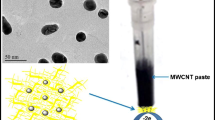
Abstract
We report on newly synthesized Ag(I)-filled multiwall carbon nanotubes as a potential sensing element in ion-selective carbon paste electrodes for the determination of free cyanide in aqueous solution. The electrode was obtained by entrapping the silver-filled nanotubes into a carbon paste and displays a Nernstian response with a slope of 59.8 ± 0.3 mV decade−1, a very wide linear range (from 21.0 nM to 0.1 M of cyanide), a lower detection limit of 13.0 nM, and a response time of <2 min. The operational lifetime is up to 3 months without significant deviation in normal function.

Silver(I)-filled Multiwall Carbon Nanotube as Sensing Element in Cyanide-selective Carbon Paste Electrode







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosentreter JJ, Skogerboe RK (1991) Trace determination and speciation of cyanide ion by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Anal Chem 63:682–688
Zagury GJ, Oudjehani K, Deschenes L (2004) Characterization and availability of cyanide in solid mine tailings from gold extraction plants. Sci Total Environ 320:211–224
Zaknun JJ, Stieglbauer K, Trenkler J (2005) Cyanide-induced a kinetic rigid syndrome: clinical, MRI, FDG-PET, β-CIT and HMPAO SPECT findings. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:125–129
Karmarkar S (2002) Anion-exchange chromatography of metal cyanide complexes with gradient separation and direct UV detection. J Chromatogr A 956:229–235
Mirmohseni A, Alipour A (2002) Construction of a sensor for the determination of cyanide in industrial effluents: a method based on quartz crystal microbalance. Sens Actuators B 84:245–251
Anzenbacher P, Tyson DS, Jursíková K, Castellano FN (2002) Luminescence lifetime-based sensor for cyanide and related anions. J Am Chem Soc 124:6232–6233
Suzuki T, Hioki A, Kurahashi M (2003) Development of a method for estimating an accurate equivalence point in nickel titration of cyanide ions. Anal Chim Acta 476:159–165
Weinberg HS, Cook SJ (2002) Segmented flow injection, UV digestion, and amperometric detection for the determination of total cyanide in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Anal Chem 74:6055–6063
Chattaraj S, Das AK (1991) Indirect determination of free cyanide in industrial waste effluent by atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyst 116:739–741
Tracqui A, Raul JS, Geraut A (2002) Determination of blood cyanide by HPLC-MS. J Anal Toxicol 26:144–148
Yari A, Kargosha K (2006) Simple photometric determination of free cyanide ion in aqueous solution with 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. Centr Europ J Chem 4:329–337
Dadfarnia S, Shabani AMH, Tamadon F, Rezaei M (2007) Indirect determination of free cyanide in water and industrial waste water by flow injection-atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 158:159–163
Ravichandran K, Baldwin RP (1981) Chemically modified carbon paste electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 126:293–300
Wang J, Kirgoz UA, Mo JW, Lu J, Kawde AN, Muck A (2001) Glassy carbon paste electrodes. Electrochem Commun 3:203–208
Ravichandran K, Baldwin RP (1983) Phenylenediamine-containing chemically modified carbon paste electrodes as catalytic voltammetric sensors. Anal Chem 55:1586–1591
Kalcher K, Grabec I (1990) Chemically modified carbon paste electrodes in voltammetric analysis. Electroanalysis 2:419–433
Ivan S, Carel V, Jiri B, Jiri Z (2001) Carbon paste electrodes in modern electroanalysis. Crit Rev Anal Chem 31:311–345
Walcarius A, Bessiere J (1997) Silica-modified carbon paste electrode for copper determination in ammoniacal medium. Electroanalysis 9:707–713
Arrigan DWM (1994) Voltammetric determination of trace metals and organics after accumulation at modified electrodes. Analyst 119:1953–1966
Fiorucci AR, Cavalheiro ETG (2002) The use of carbon paste electrode in the direct voltammetric determination of tryptophan in pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharmac Biomed Anal 28:909–915
Vytras K, Svancara I, Metelka R (2009) Carbon paste electrodes in electroanalytical chemistry. J Serb Chem Soc 74:1021–1033
Wildgoose GG, Banks CE, Leventis HC, Compton RG (2006) Chemically modified carbon nanotubes for use in electroanalysis. Microchim Acta 152:187–214
Rao CN, Satishkumar BC, Govindaraj A, Nath M (2001) Nanotubes Chem Phys Chem 2:78–105
Baughman RH, Zakhidov A, de Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes: the route toward applications. Science 297:787–792
Zhao Q, Gan Z, Zhuang Q (2002) Electrochemical sensors based on carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis 14:1609–1613
Wang J, Kawde AN, Musameh M (2003) Carbon-nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrodes for amplified label-free electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization. Analyst 128:912–916
Cook J, Sloan J, Green MLH (1997) Opening and filling carbon nanotubes. Fullerene Sci Technol 5:695–704
Sinha AK, Hwang DW, Hwang LP (2000) A novel approach to bulk synthesis of carbon nanotubes filled with metal by a catalytic chemical vapor deposition method. Chem Phys Lett 332:455–460
Ulakhovich NA, Zakieva DZ, Yu GG, Budnikov GK (1993) Voltammetric determination of cyanide ions using preconcentration at a carbon-paste electrode modified with liquid crystals. J Anal Chem (Transl of Zh Anal Khim) 48:731–733
Amine A, Alafandy M, Kauffmann JM, Pekli MN (1995) Cyanide determination using an amperometric biosensor based on cytochrome oxidase inhibition. Anal Chem 67:2822–2827
Abbaspour A, Asadi M, Ghaffarinejad A, Safaei E (2005) A selective modified carbon paste electrode for determination of cyanide using tetra-3,4-pyridinoporphyrazinatocobalt(II). Talanta 66:931–936
Sepahvand R, Adeli M, Astinchap B, Kabiri R (2008) New nanocomposites containing metal nanoparticles carbon nanotube and polymer. J Nanopart Res 10:1309–1318
Liu H, Murad S, Jameson CJ (2006) Ion permeation dynamics in carbon nanotubes. J Chem Phys 125:084713–084726
Beu TA (2010) Molecular dynamics simulations of ion transport through carbon nanotubes. I. Influence of geometry, ion specificity, and many-body interactions. J Chem Phys 132:164513–164528
Sumikama T, Saito S, Ohmine I (2006) Mechanism of ion permeation in a model channel: free energy surface and dynamics of K+ ion transport in an anion-doped carbon nanotube. J Phys Chem B 110:20671–20677
Lindner E, Toth K, Pungor E (1986) Definition and determination of response time of ion selective electrodes. Pure Appl Chem 58:469–479
Buck RP, Lindner E (1994) Recommendations for nomenclature of ion-selective electrodes. Pure Appl Chem 66:2527–2536
Macca C (2004) Response time of ion-selective electrodes: current usage versus IUPAC recommendations. Anal Chim Acta 512:183–190
Umezawa Y (1990) Handbook of ion selective electrodes: selectivity coefficients. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Pretsch E, Bakker E, Buhlmann P (2000) Selectivity of potentiometric ion sensors. Anal Chem 72:1127–1133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yari, A., Sepahvand, R. Highly sensitive carbon paste electrode with silver-filled carbon nanotubes as a sensing element for determination of free cyanide ion in aqueous solutions. Microchim Acta 174, 321–327 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0629-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0629-9