Abstract
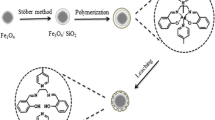
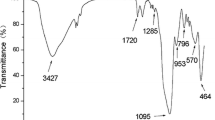
We have synthesized ferromagnetic nanoparticles with an imprinted polymer coating that is capable of adsorbing and extracting uranyl ions. The adsorbent was characterized using infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis, X-ray powder diffraction analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. The effects of sample pH, sample volume, weight of the adsorbent, contact time and of other ions have been investigated in the batch extraction mode. The performance of the material was compared to that of particles coated with a non-imprinted polymer. The adsorbent containing the imprinted coating displays higher sorption capacity and better selectivity to uranyl ions. The method was successfully applied to the determination of uranyl ions in water samples.

Magnetic separation of uranyl ions from aqueous solution using a new uranyl-imprinted material prepared by surface modification of silica coated magnetic nanoparticles




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hennion MC (1999) Solid-phase extraction: method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 856:3–24
Fontanals N, Marcé RM, Borrull F (2005) New hydrophilic materials for solid-phase extraction. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 24:394–406
Thuman EM, Mills MS (1998) Solid phase extraction, in: Principles and Practice. Wiley, New York
Pyrzyñska K, Trojanowicz M (1999) Functionalized cellulose sorbents for preconcentration of trace metals in environmental analysis. Crit Rev Anal Chem 29:313–321
Jal PK, Patel S, Mishra BK (2004) Chemical modification of silica surface by immobilization of functional groups for extractive concentration of metal ions. Talanta 62:1005–1028
Matoso E, Kubota LT, Cadore S (2003) Use of silica gel chemically modified with zirconium phosphate for preconcentration and determination of lead and copper by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 60:1105–1111
Goswami A, Singh AK (2002) 1,8-Dihydroxyanthraquinone anchored on silica gel: synthesis and application as solid phase extractant for lead(II), zinc(II) and cadmium(II) prior to their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 58:669–678
Sadeghi S, Akbarzadeh Mofrad A (2007) Synthesis of a new ion imprinted polymer material for separation and preconcentration of traces of uranyl ions. React Funct Polym 67:966–976
Esen C, Andac M, Bereli N, Say R, Henden E, Denizli A (2009) Highly selective ion-imprinted particles for solid-phase extraction of Pb2+ ions. Mater Sci Eng C 29:2464–2470
Ng S-M, Narayanaswamy R (2010) Demonstration of a simple, economical and practical technique utilizing an imprinted polymer for metal ion sensing. Microchim Acta 169:303–311
Kloskowski A, Pilarczyk M, Przyjazny A, Namieśnik J (2009) Progress in development of molecularly imprinted polymers as sorbents for sample preparation. Crit Rev Anal Chem 39:43–58
Leśniewska B, Kosińska M, Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz B, Zambrzycka E, Wilczewska AZ (2011) Selective solid phase extraction of platinum on an ion imprinted polymers for its electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination in environmental samples. Microchim Acta 175:273–282
Sellergren B (2001) Molecular imprinted polymers, 1st edn. Elsevier, Netherlands
Kabanov VA, Efendiev AA, Orujev DD (1979) Complex-forming polymeric sorbents with macromolecular arrangement favorable for ion sorption. J Appl Polym Sci 24:259–267
Shirvani-Arani S, Ahmadi SJ, Bahrami-Samani A, Ghannadi-Maragheh M (2008) Synthesis of nano-pore samarium(III)-imprinted polymer for preconcentrative separation of samarium ions from other lanthanide ions via solid phase extraction. Anal Chim Acta 623:82–88
Mosbach K (1994) Molecular imprinting. Trends Biochem Sci 19:9–14
Ewen SL, Steinke JHG (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymers using anions as templates. Struct Bond 129:207–248
Wu X (2012) Molecular imprinting for anion recognition in aqueous media. Microchim Acta 176:23–47
Prasada Rao T, Kala R, Daniel S (2006) Metal ion-imprinted polymers-Novel materials for selective of recognition inorganics. Anal Chim Acta 578:105–116
Tsukagoshi K, Yu KY, Maeda M, Takagi M (1993) Metal ion-selective adsorbent prepared by surface- Imprinting polymerization. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 66:114–120
He Q, Chang XJ, Wu Q, Huang XP, Hu Z, Zhai YH (2007) Synthesis and applications of surface-grafted Th(IV)-imprinted polymers for selective solid-phase extraction of thorium(IV). Anal Chim Acta 605:192
Gao BJ, An FQ, Zhu Y (2007) Novel surface ionic imprinting materials prepared via couple grafting of polymer and ionic imprinting on surfaces of silica gel particles. Polymer 48:2288–2297
Quirarte-Escalante CA, Soto V, De La Cruz W, Porras GR, Manríquez R, Gomez-Salazar S (2009) Synthesis of hybrid adsorbents combining sol–gel processing and molecular imprinting applied to lead removal from aqueous streams. Chem Mater 21:1439–1450
Chang XJ, Jiang N, Zheng H, He Q, Hu Z, Zhai YH et al (2007) Solid-phase extraction of iron(III) with an ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique. Talanta 71:38
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Dai J, Gao J, Xie J et al (2011) A surface ion-imprinted mesoporous sorbent for separation and determination of Pb(II) ion by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 172:309–317
Cheng Z, Wang H, Wang H, He F, Zhang H, Yang S (2011) Synthesis and characterization of an ion-imprinted polymer for selective solid phase extraction of thorium(IV). Microchim Acta 173:423–431
Zheng H, Zhang D, Wang W et al (2007) Highly selective determination of palladium(II) after preconcentration using Pd(II)-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique. Microchim Acta 157:7–11
Bi X, Lau RJ, Yang K (2007) Preparation of ion-imprinted silica gels functionalized with glycine, diglycine, and triglycine and their adsorption properties for copper ions. Langmuir 23:8079–8086
Mirsky VM, Hirsch T, Piletsky SA, Wolfbeis OS (1999) A spreader-bar approach to molecular architecture: formation of stable artificial chemoreceptors. Angew Chem Int Ed 38:1108–1110
Bystrzejewski M, Pyrzyńska K (2011) Kinetics of copper ions sorption onto activated carbon, carbon nanotubes and carbon-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Engin Asp 377:402–408
Buschow KHJ. Handbook of magnetic materials (2006) Elsevier, Vol. 16, Chapter 5: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of magnetic nanoparticles, pp 403–482.
Jang JH, Lim HB (2010) Characterization and analytical application of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Microchem J 94:148–158
Guiying J, Wei L, Shaoning Y, Youyuan P, Jilie K (2008) Novel superparamagnetic core-shell molecular imprinting microspheres towards high selective sensing. Analyst 133:1367
Ren YM, Zhang ML, Zhao D (2008) Synthesis and properties of magnetic Cu (II) ion imprinted composite adsorbent for selective removal of copper. Desalination 228:135–149
Huang C, Hu B (2008) Silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with γ-mercaptopropyltrimethoxy- silane for fast and selective solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Cd, Cu, Hg, and Pb in environmental and biological samples prior to their determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 63:437–444
Peng H, Wang S, Hu B (2011) Fast and selective magnetic solid phase extraction of trace Cd, Mn and Pb in environmental and biological samples and their determination by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 175:121–128
Prasada Rao T, Metilda P, Gladias JM (2006) Preconcentration techniques for uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) prior to analytical determination: an overview. Talanta 68:1047–1064
World Health Organization (1998) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 2nd edition WHO Health Criteria and other supporting information, vol 2. WHO/EOS/98.1, Geneva, p 283
Sadeghi S, Shykhzadeh E (2008) Solid phase extraction using silica gel functionalized with Sulfasalazine for preconcentration of uranium (VI) ions from water samples. Microchim Acta 163:313–320. doi:10.1007/s00604-008-0020-7
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodispers silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
Burton AW, Ong K, Rea T, Chan IY (2009) On the estimation of average crystallite size of zeolites from the Scherrer equation:A critical evaluation of its application to zeolites with one-dimensional pore systems. Micropor Mesopor Mater 117:75–90
Freundlich HMF (1906) Under die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470
Temkin MJ, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physiochim USSR 12:217–222
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of this work by the Birjand University Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 206 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, S., Aboobakri, E. Magnetic nanoparticles with an imprinted polymer coating for the selective extraction of uranyl ions. Microchim Acta 178, 89–97 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0800-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0800-y