė E (2005) Effect of hydroxyl and nitrate ions on the sorption of ammonium ions by sulphonic cation exchangers. Desalination 175(3):259–268. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2004.09.029
Van Staden JF, Taljaard RE (1997) Determination of ammonia in water and industrial effluent streams with the indophenol blue method using sequential injection analysis. Anal Chim Acta 344(3):281–289. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(96)00523-5
El-Shahat MF, Abdel-Halim SH, Mokhtar AED (2002) Micro determination of ammonia by a kinetic spectrophotometric method. Microchim Acta 140(1–2):51–54. doi:10.1007/s006040200068
Davison W, Zhang H (1994) Nature 367(6463):546–548
Panther JG, Teasdale PR, Bennett WW, Welsh DT, Zhao H-J (2010) Titanium dioxide-based DGT technique for in situ measurement of dissolved reactive phosphorus in fresh and marine waters. Environ Sci Technol 44(24):9419–9424. doi:10.1021/es1027713
Dong J, Fan H-T, Sui D-P, Li L-C, Sun T (2014) Sampling 4-chlorophenol in water by DGT technique with molecularly imprinted polymer as binding agent and nylon membrane as diffusive layer. Anal Chim Acta 822:69–77. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2014.03.015
Garmo OA, Royset O, Steinnes E, Flaten TP (2003) Performance study of diffusive gradients in thin films for 55 elements. Anal Chem 75(14):3573–3580. doi:10.1021/ac026374n
Zhang H, Davison W, Gadi R, Kobayashi T (1998) In situ measurement of dissolved phosphorus in natural waters using DGT. Anal Chim Acta 370(1):29–38. doi:10.1016/s0003-2670(98)00250-5
Osterlund H, Chlot S, Faarinen M, Widerlund A, Rodushkin I, Ingri J, Baxter DC (2010) Simultaneous measurements of As, Mo, Sb, V and W using a ferrihydrite diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) device. Anal Chim Acta 682(1–2):59–65. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.049
Fan H-T, Liu J-X, Sui D-P, Yao H, Yan F, Sun T (2013) Use of polymer-bound Schiff base as a new liquid binding agent of diffusive gradients in thin-films for the measurement of labile Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+. J Hazard Mater 260:762–769. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.049
Fan H-T, Sun T, Li W-J, Sui D-P, Jin S, Lian X-J (2009) Sodium polyacrylate as a binding agent in diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for the measurement of Cu2+ and Cd2+ in waters. Talanta 79(5):1228–1232. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.04.049
Chen H, Zhang M-H, Gu J-L, Zhao G, Zhang Y, Li J-R (2014) Measurement of dissolved reactive phosphorus in water with polyquaternary ammonium salt as a binding agent in diffusive gradients in thin-films technique. J Agric Food Chem 62(50):12112–12117. doi:10.1021/jf5040702
Zheng H, Han L-J, Ma H-W, Zheng Y, Zhang H-M, Liu D-H, Liang S-P (2008) Adsorption characteristics of ammonium ion by zeolite 13X. J Hazard Mater 158(2–3):577–584. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.115
Arslan A, Veli S (2012) Zeolite 13X for adsorption of ammonium ions from aqueous solutions and hen slaughterhouse wastewaters. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(3):393–398. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2011.11.003
Marañón E, Ulmanu M, Fernández Y, Anger I, Castrillón L (2006) Removal of ammonium from aqueous solutions with volcanic tuff. J Hazard Mater 137(3):1402–1409. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.069
Alshameri A, Ibrahim A, Assabri AM, Lei X-R, Wang H-Q, Yan C-J (2014) The investigation into the ammonium removal performance of Yemeni natural zeolite: Modification, ion exchange mechanism, and thermodynamics. Powder Technol 258:20–31. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.063
Dong J, Zhou X, Zhao H, Xu J, Sun Y (2011) Reagentless amperometric glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase on a ferrocene@NaY zeolite composite. Microchim Acta 174(3–4):281–288. doi:10.1007/s00604-011-0624-1
APHA(American Public Health Association), AWWA(American Water Works Association), WEF(Water Environment Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 139-152
Zhang H, Davison W (1995) Performance characteristics of diffusion gradients in thin films for the in situ measurement of trace metals in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 67(19):3391–3400
Sarioglu M (2005) Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater using natural Turkish (Dogantepe) zeolite. Sep Purif Technol 41(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2004.03.008
Li W, Zhao H, Teasdale P, John R (2002) Preparation and characterisation of a poly(acrylamidoglycolic acid-coacrylamide) hydrogel for selective binding of Cu2+ and application to diffusive gradients in thin films measurements. Polymer 43:4803–4809
Garmo OA, Davison W, Zhang H (2008) Effects of binding of metals to the hydrogel and filter membrane on the accuracy of the diffusive gradients in thin films technique. Anal Chem 80(23):9220–9225. doi:10.1021/ac801437j
Sen Z, Saud A, Altunkaynak A, Özger M (2003) Increasing water supply by mixing of fresh and saline ground waters. J Am Water Resour Assoc 39:1209–1215
Trimbee A, Prepas E (1987) Evaluation of total phosphorus as a predictor of the relative biomass of blue-green algae with emphasis on Alberta lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 14:1337–1442
Dong X-Y, Zhang X-M, Qin J-G, Zong S-B (2012) Acute ammonia toxicity and gill morphological changes of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in normal versus supersaturated oxygen. Aquac Res 44:1752–1759. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2012.03181.x
Tipping E, Rey-Castro C, Bryan SE, Hamilton-Taylor J (2002) Al(III) and Fe(III) binding by humic substances in freshwaters, and implications for trace metal speciation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(18):3211–3224. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(02)00930-4
Acknowledgments
The project received partial financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No.N130605001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21477082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 326 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Guo, T., Jiang, Z. et al. Sampling of ammonium ion in water samples by using the diffusive-gradients-in-thin-films technique (DGT) and a zeolite based binding phase. Microchim Acta 182, 2419–2425 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1576-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1576-7