Abstract
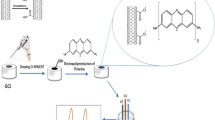
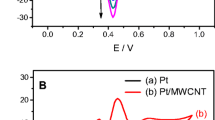
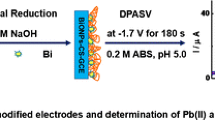
We report on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with a lead ionophore and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. It can be applied to square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Pb(II) ion after preconcentration of Pb(II) at −1.0 V (vs. SCE) for 300 s in pH 4.5 acetate buffer containing 400 μg L−1 of Bi(III). The ionophore-MWCNTs film on the GCE possesses strong and highly selective affinity for Pb(II) as confirmed by quartz crystal microbalance experiments. Under the optimum conditions, a linear response was observed for Pb(II) ion in the range from 0.3 to 50 μg L−1. The limit of detection (at S/N = 3) is 0.1 μg L−1. The method was applied to the determination of Pb(II) in water samples with acceptable recovery.

A glassy carbon electrode modified with a lead ionophore and multiwalled carbon nanotubes is successfully applied to sensitive and selective square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Pb(II) ion after preconcentration of Pb(II) at −1.0 V (vs. SCE) in pH 4.5 solutions containing 400 μg L−1 of Bi(III).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kemper T, Sommer S (2002) Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 36:2742–2747
Bannon DI, Chisolm JJ (2001) Anodic stripping voltammetry compared with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry for blood lead analysis. Clin Chem 47:1703–1704
Liu H, Jiang S, Liu S (1999) Determination of cadmium, mercury and lead in seawater by electrothermal vaporization isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 54:1367–1375
Stosnach H (2006) On-site analysis of heavy metal contaminated areas by means of total reflection X-ray fluorescence analysis (TXRF). Spectrochim Acta B 61:1141–1145
Hsieh SAK, Chong YS, Tan JF, Ma TS (1982) Determination of lead, mercury, cadmium and thallium in foods by amperometry and by atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 78:337–346
Yang W, Chow E, Willett GD, Hibbert DB, Gooding JJ (2003) Exploring the use of the tripeptide Gly–Gly–His as a selective recognition element for the fabrication of electrochemical copper sensors. Analyst 128:712–718
Wang J (2005) Stripping analysis at bismuth electrodes: a review. Electroanalysis 17:1341–1346
Manisankar P, Vedhi C, Selvanathan G, Arumugam P (2008) Differential pulse stripping voltammetric determination of heavy metals simultaneously using new polymer modified glassy carbon electrodes. Microchim Acta 163:289–295
Economou A, Fielden PR (2003) Mercury film electrodes: developments, trends and potentialities for electroanalysis. Analyst 128:205–213
Song W, Zhang L, Shi L, Li D, Li Y, Long Y (2010) Simultaneous determination of cadmium(II), lead(II) and copper(II) by using a screen-printed electrode modified with mercury nano-droplet. Microchim Acta 169:321–326
Wang J, Deo RP, Thongngamdee S, Ogorevc B (2001) Effect of surface-active compounds on the stripping voltammetric response of bismuth film electrodes. Electroanalysis 13:1153–1156
Li D, Jia J, Wang J (2010) A study on the electroanalytical performance of a bismuth film-coated and Nafion-coated glassy carbon electrode in alkaline solutions. Microchim Acta 169:221–225
Tasis D, Tagmatarchis N, Bianco A, Prato M (2006) Chemistry of carbon nanotubes. Chem Rev 106:1105–1136
Wang J, Deo RP, Poulin P, Mangey M (2003) Carbon nanotube fiber microelectrodes. J Am Chem Soc 125:14706–14707
Merkoci A (2006) Carbon nanotubes: exciting new materials for microanalysis and sensing. Microchim Acta 152:155–156
Li YH, Wang S, Wei J, Zhang X, Xu C, Luan Z, Wu D, Wei B (2002) Lead adsorption on carbon nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 357:263–266
Rao GP, Lu C, Su F (2007) Sorption of divalent metal ions from aqueous solution by carbon nanotubes: a review. Sep Purif Tech 58:224–231
Hu XG, Wang T, Wang L, Guo SJ, Dong SJ (2007) A general route to prepare one-and three-dimensional carbon nanotube/metal nanoparticle composite nanostructures. Langmuir 23:6352–6357
Perez-Jimenez C, Escriche L, Casabo J (1998) Poly(vinyl) chloride membrane cesium-selective electrodes based on doubly crowned 1, 3-calix[4]arenes. Anal Chim Acta 371:155–162
Kim JS, Ohki A, Ueki R, Ishizuka T, Shimotashiro T, Maeda S (1999) Cesium-ion selective electrodes based on calix[4]arene dibenzocrown ethers. Talanta 48:705–710
Gholivand MB, Nozari N (2001) Copper (II)-selective electrode using 2, 2′-dithiodianiline as neutral carrier. Talanta 54:597–602
Garcia CAB, Junior LR, Neto GO (2003) Determination of potassium ions in pharmaceutical samples by FIA using a potentiometric electrode based on ionophore nonactin occluded in EVA membrane. J Pharm Biomed Anal 31:11–18
Pan D, Wang Y, Chen Z, Lou T, Qin W (2009) Nanomaterial/ionophore-based electrode for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead: an electrochemical sensing platform toward heavy metals. Anal Chem 81:5088–5094
Hassan SSM, Saleh MB, Gaber AAA, Kream NAA (2003) DDB liver drug as a novel ionophore for potentiometric barium (II) membrane sensor. Talanta 59:161–166
Xu H, Zeng L, Xing S, Xian Y, Shi G, Jin L (2008) Ultrasensitive voltammetric detection of trace lead(II) and cadmium(II) using MWCNTs-Nafion/bismuth composite electrodes. Electroanalysis 20:2655–2662
He X, Su Z, Xie Q, Chen C, Fu Y, Chen L, Liu Y, Ma M, Deng L, Qin D, Luo Y, Yao S (2011) Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Cd and Pb at a bismuth glassy carbon electrode modified with Nafion, poly(2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 173:95–102
Xing Y, Li L, Chusuei CC, Hull RV (2005) Sonochemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 21:4185–4190
Xie Q, Wang J, Zhou A, Zhang Y, Liu H, Xu Z, Yuan Y, Deng M, Yao S (1999) A study of depletion layer effects on equivalent circuit parameters using an electrochemical quartz crystal impedance system. Anal Chem 71:4649–4656
Li YH, Wang S, Luan Z, Ding J, Xu C, Wu D (2003) Adsorption of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by surface oxidized carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41:1057–1062
Richard PSJ, Sakthivel C, Sriman NS (2011) Hg(II) immobilized MWCNT graphite electrode for the anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead and cadmium. Talanta 85:290–297
Salles MO, de Souza APR, Naozuka J, de Oliveira PV, Bertotti M (2009) Bismuth modified gold microelectrode for Pb(II) determination in wine using alkaline medium. Electroanalysis 21:1439–1442
Jia X, Li J, Wang EK (2010) High-sensitivity determination of lead(II) and cadmium(II) based on the CNTs-PSS/Bi composite film electrode. Electroanalysis 22:1682–1687
Bi Z, Chapman CS, Salaün P, van den Berg CMG (2010) Determination of lead and cadmium in sea- and freshwater by anodic stripping voltammetry with a vibrating bismuth electrode. Electroanalysis 22:2897–2907
Injang U, Noyrod P, Siangproh W, Dungchai W, Motomizu S, Chailapakul O (2010) Determination of trace heavy metals in herbs by sequential injection analysis-anodic stripping voltammetry using screen-printed carbon nanotubes electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 668:54–60
Kadaraa RO, Tothill IE (2008) Development of disposable bulk-modified screen-printed electrode based on bismuth oxide for stripping chronopotentiometric analysis of lead (II) and cadmium (II) in soil and water samples. Anal Chim Acta 623:76–81
do Nascimento ME, Martelli PB, Furtado CA, Santos AP (2011) Determination of lead(II) in aqueous solution using carbon nanotubes paste electrodes modified with Amberlite IR-120. Microchim Acta 173:485–493
Li HB, Li J, Yang ZJ, Xu Q, Hou CT, Peng JY, Hu XY (2011) Simultaneous determination of ultratrace lead and cadmium by square wave stripping voltammetry with in situ depositing bismuth at Nafion-medical stone doped disposable electrode. J Hazard Mater 191:26–31
Senthilkumar S, Saraswathi R (2009) Electrochemical sensing of cadmium and lead ions at zeolite-modified electrodes: Optimization and field measurements. Sens Actuat B 141:65–75
Li DY, Jia JB, Wang JG (2010) Simultaneous determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry based on graphite nanofibers–Nafion composite modified bismuth film electrode. Talanta 83:332–336
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (90713018, 21075036, 21175042, 20875029), the State Special Scientific Project on Water Treatment (2009ZX07212-001-06), the Aid Program for Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province, and State Key Laboratories of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics (200902) and of Electroanalytical Chemistry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Chen, L., Xie, X. et al. Square wave anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead(II) using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a lead ionophore and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 176, 81–89 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0697-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0697-x